Abstract
Background:
Patients myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) diagnosed with higher-risk disease have poor prognosis thus making improvements in health-related quality of life (HRQOL) a major goal of therapy. Understanding HRQOL profile of untreated patients is important to help clinicians to better target subpopulations in need of special attention from the very beginning of therapy.
Aims:
The primary objective of this study is to investigate whether HRQOL differences exist by age and gender in untreated patients with higher-risk MDS. A secondary objective is to provide age and gender pretreatment HRQOL profiles to be used as reference baseline data for comparing HRQOL of MDS patients under treatments.
Methods:
This analysis is based on 280 adult patients diagnosed with IPSS risk score of intermediate-2 (74%) and high-risk (26%), enrolled in an international prospective observational study. Median age of patients was 71 years (range 32-89), 176 were men (63%) and 104 (37%) women. HRQOL was assessed at study entry and before treatment for higher-risk disease (except for transfusions), with the EORTC QLQ-C30, the most widely used HRQOL outcome measure in MDS research. Thus, our data are likely to further ease interpretation of outcomes in many studies using this questionnaire. One hundred seventy-five patients had received at least one red blood cell transfusion at the time of baseline HRQOL assessment. HRQoL data of MDS patients were age-gender matched with those general population norms. Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney and Wilcoxon signed ranks tests were used for unmatched and matched comparisons, respectively (α=0.05). Effect sizes were also computed.
Results:
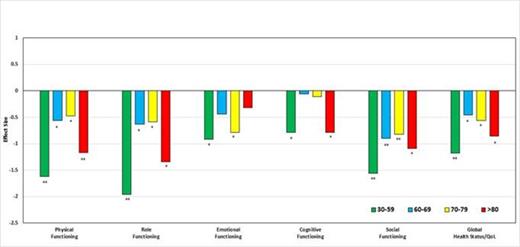
No statistically significant differences existed in any of the HRQOL domain by IPSS category (intermediate-2 versus high-risk). However, HRQOL profiles differed by age and gender and results are reported in Table 1. Women generally reported lower HRQOL scores than men, with statistically significant impairments in the global quality of life (P=0.008), role (P=0.014), emotional (P=0.024) and social functioning (P=0.028). When compared to their peers in the general population, HRQOL was found to be impaired in all age group categories (Figure 1, A and B). However, the magnitude of impairments across HRQOL domains was markedly larger in younger patients (aged 30-59 years) compared to older age groups (≥60 years). The top three largest impairments in this younger group were found for: fatigue (ES=2.47, P<0.001), dyspnea (ES=2.14, P<0.001) and role functioning RP (ES=1.96, P<0.001). This latter aspect indicates the ability to perform daily activities.
Conclusion:
Pretreatment HROQL of higher-risk MDS patients vary by age and gender and current reference data will help making more accurate comparisons with HRQOL of patients under treatment. Clinicians should also pay special attention to younger patients, as these are those most in need of HRQOL improvements.
Adjusted mean differences between MDS patients and their respective control groups by age categories (30-59 years, 60-69 years, 70-79 years and over 80) in functional aspects and global quality of life. A score below 0 line means worse outcomes for MDS patients.
*= Statistically significant (P<0.05) **= Statistically significant (P<0.001)
Adjusted mean differences between MDS patients and their respective control groups by age categories (30-59 years, 60-69 years, 70-79 years and over 80) in functional aspects and global quality of life. A score below 0 line means worse outcomes for MDS patients.
*= Statistically significant (P<0.05) **= Statistically significant (P<0.001)
Adjusted mean differences between MDS patients and their respective control groups by age categories (30-59 years, 60-69 years, 70-79 years and over 80) in symptom scales. A score above 0 line means worse outcomes for MDS patients.
*=Statistically significant (P<0.05) **=Statistically significant (P<0.001)
Adjusted mean differences between MDS patients and their respective control groups by age categories (30-59 years, 60-69 years, 70-79 years and over 80) in symptom scales. A score above 0 line means worse outcomes for MDS patients.
*=Statistically significant (P<0.05) **=Statistically significant (P<0.001)
Quality of life profile by the EORTC QLQ-C30 in higher risk-MDS patients by gender and age groups. Means scores of the EORTC QLQ-C30 are reported.
Quality of life profile by the EORTC QLQ-C30 in higher risk-MDS patients by gender and age groups. Means scores of the EORTC QLQ-C30 are reported.
Gaidano:MorphoSys; Roche; Novartis; GlaxoSmithKline; Amgen; Janssen; Karyopharm: Honoraria, Other: Advisory boards; Celgene: Research Funding. Santini:celgene, Janssen, Novartis, Onconova: Honoraria, Research Funding. Platzbecker:Celgene: Honoraria; GlaxoSmithKline: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria; Amgen, Inc.: Honoraria. Di Renzo:Celgene: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.



This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal