Abstract
INTRODUCTION:
More active high-dose regimens are needed for refractory or poor-risk relapsed Hodgkin's lymphomas (HL), where BEAM offers poor results. Post-BEAM maintenance treatment with brentuximab vedotin (BV) x 48 weeks has recently been shown in the AETHERA trial to prolong progression-free survival (PFS) compared to placebo (2-year PFS 63% vs. 51%). We previously developed a regimen of infusional gemcitabine combined with busulfan and melphalan (Gem/Bu/Mel) pursuing inhibition by Gem of DNA damage repair. The encouraging results we saw in HL patients led us to conduct a phase 2 trial of Gem/Bu/Mel in HL patients at high risk of post-ASCT relapse.
METHODS:
HL patients ages 12-65 with ≥1 of the following criteria were eligible: Persistent active disease after 1st-line chemotherapy, CR1 < 1 year, or extranodal disease at relapse/PD. Gem was administered as a loading dose of 75 mg/m2 followed by infusion at a fixed dose rate of 10 mg/m2/min over 4.5 hours on days -8 and -3 (total daily dose of 2,775 mg/m2). Each Gem infusion was immediately followed by the corresponding dose of Bu or Mel. Bu was administered intravenously from days-8 to -5 targeting a daily AUC of 4,000. Mel was infused at 60 mg/m2/day on days -3 and -2. ASCT was on day 0. Post-HDC involved field radiotherapy (IFRT) was considered to lesions >5 cm at the time of HDC or persistently PET+ at the 1-month post-HDC evaluation. The trial had 80% power to detect a 2-year PFS increase from 50% to 65%.The concurrent BEAM cohort included all patients eligible for this trial who received BEAM off study due to no financial coverage for ASCT in a trial or patient/physician preference.
RESULTS:
Eighty patients were enrolled on study between 6/11-04/15 (Table 1). There was no transplant-related mortality (TRM). The toxicity profile was manageable, including mucositis (49% G2, 40% G3), skin (22% G2, 11% G3), self-limited transaminase elevation (30% G2, 19% G3), and hyperbilirubinemia (24% G2, 19% G3) with no cases of VOD. There was 1 case of G2 pneumonitis and none of cardiac, renal or CNS toxicity. Neutrophils and platelets engrafted at median days +10 (8-12) and +12 (9-21), respectively. Eight patients received post-HDC IFRT to mediastinum ± neck ± sternum at 30.6-39.6 Gy, starting on median day +42 (41-53) post-HDC, which was well tolerated. No patients received maintenance BV.
Patient characteristics
| Variable . | Study file (N=80) . | Concurrent BEAM cohort (N=31) . | P . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median age (range) | 31 (13-65) | 39 (23-65) | 0.02 | |||
| Primary refractory / poor-risk relapse | 41% / 59% | 37% / 63% | 0.6 | |||
| # prior relapses | 1 | 80% | 70% | 0.3 | ||
| >1 | 20% | 30% | ||||
| Median # prior chemotherapy lines (range) | 2 (2-6) | 2 (2-7) | 0.3 | |||
| Prior disease-free interval (months) | <6 | 56% | 60% | 0.7 | ||
| 6-12 | 24% | 17% | ||||
| >12 | 20% | 23% | ||||
| Prior xRT | 21% | 27% | 0.6 | |||
| Relapse within prior xRT field | 10% | 3% | 0.4 | |||
| Extranodal relapse/PD | 36% | 53% | 0.08 | |||
| B symptoms at relapse/PD | 11% | 10% | 0.8 | |||
| Bulky relapse (any lesion >5 cm) | 39% | 17% | 0.02 | |||
| # risk factors (primary refract/CR1<1 yr, extranodal relapse, or B symptoms) | 1 | 74% | 77% | 0.2 | ||
| 2 | 26% | 17% | ||||
| 3 | 0% | 6% | ||||
| Prior BV | % | 14% | 25% | 0.1 | ||
| CR | 36% | 50% | 0.1 | |||
| PR | 36% | 0% | ||||
| No response (NR) | 26% | 50% | ||||
| PET+ at HDC | 32% | 7% | 0.003 | |||
| Status at HDC: CR/ PR / NR | 68% / 24% / 8% | 93% / 7% / 0% | 0.01 | |||
| Variable . | Study file (N=80) . | Concurrent BEAM cohort (N=31) . | P . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median age (range) | 31 (13-65) | 39 (23-65) | 0.02 | |||
| Primary refractory / poor-risk relapse | 41% / 59% | 37% / 63% | 0.6 | |||
| # prior relapses | 1 | 80% | 70% | 0.3 | ||
| >1 | 20% | 30% | ||||
| Median # prior chemotherapy lines (range) | 2 (2-6) | 2 (2-7) | 0.3 | |||
| Prior disease-free interval (months) | <6 | 56% | 60% | 0.7 | ||
| 6-12 | 24% | 17% | ||||
| >12 | 20% | 23% | ||||
| Prior xRT | 21% | 27% | 0.6 | |||
| Relapse within prior xRT field | 10% | 3% | 0.4 | |||
| Extranodal relapse/PD | 36% | 53% | 0.08 | |||
| B symptoms at relapse/PD | 11% | 10% | 0.8 | |||
| Bulky relapse (any lesion >5 cm) | 39% | 17% | 0.02 | |||
| # risk factors (primary refract/CR1<1 yr, extranodal relapse, or B symptoms) | 1 | 74% | 77% | 0.2 | ||
| 2 | 26% | 17% | ||||
| 3 | 0% | 6% | ||||
| Prior BV | % | 14% | 25% | 0.1 | ||
| CR | 36% | 50% | 0.1 | |||
| PR | 36% | 0% | ||||
| No response (NR) | 26% | 50% | ||||
| PET+ at HDC | 32% | 7% | 0.003 | |||
| Status at HDC: CR/ PR / NR | 68% / 24% / 8% | 93% / 7% / 0% | 0.01 | |||
At median follow-up of 33 mo (4-50) there have been 25 relapses following Gem/Bu/Mel, at median 6 (2-22) mo post-HDC (only 3 relapses after 12 mo). On univariate analyses, PET+ at HDC and primary refractoriness correlated with worse EFS (Table 2). On multivariate analyses, PET+ was an independent adverse predictor.
Prognostic analyses
| Variable . | Univariate analyses . | Multivariate analyses . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-yr EFS | P | HR (95% CI) | P | ||
| Yes | No | ||||
| PET+ | 37% | 82% | 0.00008 | 3.8 (1.7-8.9) | 0.001 |
| Primary refractory | 51.5% | 81% | 0.006 | 2.2 (0.9-5.1) | 0.06 |
| >1 relapse | 50% | 73% | 0.08 | ||
| B symptoms | 55.6% | 70.4% | 0.2 | ||
| Bulky relapse | 67% | 72% | 0.2 | ||
| Extranodal | 67% | 72% | 0.4 | ||
| Variable . | Univariate analyses . | Multivariate analyses . | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-yr EFS | P | HR (95% CI) | P | ||
| Yes | No | ||||
| PET+ | 37% | 82% | 0.00008 | 3.8 (1.7-8.9) | 0.001 |
| Primary refractory | 51.5% | 81% | 0.006 | 2.2 (0.9-5.1) | 0.06 |
| >1 relapse | 50% | 73% | 0.08 | ||
| B symptoms | 55.6% | 70.4% | 0.2 | ||
| Bulky relapse | 67% | 72% | 0.2 | ||
| Extranodal | 67% | 72% | 0.4 | ||
The BEAM cohort included 31 patients treated between 06/11-04/15 (Table 1) with no BV maintenance. There were fewer cases of PET+ tumors at HDC (P=0.003) and of bulky relapses (P=0.02) than the Gem/Bu/Mel file, but was matched for the other risk factors. It had no TRM.
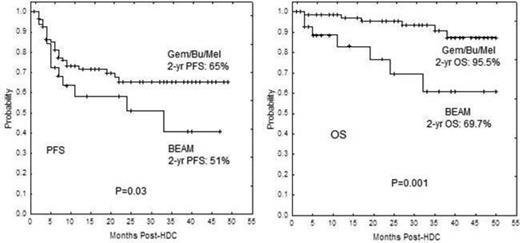
Despite a higher number of PET+ tumors at HDC, the Gem/Bu/Mel file had significantly superior 2-year PFS (65% vs. 51%, P=0.03) and 2-year OS (95.5% vs. 70%, P=0.001) than the BEAM cohort.
CONCLUSIONS:
Gem/Bu/Mel without maintenance BV was safe and effective in patients with refractory or poor-risk relapsed HL, with comparable results to those from the AETHERA trial using BEAM and maintenance BV. A randomized trial is necessary to compare Gem/Bu/Mel and BEAM.
Off Label Use: Gemcitabine, busulfan and melphalan are not FDA approved at high doses for Hodgkin's lymphoma. Alousi:Therakos, Inc: Research Funding. Andersson:Otsuka Research and Development, Inc.: Consultancy. Fanale:Merck: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria, Research Funding; Infinity: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Spectrum: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Seattle Genetics: Honoraria, Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Medimmune: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Bayer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Molecular Templates: Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Research Funding; Onyx: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal