Abstract

Background: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is the most common childhood cancer, with survival rates exceeding 90% in recent trials. Obesity is increasingly prevalent in the general population, and studies in children with ALL have correlated obesity with higher risk of persistent minimal residual disease (MRD) at the end of induction as well as worse outcome. We, therefore, determined whether obesity affected treatment response in children with ALL who were enrolled in a recent trial including MRD-guided therapy.
Methods: Patients enrolled in the Total XV study at St. Jude Children's Research Hospital from 2000 to 2007 were included in the analysis. The protocol used MRD levels prospectively for risk assignment together with age, white blood cell counts, and cytogenetic profiles. Drug dosages were based on actual (rather than ideal) body surface area. Body mass index (BMI) was calculated by using height and weight for patients older than 2 years at diagnosis. Four BMI categories (underweight, normal, overweight, and obese) based on Center for Disease Control and Prevention guidelines were used. The association between BMI categories at diagnosis and MRD, cumulative incidences of refractory/relapsed disease (CIR), and event-free survival (EFS) were evaluated. The changes in BMI percentile from diagnosis to the end of induction were also calculated.
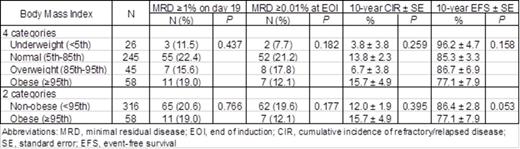
Results: Among 409 patients enrolled, 26 who were younger than 2 years with no available BMI and 9 with Down syndrome were excluded. Of the 374 evaluable patients, 26 (7.0%) were underweight; 245 (65.5%) had normal BMI; 45 (12.0%) were overweight; and 58 (15.5%) were obese. Older age at diagnosis (P = 0.008) and being on the standard/high-risk treatment arm (P = 0.040) were associated with higher BMI categories.
Among the 4 BMI categories, there was no significant difference in the proportion of patients with MRD ≥1% on day 19 of remission-induction therapy (P = 0.437) or MRD ≥0.01% at the end of induction (P = 0.182). There were also no differences in CIR (P = 0.259) or EFS (P = 0.158) among the 4 categories. EFS was significantly worse in male patients (P = 0.027) and in those with T-cell phenotype (P = 0.006), standard/high risk (P < 0.001), MRD ≥1% on day 19 (P < 0.001), or MRD ≥0.01% at the end of induction (P < 0.001).
We reanalyzed the data by using 2 BMI categories (non-obese and obese). No significant differences were observed in the proportions of patients with MRD ≥1% on day 19 (P = 0.766) or MRD ≥0.01% at the end of induction (P = 0.177), and there was no difference in CIR between the 2 categories (P = 0.395). Although not statistically significant, EFS was marginally worse in obese patients (P=0.053).
EFS among 4 or 2 BMI categories was evaluated by using a multiple Cox regression model including treatment arm, sex, race, and BMI categories as variables. No differences were observed for analysis by 4 (P = 0.368) or 2 (P = 0.151) BMI categories. In these analyses, only treatment arm (standard/high risk) remained a significant predictor (all P < 0.001).
BMI percentile change from diagnosis to the end of induction also lacked significant association with MRD, CIR, and EFS.
Conclusion: In contrast to published reports, body mass index had no effect on early treatment response as measured by MRD, incidence of relapse, or EFS in children with ALL enrolled in the Total XV study. These results indicate that obesity should not be considered an adverse prognostic factor in children with ALL in the context of contemporary treatment programs.
Association of BMI with MRD, CIR, and EFS
Evans:Prometheus Labs: Patents & Royalties: Royalties from licensing TPMT genotyping.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal