Abstract
Introduction - AML is a complex group of malignancies, with heterogeneity in morphology, cytogenetics, molecular characteristics, aggressiveness and importantly, in its response to treatment and survival outcomes. Next generation sequencing by the Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network analysed 200 primary AML cases and identified 23 genes that display recurrent somatic mutations at varying frequency in AML (NEJM 368(22):2059-2074). Defects in DNA repair are frequently identified in treatment-related AML and inherited mutations in genes of DNA repair pathways predispose patients to myeloid malignancies. For example, biallelic mutations in FANC genes, which cause the recessive heritable bone marrow failure syndrome Fanconi Anaemia (FA) are associated with high risk of progression to AML and other cancers (Kutler et al.Blood, 101:1249-1256), suggesting a potential involvement of FANC gene mutations in AML pathogenesis.
Methods - In this study we present a two-stage approach to gene discovery in AML: initial unbiased whole genome sequence (WGS) and whole exome sequence (WES) analysis of tumour DNA from a cytogenetically normal AML case at diagnosis and relapse, and corresponding germ-line DNA (prepared from mesenchymal stromal cells). Potential oncogenic mutations and changes associated with disease progression were identified. WES of a further 96 diagnostic AML samples further defined recurrent mutations and allowed identification of affected functional groups and networks in AML.
Results – WGS and WES were performed on diagnosis, non-haematopoietic and relapse samples from an index AML patient. Somatic SNVs and indels unique to the tumour samples include a number of variants in genes previously reported as recurrently somatically mutated in AML including FLT3, WT1 and IDH2. Somatic mutations in genes not previously associated with AML were also identified including a mutation in FANCD2 (p.S1412N) present in the index AML tumour DNA at diagnosis and at relapse.
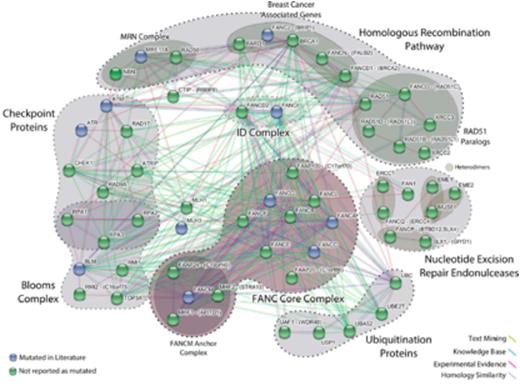
Variants in genes recurrently mutated at low frequency in AML can also be disease drivers, however separating such genes from the background level of mutation in AML requires analysis across multiple samples, and sequencing studies to determine recurrence and/or mutations in proteins involved in the same functional pathway or complex. STRING-db v9.05 (Franceschini et al. NAR, 2013(41), Database issue) was used to identify a larger network of proteins, including and associated with the FANC genes, involved in homologous recombination-mediated DNA repair. Known somatic mutations from other AML studies were mapped onto this network; as shown in Figure 1 multiple genes in this extended network are affected by somatic mutation in AML suggesting a potential role in pathogenesis. Analysis of our WES data from diagnosis samples from a further 96 Australian AML cases identified an additional two somatic mutations in genes from the extended STRING-db v9.05 FANC network. In total we identified 18 mutations in the 16 classified FANC genes and 8 variants in the BLM complex as shown in Figure 2. Two of the germline FANC gene mutations, FANCM-Q13333fs and FANCD2-R926X, are known pathogenic mutations in FA. Patients with mutations in the 8 FANC genes of the core complex form a distinct subset from those with mutations in the other 8 FANC genes. 5 of the 8 patients with mutations in the BLM complex also form a separate group while BLM complex mutations are present in 2 patients that also have FANC mutations. For the two patients with acquired changes the allele frequency for these FANC mutations is greater than 25% suggesting an early origin in disease.
Discussion. Our findings suggest that germline and somatic mutations affecting function of the FANC DNA repair pathway may be a recurrent abnormality in AML, potentially contributing to leukaemogenesis. FANC/BLM gene mutations frequently co-exist with mutations in DNMT3A and DNMT1; 46% of the patients with DNMT3A/DNMT1 mutations are also mutant for FANC or BLM complex genes representing significant over-representation (p = 0.021). Within the group of FANC and BLM patients there is also significant under-representation of FLT3-ITD mutations and mutations in N-RAS and K-RAS (p = 0.051), raising the possibility that defects in homologous DNA repair may favour cooperation with alternative signalling pathways.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal