Abstract
Background
Many studies have examined the disparities in cancer diagnosis, treatment and survival among different subgroups classified based on race, socioeconomic status and age. Not as many studies have examined disease characteristics in rural populations, perhaps because of the lack of a consensus in the United States regarding the definition of "rural". In these few studies, many disparities were reported in association with rural residence such as lower levels of utilization of cancer screening tests, lower likelihood of receiving guideline-appropriate therapy and shorter survival.
Objectives
To examine multiple myeloma disease characteristics and survival in rural patients of southern New Mexico in comparison to their urban counterparts.
Methods
Patients presented to Memorial Medical Center (MMC) and its associated cancer center from January 2003 to December 2013 with multiple myeloma were enrolled in the study. Demographic and clinical data were collected. The charts were also examined for evidence of offering or discussing Autologous Stem Cell Transplant (ASCT) as a treatment option with patients, and whether it was actually performed. Patient staging at diagnosis according to International Staging System (ISS) for myeloma was determined, if possible. Urban vs. rural classification was based on the Rural-Urban Commuting Area codes (RUCA) version 2.0; a census tract-based classification scheme that utilizes the standard bureau of census urban definition in combination with work commuting information. Categorization D of RUCA was chosen. It defines urban as all places that have 30% or more of their workers going to a Census Bureau-defined Urbanized Area.
Results
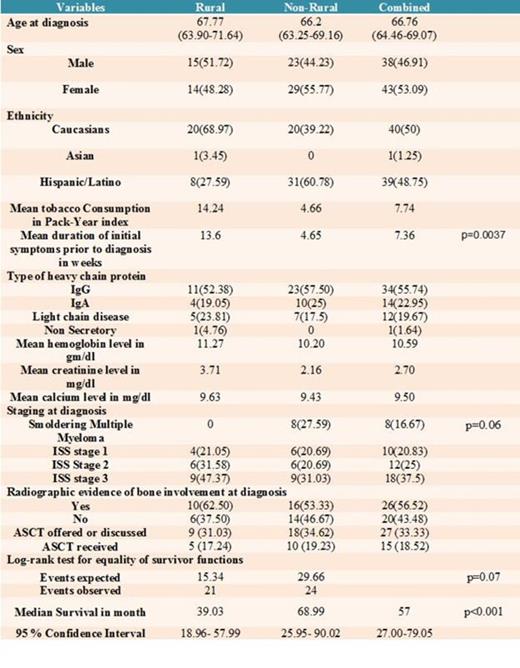
A total of 87 patients were initially enrolled in the study. Four patients were excluded because sufficient evidence to establish the diagnosis could not be verified. Two additional patients who had solitary plasmacytoma with no evidence of systemic involvement were excluded as well. Patients were classified based on their residence at the time of diagnosis as rural (29 patients) and non-rural (52 patients).
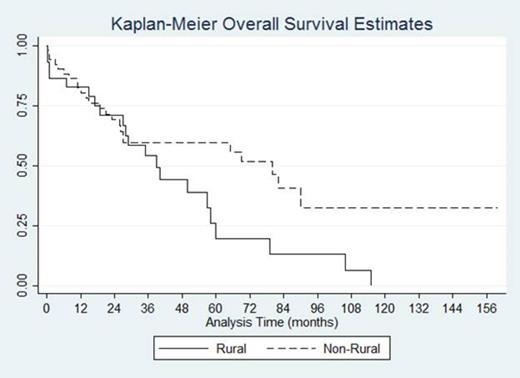
There was no difference between the mean age at diagnosis between the two groups with mean being 66.20 for non-rural group and 67.77 for the rural group. The type of heavy chain protein was generally similar for both groups with 55.74 % of patients diagnosed with Immunoglobulin G heavy chain disease. The average duration of initial presenting symptom prior to diagnosis was 7.36 weeks for the whole sample, 13.6 week for the rural group, and 4.56 weeks for the non rural group, which suggests that non-rural patients were more likely to seek medical attention sooner than their rural counterparts (p=0.0037). Tobacco consumption was higher among patients in the rural group compared to non-rural group. Nearly half (47.37%) of rural patients were diagnosed at stage 3 according to ISS staging system, while only 31.03% of non-rural patients were diagnosed at the same stage. Rural patients were more likely to be diagnosed at a more advanced disease stage (p=0.063). The nature of the chief presenting problem was generally similar in both groups with the exception of the higher likelihood of patients in non-rural group to be diagnosed at an asymptomatic stage. In the whole sample, 33.33% of patients had evidence of being offered or educated about ASCT as a treatment option, and 18.52% of patients actually receiving it. There was no different between the two groups in this regard. Median survival time for the whole sample was 57 months. Patients in the rural group had a median survival of 39.03 months (95% CI 18.96- 57.99), while non-rural patients had a median survival of 68.99 months (95% CI 25.95-90.02) ( p<0.001). Log-rank test for equality of survivor function showed survival benefit in favor of the non-rural group (p=0.07).
Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the 1st US based study that examine rural-urban difference in survival of multiple myeloma patients. Our results showed that rural patients of southern New Mexico state had longer period of symptoms prior to diagnosis, were diagnosed at a more advanced stage and had worse survival compared to their non-rural counterparts. This is perhaps a result of many challenges that face health care in rural population. It is recommended to encourage the efforts aiming to enhance health care services in rural areas, to minimize the disparities in health care between rural and urban populations.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal