Abstract
Anthracyclines (AC) still constitute the mainstay of the 1st line treatment in lymphoma: their use, however, is limited by the occurrence of Cardiac Toxicity (CT). The exact prevalence of AC CT occurring after widely used regimens such as R-CHOP or ABVD is unknown and there is uncertainty about the best monitoring method and possible prophylactic or therapeutic interventions.
METHODS: We started a prospective observational trial in lymphoma patients undergoing treatment with conventional or liposomal AC. We used a comprehensive approach to monitor for AC CT, using a telemedicine(TM) system integrating echocardiography, ECG and biomarkers (Troponin I - TnI).
RESULTS: In this final analysis, 95 patients completed the planned treatment (52 males and 43 females). Median age was 56.03 years (range 19.1 to 78.5 years), and 36 patients were > 65 years. 23 were HL and 72 NHL (DLBCL was the most represented subtype with 47 cases). Liposomal AC was used in 31 patients and classical AC in 64, with mean cumulative doses of 283.33 and 272.76 mg/sqm, respectively.
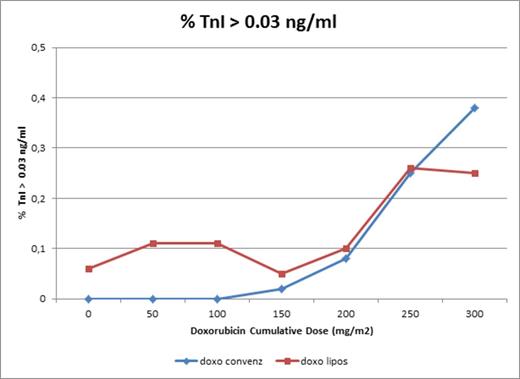
10/95 patients (11%) developed a TnI rise above 0.08 ng/ml and 39/95 (41%) above 0.03 ng/ml. With both cut-offs, the rises occurred more frequently at cumulative doses >200 mg/sqm. The major arising occurred in the group underwent classical AC, while in the group underwent liposomal AC although the value before first infusion was in 10% more than 0.03 at the cumulative dose of 300 mg /sqm there's a plateau of troponin value.
Thanks to this monitoring system we noticed 2 Acute cardiac toxicity events with resolution in 100% of cases. Furthermore in those cases where has registered a subclinical CT has begun a prompt Cardiological therapy by ACE inhibitors and Beta Blocker to reduce the relative risk of Cardiological events.
CONCLUSIONS: Even with low cumulative doses, with a median follow up of 13 months, subclinical signs of AC CT were found in at least 11% of patients. The use of liposomal AC allow the safe treatment of patients with a previous heart disease diagnosis rather it seem protective in the higher cumulative doses.
A longer follow up will be able to clarify the impact of arising of TnI more than 0.03 and 0.08 on the developing of AC CT in all our series.
On the basis of our experience a multicentric trial has begun on behalf Italian Lymphoma Foundation (FIL)
In a low-risk setting for AC CT, a monitoring strategy combining clinical, imaging, instrumental and biomarker data seems to enhance the sensitivity of separate methods. This strategy is feasible and resource-saving thanks to the integration in a TM system.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal