Abstract
Introduction
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and has an aggressive natural history. R-CHOP has improved patient (pt) survival and established a standard of first line care. In the rituximab era the prognosis for relapsed DLBCL is poor, with salvage chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) only curing a small proportion (<25% of all relapses) of those with adequate performance status. Relapsed DLBCL in those unfit for ASCT or post-ASCT is rarely curable, and remains an unmet clinical need.
AZD1152 (barasertib) is a highly selective and potent Aurora B kinase inhibitor. Aurora B kinase has an important function at the spindle assembly check-point in mitosis. The kinase is overexpressed in 48% of DLBCL. Exposure of high grade lymphoma B cells to AZD1152-HQPA in vitropotently induced growth arrest and apoptosis via caspase-dependent and independent mechanisms.
AZD1152 was well tolerated in a phase I study in relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukaemia. We performed a phase II single arm open-label trial to determine the efficacy and tolerability of AZD1152 in relapsed/refractory DLBCL pts who had failed or were ineligible for salvage/high dose chemotherapy and had received at least one line of potentially curative immunochemotherapy.
Methods
Pts with relapsed/refractory (de novoor transformed indolent NHL) DLBCL with measurable disease (at least a non-irradiated single lesion (>1.5cm)) were treated with up to six cycles of 96-hour continuous intravenous (iv) infusions of AZD1152 as an inpt every 3 weeks.
Due to concerns over possible precipitation of drug in the line, regular 4 hourly saline flushes were required via each lumen to maintain patency. Prophylactic G-CSF was permissible per ASCO guidelines. Ongoing cycles were commenced when neutrophils recovered to ≥1.0x109/L and platelets to ≥50x109/L.
The primary endpoint was overall response rate (ORR). Secondary end-points were progression-free survival (PFS) at one year, % change in tumour size, and safety measured by the incidence and severity of adverse events (AEs). Response assessment using FDG-PET was completed at day 15 of cycle 2. Pts with stable disease (SD), minimal, partial (PR) or complete response (CR) according to Cheson criteria remained on protocol, but those with progressive disease (PD) were taken off study.
As data that suggests MYC overexpression may enhance responses to aurora B kinase inhibition, MYC by IHC and FISH for c-MYC translocation was performed. All diagnostic specimens were reviewed by specialist haemato-pathologists.
Results
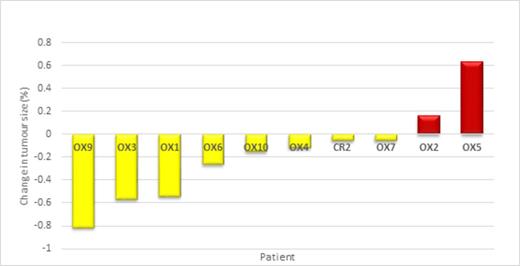
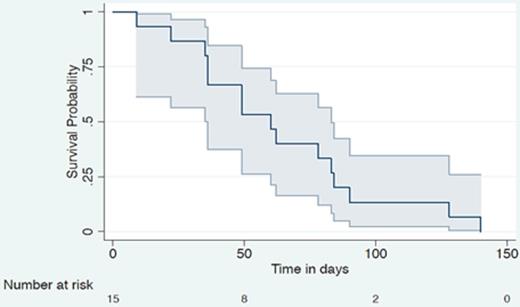
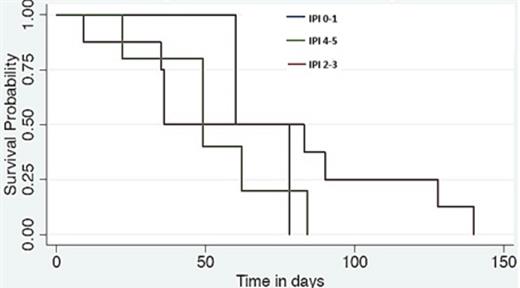
Fifteen pts were enrolled in 20 months, and received 1-6 cycles. Overall, 42 cycles were administered (41 at full dose). One pt completed all six planned cycles. The cohort included 8 males and 7 females, with a median age of 65 (35-74 years). 13% had a low International Prognostic Index (IPI) (0-1), 53% an intermediate IPI (2-3) and 33% a high IPI (4-5). The best ORR was 20% (see Fig 1 for tumour percentage reduction) with no cases of CR and 3 PR. 33% obtained SD for between 2-6 cycles. The median PFS was 60 days (95% CI 36-84 days) (see Fig 2). IPI (p=0.584) (See Fig 3), gender (p=0.113), disease bulk at diagnosis (p= 0.654) or c-MYC dysregulation (p=0.331) did not predict PFS. Early discontinuation occurred in 14 pts from PD.
Safety
Most AEs were grade 1-2. 18 episodes of neutropenic fever occurred, including one grade 4 bacteraemia. There were no fatal SAEs and each episode resolved with iv antibiotics and G-CSF. All other toxicities were transient, manageable and expected. 13% of pts developed a total of 2 episodes of mucositis following 42 total doses. Neutropenia (grade 3-4), diarrhoea and nausea were common but manageable and expected. No Suspected Unexpected Serious Adverse Reactions occurred.
Conclusions
Three-weekly AZD1152 was safely administered to pts with relapsed DLBCL. Responses were seen, providing a proof of concept that Aurora B kinase is a valid target in DLBCL. However, efficacy was modest. The infusate delivery was cumbersome. Dose intensity was maintained during treatment. Important but manageable AEs included neutropenic fever and mucositis. Aurora B kinase is a rational target for further investigation. NCT01354392.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal