Abstract
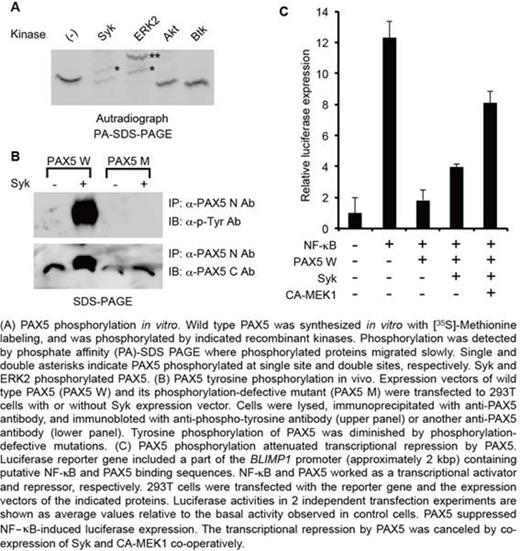
Pax5 is an essential transcription factor to maintain B cell identity. Pax5 is expressed in stages from pro-B to mature B cells and promotes the B cell differentiation program by transcriptional activation of many B cell receptor (BCR)-related genes such as CD19, CD79a, and BLNK. On the contrary, it inhibits plasma cell differentiation by suppressing the expression of BLIMP1 and XBP-1, transcription factors essential for plasma cell differentiation. After BCR stimulation by antigen, upregulation of BLIMP1 and XBP-1 and subsequent suppression of PAX5 by BLIMP1 were observed and thought to be the trigger of plasma cell differentiation. We previously demonstrated that serine phosphorylation of PAX5 by ERK1/2, a main component of BCR signal, attenuated the BLIMP1 suppression by PAX5 and that the PAX5 phosphorylation might be the initial event for plasma cell differentiation (Yasuda T et al, J Immunol. 2012; 188: 6127-34). Here, we investigated additional PAX5 phosphorylation by BCR signal and found that another BCR signal component, Syk, caused PAX5 phosphorylation in vitro (Figure A). We identified the tyrosines that were phosphorylated by Syk in vitro by making phosphorylation-defective mutants, and confirmed that Syk phosphorylated PAX5 at the same sites in vivo (Figure B). In the luciferase reporter assays, PAX5 tyrosine phosphorylation by Syk attenuated the BLIMP1 suppression by PAX5, similarly to its serine phosphorylation by ERK1/2, and both phosphorylations co-operatively worked for it (Figure C). Furthermore, we demonstrated that B cell receptor stimulation with anti-IgM antibody induced Syk and ERK1/2 activation, tyrosine and serine phosphorylation of endogenous Pax5, and upregulation of Blimp1 mRNA. These results suggested that PAX5 phosphorylations by Syk and ERK1/2 co-operatively work for the cancelation of transcriptional repression of Blimp1 by PAX5 after BCR activation by antigen. This might be a trigger of plasma cell differentiation. Our findings give a new insight into the regulation of the terminal differentiation of B cells.
Naoe:Zenyaku Kogyo: Research Funding; Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma: Research Funding; Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co. LTD: Research Funding; Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. LTD: Research Funding; Novartis Pharma,: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co. LTD: Research Funding; FUJIFILM Corporation: Research Funding. Kiyoi:Zenyaku Kogyo: Research Funding; Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma: Research Funding; Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co. LTD.: Research Funding; Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. LTD: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; FUJIFILM Corporation: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal