Abstract
Introduction: Refined risk-classification of patients (pts) with MDS allows for improved treatment selection for individual pts. The Revised International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS-R) has recently been validated as a prognostic tool in lower-risk MDS pts with deletion 5q [del(5q)], who were treated with LEN in the MDS-004 study (Sekeres et al. Blood Cancer J 2014; in press). P53 nuclear protein expression, as assessed by immunohistochemistry (IHC), predicted overall survival (OS) and risk of progression to acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in lower-risk MDS pts with del(5q) (Saft et al. Haematologica 2014;99:1041-9). This analysis evaluated the prognostic value of adding p53 IHC to IPSS-R to predict OS and AML progression in pts with lower-risk MDS with del(5q).
Methods: In a subset of 85 pts from MDS-004 with bone marrow (BM) biopsies available, p53+ staining (≥ 1% IHC+++ BM cells) was visualized by IHC. Twenty-four pts had missing IPSS-R scores; 1 due to lack of baseline cytogenetic data and 23 because of missing exact BM blast percentage. Thus, 61 pts (42 initially treated with LEN and 19 with placebo) had IPSS-R and p53 IHC data available; 89% of pts in the placebo group crossed over to LEN 5 mg at Week 16. The IPSS-R Very Low and Very High risk groups with < 5 pts were combined with the Low and High risk groups, respectively. AML-free survival (AFS), OS, and time to AML progression within p53 IHC status (p53+ vs p53−), and IPSS-R risk groups were characterized by the Kaplan-Meier method with differences evaluated by the log-rank test.
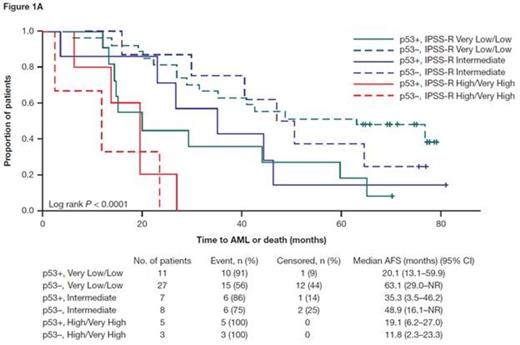
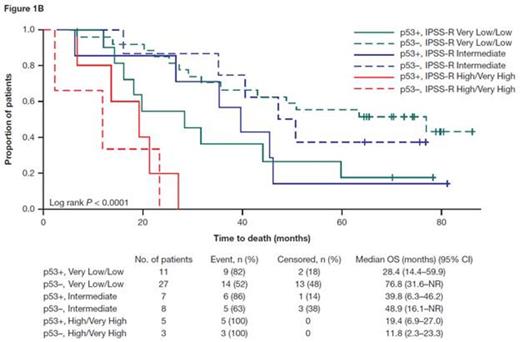
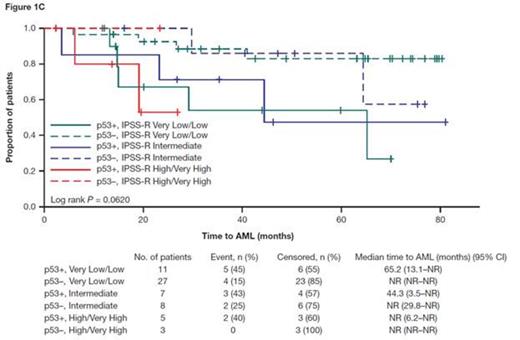
Results: Of 61 pts, 38% were p53+. There was a linear increasing trend in the proportion of pts with p53+ across IPSS-R risk groups from Very Low/Low, Intermediate to High/Very High (29%, 47% and 63%, respectively; Cochran-Armitage trend test P = 0.050). The 3 IPSS-R risk groups significantly predicted AFS and OS (log-rank P < 0.001 for both AFS and OS), but not time to AML progression (P = 0.335). Overall, AFS, OS, and time to AML progression differed significantly between p53+ versus p53− pts (23.9 vs 47.9 months for median AFS, P = 0.003; 27.0 vs 50.6 months for median OS, P = 0.005; and 44.3 months vs not reached [NR] for median time to AML progression,P = 0.003). In the IPSS-R Very Low/Low risk group (n = 38), AFS, OS, and time to AML progression were significantly worse in p53+ versus p53− pts (20.1 vs 63.1 months for median AFS, P = 0.011; 28.4 vs 76.8 months for median OS, P = 0.031; and 65.2 months vs NR for median time to AML progression, P = 0.014). Results for all IPSS-R risk groups in pts with p53 and IPSS-R data are presented in the Figure. The lack of significant differences between p53+ versus p53− pts in the Intermediate and High/Very High risk groups is likely due to the small sample size of these groups.
Conclusions: In this exploratory subset analysis of lower-risk MDS pts with del(5q), p53 IHC status in the IPSS-R Very Low/Low risk group significantly impacted AFS, OS, and AML progression. These data support the addition of p53 mutational analysis to prognostic risk assessment which should help inform the selection of appropriate treatment for individual MDS pts with del(5q). These results need to be validated in a large sample set, which will be accomplished as part of the ongoing efforts to include prognostic molecular mutations in future updates of IPSS-R
AFS (A), OS (B), and time to AML progression (C) in pts with p53 and IPSS-R data (N = 61)
AFS (A), OS (B), and time to AML progression (C) in pts with p53 and IPSS-R data (N = 61)
Shiansong Li:Celgene Corporation: Employment, Equity Ownership. Greenberg:Celgene: Research Funding; Onconova: Research Funding; GSK: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; KaloBios: Research Funding. Sekeres:Amgen Corp.: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Boehringer-Ingelheim Corp.: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene Corporation: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Dreyfus:Novartis: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria. Fenaux:Novartis: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding. Swern:Celgene: Employment, Equity Ownership. Sugrue:Celgene: Employment, Equity Ownership. Hellstrom-Lindberg:Celgene: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal