Abstract
BACKGROUND
Graft versus host disease (GVHD) remains a major complication after allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (PBSCT). Post-transplant cyclophosphamide (CY) has been shown to mitigate risk of GVHD after T-cell replete HLA haploidentical (haplo) bone marrow transplantation. We sought to identify the benefit of post-transplant CY in various diseases following myeloablative PBSCT.
METHODS
We treated 71 patients with post-transplant CY following allogeneic PBSC (T-cell replete) HLA matched unrelated donor (MUD), HLA mismatched unrelated donor (mMUD), haplo, and HLA matched related donor (MRD) transplant. The conditioning regimens were fludarabine (160 mg/m2)/busulfan (AUC 12-20,000) (+/- TBI 4 Gy for haplo) for myeloid malignancies, fludarabine (160 mg/m2)/TBI 10 Gy (or 8 Gy for haplo) or CY/TBI 12 Gy for lymphoid malignancies (total CY dose 120 mg/m2 including post-transplant CY). GVHD prophylaxis consisted of post-transplant CY 50 mg/m2 on day +3 (and day +4 for haplo), tacrolimus, day +5 to +100 (then taper over 3 months) and mycophenolate mofetil, day +5 to day +35. All patients received G-CSF (5 mcg/kg/day) starting day +5 until neutrophil engraftment. All patients received prophylactic antifungal (until day +75), antiviral (for one year), PCP prophylaxis (day +30 to +180) and antibacterial therapy (until day +100) or longer if on high-dose steroid.
RESULTS
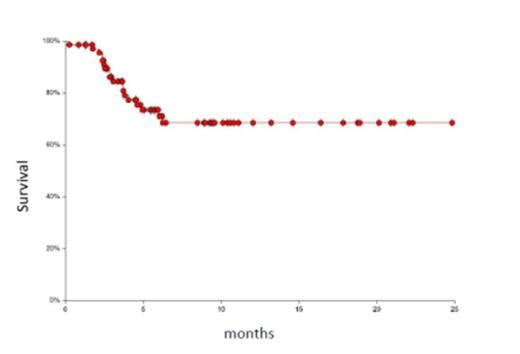
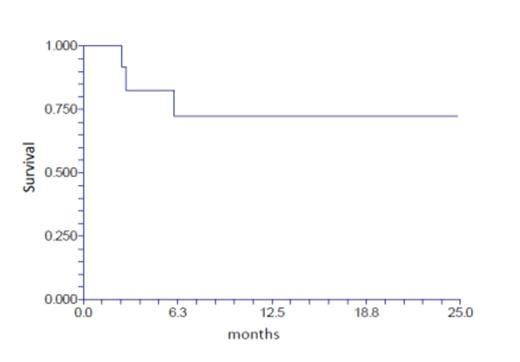
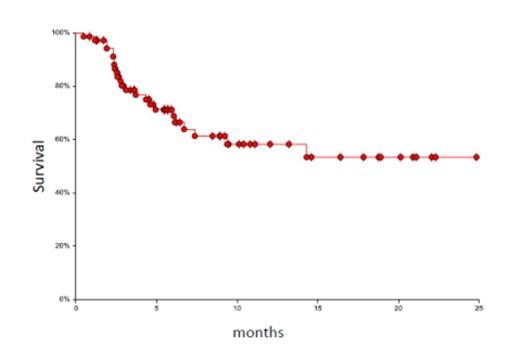
The 71 patients were treated between July 2012 and July 2014 at our institution. The donors were MUD, mMUD, haplo, or MRD (N = 46, 11, 13, 1 respectively). Patients had acute myeloid leukemia (n = 31 either in first or subsequent remission) including one patient with blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm, myelodysplastic syndrome (n = 13), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (n = 5, all in CR1 or 2), non-Hodgkin lymphoma (n = 5), Hodgkin lymphoma (n = 3), primary myelofibrosis (n = 6), chronic myeloid leukemia (n = 4), chronic lymphoid leukemia (n = 1), severe aplastic anemia (n = 2), and erythropoietic porphyria (n = 1). The median age of patients was 50 years (range: 17-72), 36 were males and 62 were Caucasians. Five patients had prior autologous transplant. All patients engrafted except one halpo patient who was successfully re-transplanted with repeat haplo (different donor) using non-myeloablative regimen (FLU/CY/TBI 4 Gy). Neutrophil and platelet engraftment occurred after a median of 12 days (range: 6-18) and 13 days (range: 5-40). The cumulative incidence of acute GVHD grade II-IV and III-IV was 16% and 8% respectively. The cumulative incidence of chronic GVHD was 54% (mild, moderate and severe; 22%, 24% and 8%). The overall cumulative relapse rate was 20%, however, 65% of AML patients relapsed after MUD transplant (n = 23) while none of them relapsed after mMUD or haplo transplant (n = 8). The overall non-relapse mortality (NRM) was 14% (total of 10 patients died as follows: GVHD; 2, infections; 4, hepatic failure; 1, toxic epidermal necrolysis; 1, pulmonary embolism; 1, lung injury; 1). The 1-year overall survival was 68% (95% CI: 54-79) (figure 1) and the 1-year disease-free survival (DFS) was 58% (95% CI: 43-71) (figure 2).
CONCLUSION
The use of post-transplant CY following myeloablative (using disease-specific preparative regimens) T-cell replete PBSCT of HLA-matched/mismatched unrelated and haploidentical donors is feasible with acceptable risk of acute and chronic GVHD, and NRM. The use of one dose of post-transplant CY after MUD transplant was associated with high risk of relapse in AML patients. Caution is to be exercised in designing clinical trials of MUD transplant for AML using post-transplant CY.
DISCLOSURES: See Conflict of Interest (COI) Disclosure statements submitted by all authors
Off Label Use: Cyclophosphamide used after stem cell transplant for graft vs host disease prophylaxis in haploidentical, matched and mismatched unrelated donor T cell replete myeloablative transplants..
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal