Abstract
Megakaryocytopoiesis, the process by which hematopoietic stem cells develop into mature megakaryocytes (MK), and thrombopoiesis, platelet production/release, are critical for blood homeostasis. We tested the hypothesis that the Rho guanine exchange factor, ARHGEF12 (also known as LARG), is critical for MK differentiation and platelet functions based on the following: 1) ARHGEF12 is part of a recurrent translocation with MLL in acute myeloid leukemia. 2) Both published microarray datasets and deep-sequencing data from our lab on primary human CD34+ cells differentiating into MKs show that ARHGEF12 expression goes up dramatically during MK differentiation. 3) ARHGEF12 is one of the most highly expressed guanine exchange factors in platelets. 4) ARHGEF12 forms a complex with G proteins and stimulates Rho-dependent signals. It is known that platelet activation can be initiated by extracellular stimuli working through G protein-coupled receptors and Rho signaling, suggesting that ARHGEF12 may function in platelet activation. 5) Mice with KO of RhoA (a known ARHGEF12 substrate) in the MK-lineage have macrothrombocytopenia and defective platelet activation.
To test this hypothesis, we used ARHGEF12 shRNA mediated KD and an ARHGEF12 specific pharmacological inhibitor (Y16) in both murine and human primary cells, and characterized a LARG KO mouse model for MK and platelet phenotypes, and found:
ARHGEF12 is differentially upregulated during MK differentiation and is enriched in platelets
Using quantitative RT-PCR and western blot analysis at different timepoints of primary FACSorted Mk progenitors induced to differentiate into mature MK in vitro, ARHGEF12 RNA and protein expression increases during MK differentiation in both the murine and human systems. Also western blot analysis of murine platelet rich plasma shows that ARHGEF12 protein is highly expressed in platelets.
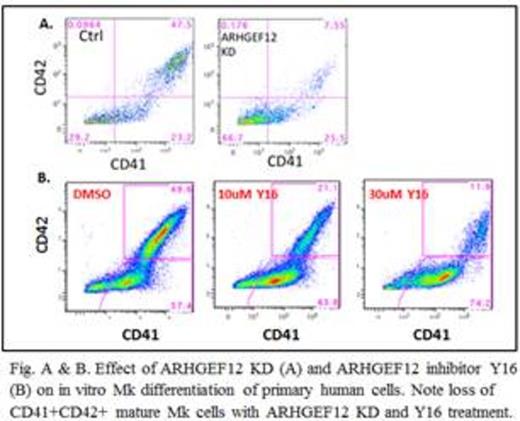
ARHGEF12 is essential for human MK differentiation
To test the function of ARHGEF12 in Mk differentiation, we used lentiviral shRNA to knockdown ARHGEF12 in FACSorted primary human Mk progenitors from mobilized peripheral blood differentiated in vitro to MK. The results show that ARHGEF12 knockdown blocks MK polyploidization (not shown) and maturation (Fig. A). This was confirmed using a published ARHGEF12 inhibitor (Y16) in the differentiation culture of human MK progenitors, in which there was a dose-dependent block in MK differentiation (Fig. B). These data suggested that ARHGEF12 is essential for human MK differentiation.
We researched the function of ARHGEF12 in the murine system using a constitutive ARHGEF12 knockout mouse model. The mice have enlarged platelets (p=0.07) and a decreased platelet count (p=0.01). However, the knockout mice have normal BM cellularity with no change in megakaryocyte number or ploidy, suggesting that ARHGEF12 is dispensable for murine MK differentiation in vivo.
ARHGEF12 is essential for platelet function in both the murine and human systems:
To test whether ARGEF12 functions in platelet activation, we compared WT versus KO platelet activation in vitro. We tested activation in response to ADP, U46619 (Thromboxane), ADP+U46619, and Thrombin. KO plateelts have significantly reduced activation in response to U46619 and thrombin, with no effects on ADP-induced activation. Analogous studies using the ARHGEF12 inhibitor (Y16) on WT platelets revealed supportive evidence. Lastly, we tested ARHGEF12 function in human platelet aggregation using the Y16 compound. Consistent with the murine data, Y16 blocked platelet aggregation in response to both U46619 and Thrombin. Taken together, these data strongly suggest that ARHGEF12 is essential for platelet function and acts downstream of the Thromboxane and Thrombin receptors.
In summary, we found that ARHGEF12 is differentially up-regulated in MK differentiation both in human and in mouse system,. It plays a critical role in human Mk differentiation but is dispensable in murine MK differentiation, and ARHGEF12 is critical for platelet functions in both human and mouse systems, potentially acting downstream of Thromboxane and Thrombin receptors.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal