Abstract
Smoldering multiple myeloma (SMM) is an asymptomatic plasma cell disorder whose risk of progression to symptomatic MM (MM) is highly variable. Therefore, the identification of predictors of progression into MM is a relevant end point. Several markers (serum M protein, percentage of bone marrow plasma cells, free light chain, FLC, ratio, immunophenotyping of aberrant plasma cells and focal lesions, FLs at MRI) have already been established to identify sub-groups of SMM patients (pts) with a highest risk of progression into MM. Among imaging methods, FDG-PET/CT is a reliable technique for assessing early skeletal involvement and for predicting outcomes at the onset of MM. However, no data are available regarding the impact of PET/CT FLs in SMM on time to progression (TTP) into symptomatic disease.
To address this issue, we prospectively studied pts with a suspected diagnosis of SMM with FDG-PET/CT. A cohort of 73 pts, with a median age of 61 years old (range 27-83) and a confirmed diagnosis of SMM, followed for a median of 2.2 years, is herein reported. By study design, all the pts were studied with PET/CT at baseline. Bone marrow involvement was described as negative, diffuse or focal. The number of FLs, as well as size and associated standardized uptake values (SUV) were recorded. For each FL, the presence of eventual underlying osteolytic lesion was investigated by the CT part of the scan; pts with osteolytic lesions were excluded from the present study, as they were considered as having symptomatic MM. Follow-up took place every 3-4 months and included clinical history, serum and urine markers and PET/CT plus axial MRI for occurrence of symptoms or an increase in M component. Progression to MM was defined by the presence of CRAB features. Skeletal progression was defined by the appearance of one or more sites of osteolytic bone destruction, pathological fractures and/or soft masses at PET/CT or MRI. The start of systemic therapy was defined as the date of event for the analysis of TTP.
Baseline patient characteristics were as follows: 83% had IgG isotype, 8% IgA and 9% BJ, with a median M component of 2.5 g/dL; 70% had ISS stage I, 23% stage II and 7% stage III. Median plasma cell involvement on bone marrow (BMPC) was 30% (range 5-100%), with 16% of the pts having more than 60% BMPC. The median serum involved/uninvolved FLC ratio was 14.39 (range 1.28-2255), with 11% of the pts presenting with a ratio ≥ 100. PET/CT was negative in 64/73 pts (88%) and positive in 9/73 (12%) of them; 5 pts had 1 FLs, 1 pt 2 FLs, 2 pts more than 3 FLs and 1 pt a diffuse bone marrow involvement. Median SUV max value was 4.45 (range 2.5-5.2). No significant differences between patients with positive or negative PET/CT were found regarding the other baseline characteristics.
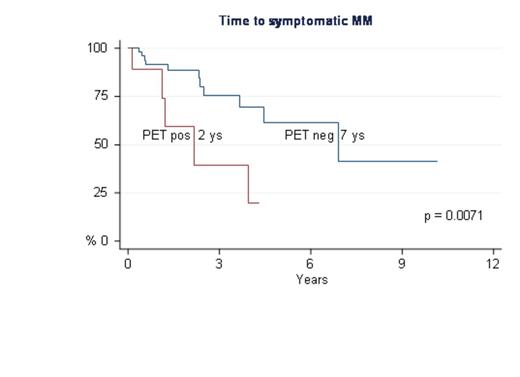
At the time of the present analysis, 63% of the pts remained in the asymptomatic phase while 37% of them progressed to MM, in a median time of 4 years, including 21% with skeleton involvement, with/without the appearance of other CRAB symptoms, and 16% with exclusive serological signs of progression. Sixty six per cent of the pts with positive PET/CT progressed to MM in comparison to 33% of the pts with negative PET/CT (P = 0.034). The relative risk of progression of the pts with a positive PET/CT was 2.3 (95% CI 09.-5.9, P= 0.06). Moreover, the relative risk of skeletal progression was 4.0 (95% CI 1.3-12, P= 0.013), with a median TTP of 2.2 years for pts with positive PET/CT versus 7 years for those with negative PET/CT (figure 1). The probability of progression within 2 and 3 years for pts with positive PET/CT was 48% and 65%, respectively, in comparison to 32% and 42% for negative pts.
In conclusion, approximately 10% of the pts with SMM have a positive PET/CT, mainly with few FLs, without underlying osteolytic lesion, with a low FDG uptake. PET/CT positivity significantly increased the risk of progression of SMM into active MM. PET/CT could become a new risk factor to define high risk SMM. A larger cohort of pts will be presented at the meeting. Further studies are warranted to find and optimal cut off point of FLs to capture the higher risk of progression at 2 year and to merge with other prognostic factors.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal