Abstract
We have designed a novel approach for treating tumors utilizing a combination of active immunotherapy and targeted kinase inhibition. We injected tumors with unmethylated CG-enriched oligodeoxynucleotides (CpG), an agonist for the toll like receptor 9 (TLR9). This in situ CpG injection resulted in local tumor eradication by NK cells and macrophages but on its own was not able to induce a systemic anti-tumor immune response. Ibrutinib is an irreversible inhibitor of Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk), a key enzyme in the signaling pathway downstream of B Cell receptor (BCR) is now known to also inhibit ITK, a key enzyme in the survival of Th2 T cells. By doing so, it can shift the balance to the more effective Th1 immune response.
In our murine model, the combination of in situ injection of CpG and systemic treatment with Ibrutinib resulted in eradication of tumor cells not only in the local site but also at distant sites. This anti-tumor immune response required both CD4 and CD8 T cells as the effect was lost in nude, scid and T cell depleted mice. Additionally, transferred T cells from animals previously treated with CpG and Ibrutinib protected na•ve mice from tumor challenge.
This immune-enhancing effect of Ibrutinib is unexpected. It reflects on the mechanism of action of the drug against B cell malignancies and it provides a novel way of enhancing anti-tumor immune responses against other types of cancer.
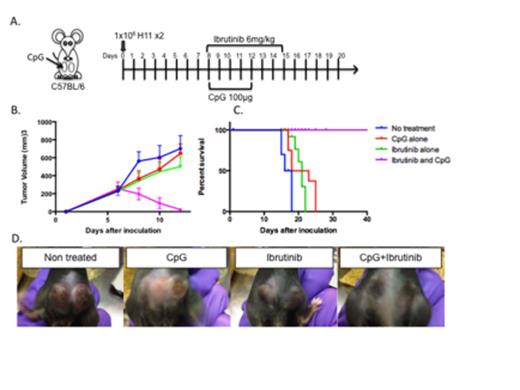
A. six to eight weeks BALB/C mice were inoculated with 1x106 H11 cells s.c. into the right and left sides of their abdomen, tumor growth was monitored with a digital caliper. Therapy was started when tumors reached a size of 0.7-1cm in the largest diameter, CpG (100µg/injection) was given intratumorally to the left tumor every day in days 1-5, Ibrutinib (6mg/kg) was given daily, intraperitonealy (IP) on days 1-8. B. Growth curve of the right (non-treated) tumor C. Mice survival D. Mice at day 4 after treatment.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal