Abstract
Background: Prior studies have demonstrated unique clinicopathologic features of the BV of MCL including an inferior response to chemotherapy and poor long-term outcomes as compared to other MCL variants in the pre-rituximab era. A paucity of data precludes whether the use of rituximab or intensified therapy can overcome the inferior outcome associated with the BV.
Methods MCL patients (n=169) treated by NLSG between 1983 and 2010 were included. Morphologic variants were classified based on published WHO criteria. We compared disease characteristics, therapy and outcomes according to MCL subtypes using the Kruskal Wallis or Chi-square tests. Univariate probabilities of progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were estimated using the Kaplan Meier method. Multivariate analyses were performed using Cox proportional hazards regression to evaluate differences in outcomes of MCL subtypes while adjusting for prognostic covariates.
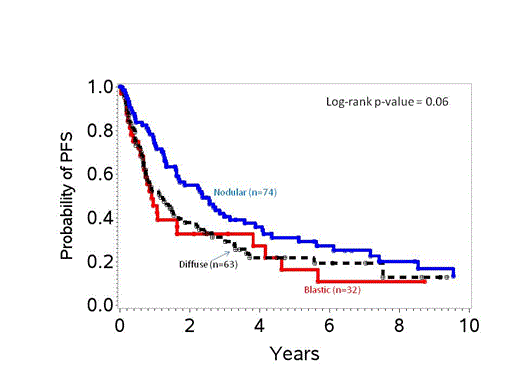
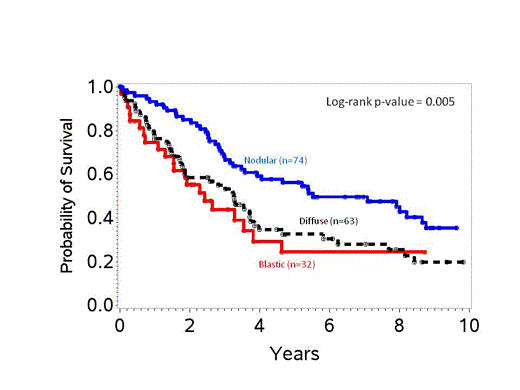
Results The study population included 19% BV, 37% diffuse and 44% nodular subtypes. BV, diffuse and nodular subtypes differed in the median age (61 vs. 68 vs. 59, p=.002) and stage III/IV disease (81% vs. 79% vs. 93%, p=.05) at diagnosis, but did not differ in the distribution of sex, Karnofsky performance status (KPS), MCL international prognostic index (MIPI), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level, B-symptoms, or extranodal involvement. Patients received the following therapies: intensified therapy such as Cyclophosphamide, Vincristine, Doxorubicin, and Dexamethasone (Hyper-CVAD) +/- Rituximab (R) (30%), Cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP)-R-like (24%), CHOP-like (35%) or others (11%). Approximately one-third received autologous (25%) or allogeneic (8%) SCT. There was a significant difference in the type of chemotherapy given in each group (p=.002) but not in the use of radiation therapy or proportion in each group receiving autologous/allogeneic stem cell transplant (SCT). Median follow-up across MCL subtypes was similar. Overall response rate was similar for BV, diffuse and nodular subtypes (68% vs. 65% vs. 80%, p=.44). The 5-year progression-free survival for BV vs. diffuse vs. nodular was 16% vs. 22% vs. 31%; p=.06, (Figure 1) and 5-year OS was 24% vs. 32% vs. 56% respectively; p=.005, (Figure 2). In multivariate analysis, compared to BV, diffuse subtype had similar risk of disease progression or death (hazard ratio, HR of 0.78, 95% confidence interval (CI) of 0.48-1.26) whereas nodular subtype had lower risk (HR 0.62, 95% CI 0.39-0.99). Additionally, low or intermediate MIPI, good KPS, absence of B-symptoms and undergoing SCT were associated with lower risk of progression or death. A subset univariate analysis of BV demonstrated no survivors beyond 5 years after conventional chemotherapy, whereas 33% remained alive at 10 years after intensified therapy.
Conclusions BV and nodular MCL presented at a somewhat younger median age compared to diffuse MCL, and BV and diffuse MCL was more likely to present as stage I/II disease, compared to nodular MCL. The PFS and OS of BV MCL are similar to diffuse MCL but OS is worse than nodular MCL. The use of SCT may improve survival in MCL including BV variant.
PFS of different subtypes of MCL
OS of different subtypes of MCL
Armitage:Ziopharm Oncology: Consultancy; GlaxoSmithKline: Consultancy; Spectrum Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy; Tesaro bio Inc: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal