Abstract
Introduction: The guardian™ program is a large, multinational trial program designed to support the registration of turoctocog alfa (NovoEight®), a new B-domain–truncated recombinant Factor VIII (FVIII) molecule. A total of 214 patients with severe hemophilia A without inhibitors were enrolled in the guardian™ program as of 1 Sept 2012. Two open-label, non-controlled, phase 3a trials assessing the efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics of turoctocog alfa in previously treated patients (PTPs) ≥12 years old (guardian™1) or PTPs <12 years old (guardian™3) were conducted; upon completion, participants could enter an extension trial (guardian™2) that is ongoing. Patients received turoctocog alfa as prophylaxis and to treat bleeds. The primary endpoint was incidence of FVIII inhibitors (≥0.6 Bethesda Units) and a key efficacy endpoint was the annualized bleeding rate (ABR).
Methods: For inclusion in this post-hoc analysis, PTPs must have participated in guardian™2 and either guardian™1 or 3, had ≤1 week of surgery treatment in guardian™1/guardian™3 (initial period), and had ≥3 months of exposure to turoctocog alfa prophylaxis during a selected time period (1 January 2012 – 30 June 2013) in guardian™2. This guardian™2 time period was selected to obtain a group of patients who had participated in the trial for an adequate duration to enable comparison over time. Starting dose of turoctocog alfa was 20 IU/kg in guardian™1 and was determined by the investigator in guardian™3; doses were adjusted based upon clinical criteria, at the discretion of the physician.
This analysis investigated the relationship between change in ABR from guardian™1/guardian™3 to guardian™2 and average ABR during these periods. Change in ABR was defined as the change in number of bleeds per year and average ABR was defined as (ABR [guardian™1/guardian™3] + ABR [guardian™2]) /2 for each patient. Change in ABR versus the ratio of mean weekly preventive dose was also investigated, with ratio defined as (mean weekly dose [guardian™ 2] / [mean weekly dose [guardian™1/guardian™3]) for each patient. Analyses were descriptive; statistical analyses were not conducted.
Results: A total of 166 patients met inclusion criteria for this analysis (111 from guardian™1 [21 adolescents 12–17 years old and 90 adults ≥18 years old] and 55 from guardian™3 [27 children ≤5 years old and 28 children 6–11 years old]). For this subgroup of patients with prolonged extension study exposure, overall median ABR in guardian™1 was 4.0 bleeds/patient/year (range: 0.0–38.4), and in guardian™3 was 3.8 bleeds/patient/year (range: 0.0–34.7); overall median ABR during guardian™2 was 1.6 bleeds/patient/year (range: 0.0-18.8). ABR by age is shown in table 1.
Table 1: Median annualized bleeding rate and reduction over time
| . | guardian™1/ guardian™3 . | guardian™2 . | % reduction during extension . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adults | 4.2 | 1.3 | 69% |
| Adolescents | 4.0 | 1.5 | 63% |
| Children 6–11 years | 3.6 | 2.3 | 36% |
| Children ≤5 years | 3.8 | 2.0 | 47% |
| . | guardian™1/ guardian™3 . | guardian™2 . | % reduction during extension . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adults | 4.2 | 1.3 | 69% |
| Adolescents | 4.0 | 1.5 | 63% |
| Children 6–11 years | 3.6 | 2.3 | 36% |
| Children ≤5 years | 3.8 | 2.0 | 47% |
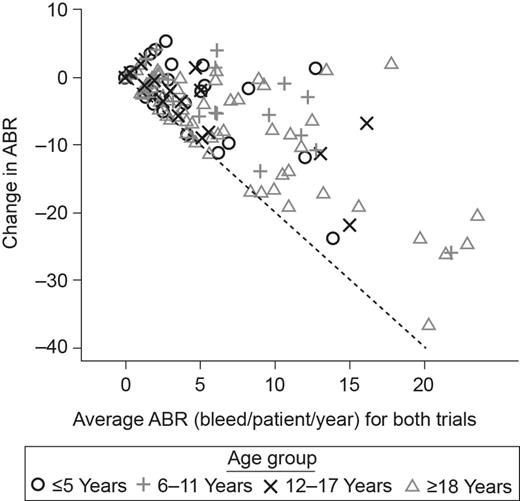
The majority of patients had a reduction in ABR during the trials (Fig. 1). The patients with the highest ABR during the initial period were those with the largest reduction in ABR. When the change in ABR was examined by age, older patients tended to have a larger reduction in ABR than younger patients. For some patients, ABR in guardian™2 was higher than in the initial period. There was no clear correlation between dose and ABR (figure not shown in abstract). Within age groups, weekly doses were highly variable. The majority of patients showed an increase in dose over the analyzed period, most by approximately 20% compared with the initial dose (figure not shown).
Change in ABR versus average ABR for guardian™1/guardian™3 and guardian™2.
Change in ABR versus average ABR for guardian™1/guardian™3 and guardian™2.
Conclusions: For PTPs on long-term prophylaxis with turoctocog alfa, change in ABR over time may be correlated with initial ABR levels. Patients who initiated with high ABR levels (and therefore likely poor joint status) tended to have the most pronounced reduction in ABR while, for others, low ABR was maintained. Older patients likewise tended to have a larger reduction in ABR than younger patients. No clear correlation was found between dose and ABR, indicating that dose changes may occur due to considerations other than bleeding frequency. Slight increases in dose over time likely represent individualized dose adjustments by physicians aimed to optimize treatment outcomes.
Ozelo:Novo Nordisk, Baxter and Bayer: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Bayer, CSL Behring and Novo Nordisk: Research Funding. Janic:Novo Nordisk, Baxter, Bayer, Pfizer and Octafarma: Honoraria; Novo Nordisk, Baxter and Bayer: Speakers Bureau; Novo Nordisk, Baxter, Bayer and Pfizer: Research Funding. Matytsina:Novo Nordisk A/S: Employment. Landorph:Novo Nordisk A/S: Employment. Zeuthan:Novo Nordisk A/S: Employment. Santagostino:Pfizer: Research Funding; Bayer, Pfizer, Baxter, CSL Behring, Novo Nordisk and Grifols: Consultancy; Biotest, Kedrion and Octapharma: Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal