Abstract
Background: Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1), a key regulator of cell cycle progression and accurate spindle assembly, is an attractive target for cancer drug discovery. We have previously shown that volasertib (BI 6727), a potent and selective small-molecule inhibitor of Plk, induces a distinct mitotic arrest phenotype in prometaphase (“polo-arrest”) with subsequent apoptosis in a variety of different cancer cell lines, irrespective of their mutational status. When used in vivo, volasertib administered intravenously shows potent anti-tumor activity in xenograft models of human epithelial cancers at well-tolerated doses. The present study was designed to extend the analysis of volasertib to additional preclinical models of human AML, including bone marrow samples from AML patients. Volasertib is the most advanced Plk inhibitor in clinical development and has demonstrated encouraging results in phase II clinical trials. It is currently being investigated in a phase III clinical trial in patients with previously untreated AML, who are ineligible for intensive remission induction therapy.
Methods: A panel of human AML cell lines was used to evaluate pharmacodynamic biomarker modulation and anti-tumor effects of volasertib in vitro using FACS analysis, Western blot analysis and proliferation assays. This in vitro analysis of established AML cell lines was extended to proliferation assays using bone marrow samples from AML patients. In vivo anti-tumor activity of volasertib was tested in subcutaneous xenograft models as well as in multiple disseminated xenograft models of AML. Single-agent efficacy of volasertib and combination therapies were evaluated with existing and emerging AML drugs, including an approved cytotoxic drug (cytarabine), hypomethylating agents (decitabine, azacitidine) and a signal transduction inhibitor targeting FLT3 (quizartinib).
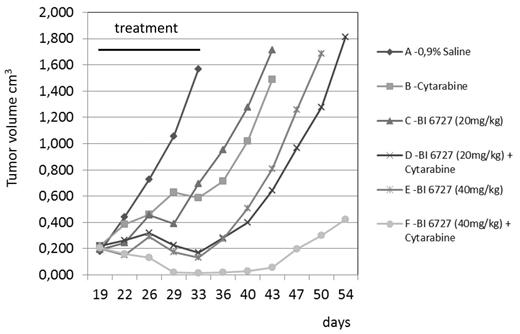
Results: Volasertib potently inhibited proliferation of established AML cell lines in vitro with EC50 values of 16-169 nM. Proliferation assays with 15 ex vivo bone marrow samples from AML patients showed EC50 values of 8-8800 nM with a median EC50 of 37 nM. Volasertib showed potent anti-tumor activity at well tolerated doses in 3 subcutaneous xenograft models of AML (MV4-11, Molm-13 and a patient-derived AML model AML-6252). While single-agent volasertib at medium dose level (20 mg/kg q7d i.v. for 2 cycles) and single-agent cytarabine (100 mg/kg q3-4d i.p. for 2 cycles) showed moderate efficacy in the AML-6252 AML model, the combination showed improved efficacy. Moreover, efficacy of single-agent volasertib at high dose level (40 mg/kg q7d i.v. for 2 cycles) could be further improved by adding cytarabine to the treatment regime (Figure 1). A combination of volasertib with decitabine or azacitidine was tested in the MV4-11 subcutaneous AML xenograft model. Either combination therapy showed improved efficacy compared to the respective single-agent treatment groups. Volasertib showed also improved anti-tumor activity when tested in combination with the Flt-3 inhibitor quizartinib (5 or 10 mg/kg qd po for 2 cycles) in the MV4-11 AML model. While tumors in the quizartinib single agent treatment groups started to regrow around day 60 post treatment start, a combination with volasertib could control tumor growth long term until the study was terminated (day 87 post treatment start). Efficacy of volasertib was also tested in 3 disseminated xenograft models of AML (MV4-11, Molm-13 and THP-1). Efficacy read out in these disseminated models was based on tumor load measurements as detected by bioluminescence imaging and increased lifespan. Volasertib prolonged survival compared to vehicle treated animals in all three disseminated models of AML.
Conclusions: These results indicate that volasertib is highly efficacious as a single agent in preclinical models of AML and shows potential for improved efficacy and good tolerability in combination with existing and emerging AML drugs.
Efficacy of volasertib in combination with cytarabine in a patient-derived AML model (AML-6252)
Efficacy of volasertib in combination with cytarabine in a patient-derived AML model (AML-6252)
Rudolph:Boehringer Ingelheim RCV: Employment. Off Label Use: Volasertib is an investigational agent. Albrecht:Boehringer Ingelheim RCV GmbH & Co KG: Employment. Geiselmann:Boehringer Ingelheim RCV GmbH & Co KG: Employment. Impagnatiello:Boehringer Ingelheim RCV GmbH & Co KG: Employment. Garin-Chesa:Boehringer Ingelheim RCV: Employment. Wernitznig:Boehringer-Ingelheim: Employment. Moll:Boehringer-Ingelheim: Employment. Kraut:Boehringer Ingelheim RCV: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal