Abstract
Backgrounds:
Treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) not eligible to high dose therapy represents an unmet medical need. Histone deacetylases (DACs) regulate chromatin structure and function and are involved in crucial mechanisms of lymphoma cell growth. Panobinostat showed encouraging therapeutic activity in Hodgkin lymphoma, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and other non-Hodgkin lymphomas, in studies conducted in lymphoma cell lines and in vivo in patients with advanced hematologic malignancies. Moreover, recent studies showed a potent activity of Panobinostat in DLBCL.
Purpose:
On this basis we performed a prospective, multicenter, phase II single arm study, to evaluate safety and efficacy of single agent Panobinostat as salvage therapy for R/R DLBCL adult patients and to evaluate a possible relationships between response and any biological features.
Patients and Methods:
Adult patients with R/R DLBCL who already performed high-dose chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) or were not eligible for ASCT were included. The treatment plan included 6 induction courses with Panobinostat monotherapy followed by other 6 courses of consolidation; patients achieving complete response (CR), partial response (PR) or stable disease (SD), underwent maintenance for a maximum of 36 courses. In each 28-days course, Panobinostat was administered orally at the dosage of 40 mg/day three-times every week; dose adjustments for patients unable to tolerate the protocol-specified schedule were provided. The primary objective was to evaluate Panobinostat activity in terms of overall response (OR) according to the Cheson 1999 criteria; secondary objectives were: CR rate, time to response (TTR), progression-free survival (PFS), safety and feasibility of Panobinostat. We included evaluation of the impact of pharmacogenetics, immunohistochemical patterns and patient's specific gene expression and mutations as potential predictors of response to Panobinostat as explorative objectives. To this aim a pre-enrollment new tissue biopsy was mandatory.
Results
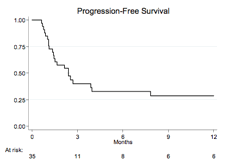
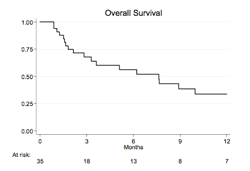
Thirty-five patients, 21 males (60%), were enrolled between June 2011 and March 2014. Clinical characteristics were: median age 73 (range 65-75), stage IV in 18 (55%), B-symptoms in 9 (28%), increased LDH in 24 (69%), high-intermediate or high International Prognostic Index (IPI) in 18 (51%). Patients received a median of 2 prior lines of therapy (range 1-4). At the end of induction phase, 7 responses (20%) were observed, including 4 CR (11%), while 28 patients (80%) discontinued treatment due to progressive disease (PD) in 21 (60%) or adverse events in 7 (20%). Median TTR in 9 responders was 2.6 months (range 1.8-12). With a median follow up of 6 months (range 1-34), the estimated 12 months PFS and OS were 27% and 30.5%, respectively. In univariate analysis, favourable IPI score and cutaneous involvement at enrollment showed a trend toward a higher ORR (p=0.007 and 0.061, respectively); pharmacogenetics, immunohistochemical and gene expression profile studies are still ongoing. No toxic deaths were reportewd; 18 patients died, 17 due to lymphoma progression and one for allogeneic transplant related complications, performed after PD. Grade 3-4 thrombocytopenia and neutropenia were the most common toxicities (in 29 (83%) and 12 (34%) patients, respectively), while grade 3-4 extra-hematological toxicity included diarrhoea in 4 (12%), infectious complications in 1 (3%) and supraventricular arrhythmia in 2 patients (6%).
Conclusions
The results of this study indicate that Panobinostat might be remarkably active in some patients with R/R DLBCL, showing durable CR. Feasibility was impaired by relevant hematological toxicity, mainly frequent and dose limiting grade 3-4 thrombocytopenia. Data that will be obtained from biological exploratory studies could hopefully be useful to better address the use of Panobinostat in peculiar subsets of patients.
Off Label Use: Panobinostat in DLBCL.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal