Abstract
The diagnosis of von Willebrand Disease (VWD) remains a challenge of daily hematology practice. Ristocetin cofactor activity (VWF:RCo) is an important parameter for the diagnosis of VWD and is also essential for its management. However, reproducibility of the available tests for VWF:RCo is still a major issue, as evidenced by coefficient of variations (CV) as high as 30%, 45% and 27% in the ECAT, NEQAS and PALQ external quality assessment program. Classical methods to measure VWF:RCo include light-transmission platelet agregometry (LPA) and visual agglutination with formaldehyde fixed human platelet (VA), and more recently, VWF activity based on automated latex immunoassay (LIA). The glycoprotein (GP) Ibα is the main receptor for von Willebrand factor (VWF) in the platelet membrane. Currently, two automated methods with immobilized GPIbα have been developed to improve the sensitivity and specificity of VWF:RCo. One of them is performed with ristocetin while the other one uses a mutant GPIbα with gain of function and does not require ristocetin.
This study aims to compare the two assays using immobilized GPIbα with other four assays for VWF functional determination, in patients with confirmed and under investigation for VWD.
We evaluated six different VWF functional assays: VWF:RCo LPA (Chrono-Log); VA (Siemens); VA in house (with ristocetin from Chrono-Log); automated-LIA (Hemosil); in comparison to two assays using immobilized GPIbα with or without ristocetin, the GPIbα-ristocetin (Hemosil), and GPIbα-mutant (Siemens Innovance). Reference ranges for each method were established in 20 healthy adults. Plasma samples collected at the same time from 40 individuals were used in this comparative study, with 25 type 1 VWD, 2 type 3 VWD, and 13 under investigation. Diagnosis of VWD was based on bleeding history (evaluated by MCMDM-1VWD Bleeding Score), historical levels of VWF antigen (VWF:Ag) by ELISA, and VWF:RCo (assayed by LTA or VA) obtained from medical records. Statistical analysis were performed based on linear regression (Spearman correlation), agreement test (Altman Bland), and chi-square test using Prism 6.0.
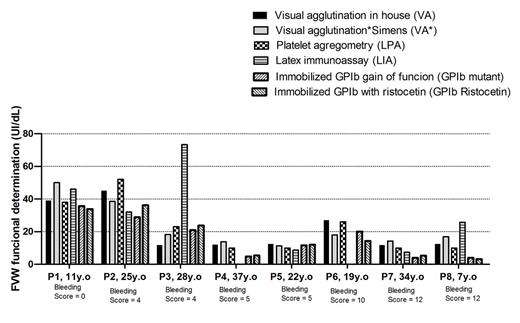
When all 40 patients were evaluated for both methods, GPIbα-ristocetin and GPIbα-mutant, we observed a good coefficient of correlation (r = 0.8954; p<0.0001). However, when 7 type 1 VWD patients, and 1 under investigation case were evaluated for the six methods, the two using immobilized GPIbα showed lower median (16.78 ± 4.62 with GPIbα-ristocetin, and 16.28 ± 4.29 with GPIbα-mutant), when compared with the other four assays (LTA: 22.38 ± 5.5; VA in house: 21.45 ± 4.87; VA Siemens: 22.65 ± 4.9; and LIA: 24.19 ± 9.0). In this group, when the bleeding score (BS) were ≥ 5, the VWF functional results were lower than 25 IU/dL, using all six methods (figure). Among 13 individuals under VWD investigation, GPIbα-ristocetin and GPIbα-mutant showed good agreement with the LTA/VA results and clinical history, and we could concluded that 4 have VWD, and for 4 individuals VWD was excluded. However, 2 individuals with no history of bleeding presented abnormal results for GPIbα-ristocetin and GPIbα-mutant, showing probably false positive results. One patient with no bleeding history, and abnormal LTA/VA results had normal GPIbα-ristocetin and GPIbα-mutant results, demonstrating poor reproducibility and precisian of the classical methods. On the other hand, two patient with BS 6, the diagnosis of VWD was demonstrating only by immobilized GPIbα methods.
The VWF:RCo is a cumbersome assay and can be affected by polymorphisms present in the ristocetin binding site of VWF. Recently, new technologies have been developed to improve the VWF functional evaluation. It is consensus that methodologies using platelets are more accurate than other methods. Therefore, immobilized GPIbα has the objective to improve the sensitivity and specificity. Besides good results of concordance between immobilized GPIbα in the group of VWD patients and for 62% individual under investigation, we also observed false positive results related with these methods. The presence or absence of ristocetin on the immobilized GPIbα setting appear not engender different results in this study. In general, this new technologies present better precision compared to VA and LTA.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal