Abstract
Background. Heat shock family proteins (HSP) are induced by cellular stress, and act as molecular chaperones regulating protein folding, conformation and proteosomal degradation, thereby affecting cell stability, cycling, and apoptosis. High levels of some HSP have been observed in AML and high HSP90 is prognostically adverse. Cell line studies show that HSP protects AML cells against chemotherapy or other stresses and that inhibition of HSP 27, 70 or 90 has antileukemic activity. HSP proteins have typically been studied individually, and in small series. Interactions with multiple signaling and functional pathways are suspected, but the actual relationship in primary AML samples is unknown. We therefore investigated the protein expression of members of the HSPA, B and C groups, HSP 70, 27 and 90, Hugo Names HSPA1A_L, HSPB1 and HSP90AA1_B1, respectively, in a large series of 511 AML patients and compared expression to 228 other simultaneously measured proteins.
Methods. We made a reverse phase protein array (RPPA) with protein from leukemia enriched cells from 511 new AML patients. Both bone marrow (BM, n=387) and peripheral blood (PB, n=283) samples were used, with 140 cases having both. The RPPA was probed with 231 strictly validated antibodies, including antibodies against HSP27, 70 and 90. Expression was compared to that of normal bone marrow derived CD34+ cells. Interaction networks with the other 228 proteins were generated from the RPPA data using glasso and supplemented by the literature of known interactions.
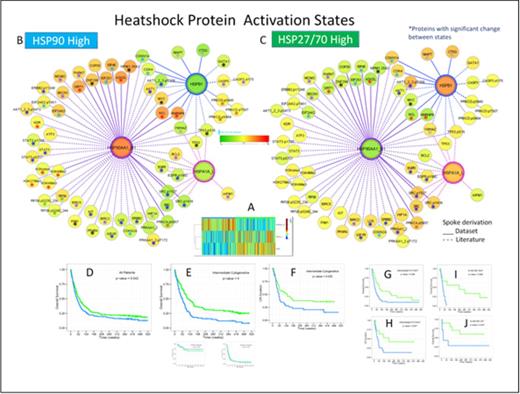
Results: A heatmap of HSP27, 70 and 90 expression was generated and hierarchical k-and means clustering performed (Fig 1A). Using the Prototype Clustering method an optimal division into two clusters C1) characterized by High HSP27 and 70 but low HSP90 and C2) characterized by High HSP90 and low HSP27 and 70 expression. Patients with high HSP90 had significantly higher % BM Blasts (63.6% vs. 42%), WBC (40.8K vs 16.9K), %PB blasts (44 vs. 17%), LDH levels, concurrent infection 34% vs. 12%), FLT3-ITD (25 vs. 13%) or FLT3-D835 mutation (8% vs. 4%) (all P < 0.00001) compared to those with High HSP27 & 70. HSP90 High patients were less likely to have an antecedent hematological disorder (26 vs. 47%, P < 0.00001). Other clinical features, age, gender, cytogenetics, RAS mutation, NPM1 mutation did not differ. Overall survival for all patients (Fig D) was inferior for those with High HSP90 (42 vs. 60 weeks, p = 0.04), but this was based solely on those with intermediate cytogenetics (Fig E) (48 vs. 91 weeks p =< 0.00001), whether FLT-3 mutant (Fig G) (30 vs. 78 weeks, p=0.025) or Wildtype (Fig H, p = 0.037). This was seen in NPM1-WT/FLT3- WT (p=0.03), NPM1-Mut/FLT3 -Mut (fig I, p=0.006) and NPM1-Mut/FLT3 WT (fig J, p=0.08). High HSP90 patients also had inferior remission duration (Fig F, 39 vs. 84 weeks, p=0.025). Networks (Fig B & C) of proteins with expression strongly (p <.00001) correlated with the HSP in the literature (dashed spoke) or the dataset (solid spoke) are shown. Differential expression between the two groups are shown in Fig C (*). Among those with differential expression, levels were higher in the HSP90 high group for histone methylation associated proteins ASH2L, SIRT1, hnRNPK, Nucleolin, proliferation regulators Myc, EIF2S1, EIF2AK2, EIF4E, and for apoptosis/autophagy proteins Beclin1, Park7, MDM2 and BCL2. In contrast protein levels were lower in HSP90 High for : AKT1.pT308, BIRC2, CDKN1A, CDKN2A, CDK4, EGFR 7 pEGFR, ERBB2, HIF1α, IGF1R, LCK PKCα, SRC & pSRC.
Conclusions. AML is characterized by dichotomous expression of HSP proteins 27, 70 and 90. HSP expression pattern is associated with FLT3 mutation but not cytogenetics. HSP90 expression is prognostically adverse, exclusively among those with intermediate cytogenetics. High HSP90 expression is associated with higher WBC and PB and BM blast percentages, suggesting a proliferative advantage. This may arise through the effects of Myc and through increased gene expression arising from increased histone3K4 trimethylation from ASH2L and decreased histone 3 acetylation due to increased Sirt1 levels. Therapeutics directed at interfering with HSP function will need to consider which HSP pattern a patient exhibits to target the correct family members.
Borthakur:Tetralogic Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal