Abstract
The main functions of Natural Killer (NK) cells are early protection against viruses or tumour cells and production of cytokines that regulate immune functions. NK cells are the first lymphoid cells to repopulate the marrow after Stem Cell Transplantation (SCT) and reach normal levels within 1 month after transplant. Acquisition of both, inhibiting and activating receptors on developing NK cells is an important step in their functional maturation. Previous studies showed the beneficial effect of NK alloreactivity in prevention of relapse, especially in the setting of haploidentical SCT. The aim of this study is to compare the reconstitution of the NK cell compartment during the first 3 months after unmanipulated haploidentical peripheral blood SCT (Haplo) and HLA-identical sibling peripheral blood SCT (HLA-id).
11 adult patients received SCT (7 Haplo and 4 HLA-id) at Gregorio Marañón Hospital (Madrid-Spain) from November 2012 to April 2013. Conditioning regimen comprised fludarabine, cyclophosphamide and busulfan for Haplo SCT and fludarabine and busulfan or fludaribine and melphalan for HLA-id SCT. Prophylaxis for acute graft-versus-host disease consisted of high dose cyclophosphamide on days +3 and +4, cyclosporine A and mycophenolate mofetil for Haplo and Cyclosporine A and methotrexate for HLA-id. Patient´s characteristics and transplant outcomes are shown in table 1. We analysed reconstitution patterns and phenotype of NK at day +15, +30, +60, and +90 after transplantation by multi-color flow cytometry on FC500 Beckman Coulter® cytometer using the following anti-human monoclonal antibodies: CD3 FITC, CD56 ECD, CD45 PC7, NKG2A PC7, NKp30 PC5, NKp44 PE, Nkp46 PC5, and NKG2D PE (Beckman Coulter®). For comparison between the two groups Mann–Whitney U-test was used.
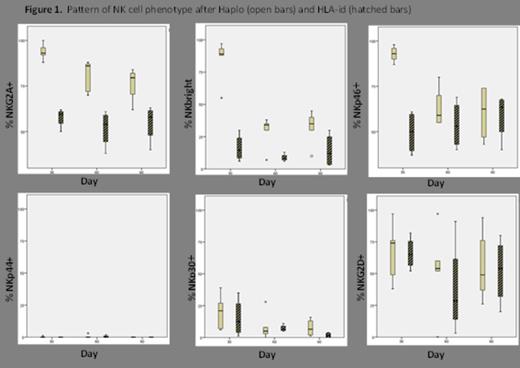
2/7 patients who received Haplo SCT died early in the post-transplantation period (day +50 and +66), and were excluded of the analysis because NK cells were not recovered by those days. NK cells reached normal levels by day +30: median 71 cells/µl (21-1089)) after Haplo; median 213.5 cells/µl (113-499) after HLA-id, and remained at high levels through follow up, with no significant differences between the two groups. Similarly to previous studies, a large percentage of NKbright cells was observed at day +30 after Haplo (median 89% of NK cells (55-97%)), a percentage that tended to decrease at day +60 (30% (7-38%)) and +90 (35% (10-45%)). Interestingly the percentage of NKbright cells after HLA-id SCT at day +30 (median 14.5% of NK cells (6-30%)) compared with Haplo, was significantly lower (p=0.016). This was accompanied by a significantly lower expression of inhibitory receptor NKG2A after HLA-id SCT than after Haplo: 59.5% (50-62%) versus 92.5% (50-62%) at day +30; 54% (38-61%) versus 86% (70-88%) versus at day +60 (p=0.016). Activating receptors NKp44 and NKp30 showed a low expression after both types of SCT throughout the first 3 months after transplantation. By contrast, activating receptor NKp46 levels were significantly higher at day +30 after Haplo than after HLA-id SCT (93% (87-98%) versus 50% (37-51%)) (p=0.016). Finally, high and similar proportions of activating receptor NKG2D were observed in both types of SCT. Figure 1 illustrates the recovery of the NK cell receptor phenotype for each type of SCT.
Our data showed an early and fast recovery of NK cells after Haplo and HLA-id SCT. However, phenotypic maturation of NK cells appears to be different for each type of transplant. NK cells generated after Haplo exhibit a more immature phenotype, characterized by a higher proportion of NKbright cells, and a higher expression of NKG2A at day +30. Interestingly expression of NKp46 was significantly higher after Haplo than after HLA-id SCT. Other authors have reported cytotoxic activity of these NK cells with high expression of NKp46, suggesting that cytotoxicity may be preserved in these immature NK cells. NKp30, NKG2D and NKp44 expression is less affected by the type of SCT.
This work has been partially supported by Project “Evaluación de la reconstitución inmune después del trasplante haploidéntico de progenitores hemopoyéticos sin depleción T” from Fundación Mutua Madrileña.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal