The median age of patients diagnosed with multiple myeloma (MM) is approximately 70 years old. It is an uncommon malignancy in persons younger than 40 years, representing only 2% of all patients diagnosed with MM. It has been suggested that young patients may present with more aggressive and less common disease features, frequently delaying the initial diagnosis and thereby affecting outcomes. With this background, we explored the outcome of young MM patients presenting to our institution over the past thirteen years.
We performed a retrospective review of a cohort of 236 patients with MM who received treatment for active MM at the University of California, San Diego Moores Cancer Center between January 2000 and July 2013. The demographics and disease features of patients up to 40 years of age at diagnosis were analyzed using descriptive statistics. The survival outcomes of these young patients were compared with the remainder of the cohort using the Kaplan-Meier method.
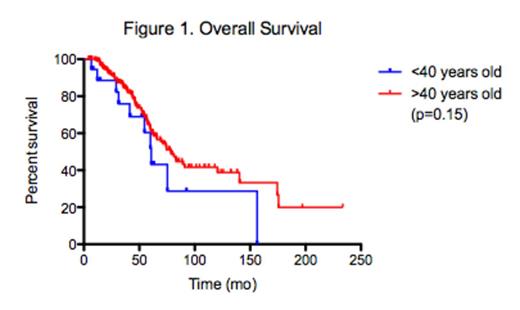
Nineteen (6.5%) out of the 236 patients with MM were ²40 years of age at diagnosis, with a median age of 35.5 years old. The median follow-up of this group of young patients was 42 months (range 5-92). The patient and disease characteristics are outlined in Table 1. Seven young patients (37%) had MM with no heavy chain component, including light chain only secreting or non-secretory disease. Seven patients (37%) had a non-IgG paraprotein. Nine (56%) patients presented with extramedullary plasmacytomas. Two (10%) patients had plasma cell leukemia. All patients received at least one treatment regimen that included a novel agent. Fifteen patients (79%) had received high-dose therapy, and four patients (21%) underwent allogeneic stem cell transplantation (SCT) after at least one prior autologous SCT. The 5-year and 7-year overall survival (OS) from diagnosis was 51.7% and 28%, respectively, and the median OS was 60.7 months. In contrast, the median OS of patients ≥41 years old at diagnosis was 78.6 months (p=0.15, figure 1).
Baseline characteristics of newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients ²40 years
| Parameter . | No. of Evaluable Patients . | Values . |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 19 | Median 35.5 (range 22-40) |
| Gender (M: F) | 19 | 1:1.4 |
| Performance Status (≥2) | 19 | 2 (10%) |
| Durie Salmon Stage at Diagnosis: 1 2 3 | 19 | 1 (5%) 2 (10%) 16 (84%) |
| Subtype: IgG IgA IgD | 12 | 5 (26%) 6 (31%) 1 (5%) |
| No Heavy Chain Component: Non-secretory Light chain only Lambda Kappa | 7 | 2 (10%) 5 (26%) 3 2 |
| Cytogenetics FISH | 17 6 | Abnormal: 1 (5%) Abnormal: 6 (31%) |
| Plasma Cell Leukemia | 2 (10%) | |
| Plasmacytoma(s) | 6 (31%) | |
| Renal Failure | 6 (31%) | |
| AL Amyloidosis | 1 (5%) |
| Parameter . | No. of Evaluable Patients . | Values . |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 19 | Median 35.5 (range 22-40) |
| Gender (M: F) | 19 | 1:1.4 |
| Performance Status (≥2) | 19 | 2 (10%) |
| Durie Salmon Stage at Diagnosis: 1 2 3 | 19 | 1 (5%) 2 (10%) 16 (84%) |
| Subtype: IgG IgA IgD | 12 | 5 (26%) 6 (31%) 1 (5%) |
| No Heavy Chain Component: Non-secretory Light chain only Lambda Kappa | 7 | 2 (10%) 5 (26%) 3 2 |
| Cytogenetics FISH | 17 6 | Abnormal: 1 (5%) Abnormal: 6 (31%) |
| Plasma Cell Leukemia | 2 (10%) | |
| Plasmacytoma(s) | 6 (31%) | |
| Renal Failure | 6 (31%) | |
| AL Amyloidosis | 1 (5%) |
In this single center study with long follow up, we demonstrate that patients diagnosed with MM ²40 years of age exhibit several high-risk features and frequently present with advanced stage disease. Despite the use of novel agents in this population, there is a statistical trend towards a worse outcome with an 18-month difference in median overall survival when compared to older patients with MM. More aggressive treatment strategies are needed to improve survival in this young patient population.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal