Abstract
Statins and tocotrienols modulate the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway by inhibiting the 3-hydroxy-3- methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase. Tocotrienols modulate HMG-CoA reductase by post-transcriptional downregulation. In addition, tocotrienols contain a farnesol moiety in its side-chain that triggers degradation of HMG-CoA reductase. These effects lead to suppression of cell proliferation, cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis. Several studies have shown that statins have suppressive effects in in vitro experiments on acute myelocytic leukemia cell lines. Since both statins and gamma-tocotrienol are associated with decreased cholesterol biosynthesis, we hypothesized that if the cytotoxicity of these drugs on cancer cells is related to impaired biosynthesis of cholesterol, combination of them could synergize in cytotoxicity on leukemic cells.
K-562 and HL-60 leukemia cells were grown in Iscove's Modified Dulbecco's medium with penicillin/streptomycin, 10% fetal bovine serum and 20% fetal bovine serum added respectively. K-562 and HL-60 leukemia cells were seeded in 96 well plates, grown overnight, and treated for 24, 48 and 72 hours with simvastatin in concentrations of 1,2,4, and5 µM; gamma-tocotrienol in concentrations of 20, 40, and 80 µM; and a combination of the two drugs in the same concentrations. For 24 hour dose, cells were seeded at a density of 5000/well and for 48 and 72 hour doses, at 3500/well. Following the treatment, MTS/PMS reagent (Promega, Madison, WI), [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium, inner salt] mixed with and an electron coupling reagent (phenazine methosulfate), was added at 40 µg/well and incubated at 37°C for 2 hours. We measured the solubilized formazan crystals at 450 nm as an indicator of cytotoxicity. The presence of ATP as an indicator of cell viability was measured with the CellTiter Glo® assay (Promega). Cells were again seeded, grown overnight, and dosed as indicated above. Following treatment, the assay was conducted as specified by the manufacturer.
Both simvastatin and gamma-tocotrienol induce cytotoxicity in K-562 and HL-60 cell lines by the MTS and Cell Titer Glo Assays. The IC50 at 72 hour incubation are as follows 1) HL-60: simvastatin - 16.543 uM, gamma tocotrienol - 36.297 uM; 2) K-562: simvastatin - 5.235 uM, gamma tocotrienol - 34.947 uM. We used CompuSyn to calculate the IC50. When combined, simvastatin and gamma-tocotrienol exhibit synergy at lower concentrations when examined by isobologram analysis.
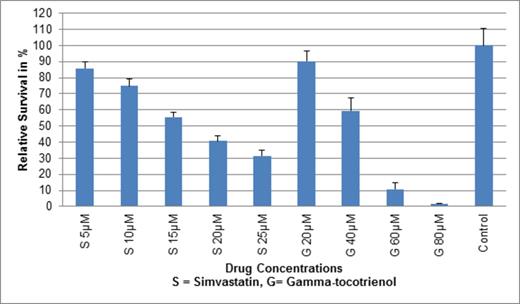
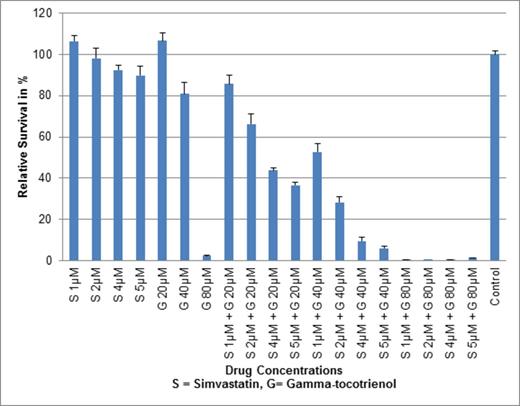
Synergistic Cytotoxicity of Simvastatin and Gamma-tocotrienol on HL60 cells (72 hour dose in CellTiter Glo® assay)
Synergistic Cytotoxicity of Simvastatin and Gamma-tocotrienol on HL60 cells (72 hour dose in CellTiter Glo® assay)
Gamma-tocotrienol, an isoform of vitamin E, and simvastatin, a cholesterol lowering drug exhibit synergy in induction of cytotoxicity in K-562 and HL-60 leukemia cell lines. Rescue experiments and mechanistic pathway analysis are being explored to confirm these observations.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal