Abstract
Burkitt lymphoma (BL) is an aggressive mature B-cell malignancy and is the most common non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) in children and adolescents (Cairo et al., Blood, 2007; Miles/Cairo et al., BJHaem, 2012) and the survival of pediatric Burkitt lymphoma (PBL) has significantly improved over the past 30 years through the introduction of short and intensive multi-agent chemotherapeutic regimens (Cairo et al, JCO, 2012). Patients with PBL who relapsed or progressed have chemotherapy resistant disease and can rarely be salvaged after re-induction and retreated (Cairo et al., JCO, 2012; Miles/Cairo et al., BJHaem, 2012). CD20 is expressed in over 98% of PBL (Perkins/Cairo et al, Clin Adv Hematol Oncol,2003). Targeting CD20 with rituximab in combination with chemotherapy has been utilized successfully in PBL (Goldman/Cairo, Leukemia, 2013). Targeting CD20 with monoclonal antibodies has been observed to alter signaling pathways, including MAPK, PI3K/AKT and NF-κB, by changing the expression of regulators of apoptosis leading to cell death and/or sensitizing cells to the effects of cytotoxic chemotherapeutic agents (Barth/Cairo, BJH, 2013; Mathas et al., 2000, Can. Res.; Jazirehi et al., Can. Res., 2005). CD20 is uniformly expressed in mature B cells and has been considered an effective target for immunotherapy because CD20 is not only widely expressed in mature B-cell but plays a role in human B-cell proliferation (Tedder et al., Immunol. Today, 1999). However, the mechanism(s) and function of CD20 is still poorly understood in B-cells, especially in BL. Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nucleases (TALENs) technologies have been developed for precision targeted genome editing in a variety of organisms and stem cells for new experimental and therapeutic tools (Sander et al., Nat. Biotech., 2011; Miller et al., Nat. Biotech., 2011).
We hypothesize that 1) TALEN technology is suitable for the modification of CD20 gene expression in B cells and 2) TALENs-mediated CD20 knockout model will be provide useful tool for understanding the mechanism and function or CD20 and the potential use of CD20 antibodies as therapeutic agents in BL.
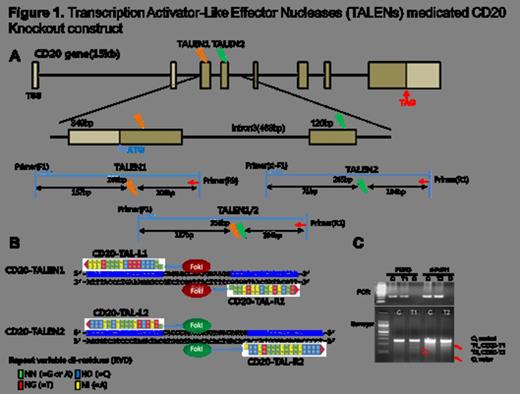
CD20 TALENs were constructed based on REAL (restriction enzyme and ligation) assembly methods (Sander et al., Nat. Biotech, 2011; Lee/Cairo et al, ASH, 2012) for CD20 gene modification. CD20 TALEN pairs or combinations were transfected into 293 and Raji cells using lipofectamin reagent (Invitrogen) and Amaxa nucleofection kit, respectively. Genomic DNA and total RNA were isolated using genomic DNA extraction kit (Promega) and Trizol reagent (Invitrogen). Surveyor mutation detection assay (Transgenomic) was used for CD20 TALENs validities and confirmed by sequencing analysis (Genewiz). Quantitative RT-PCR was performed by CFX96 Real-time system (Bio-rad) using qScript™ cDNA Synthesis Kit (Quantas) and SsoFast™ EvaGreen® Supermix (Bio-rad). Western blotting was performed for measurement of protein level and statistical significance was determined by a one tailed paired Student t-test.
Two pairs of functional CD20 TALENs (T1and T2) targeting endogenous CD20 gene generated and confirmed their validities with gene modification caused by non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) in TALENs mediated 293 [Figure 1]. There was significant reduction of CD20 mRNA expression in T1, T2 and combined T1/T2 (T12) transfected in Raji compared to empty vector transfected Raji (50%, p<0.003; <40%, p<0.004 and 70%, p<0.003, respectively). To isolate of CD20 knockout single clone, transiently T12 transfected Raji cells were seeded into 96 well plates and screened by PCR genotyping. CD20 stably knockout clones, CD20-T12-29-1 and CD20-T12-29-5 (+/-) showed a significant decrease of CD20 mRNA (90% reduction, p<0.004; 70% reduction, p<0.002, respectively). We also observed a significant reduction of CD20 protein level by western blotting in single clones, CD20-T12-29-1 (no detectable CD20), CD20-T12-29-5 (97% reduction, p<0.002), CD20-T12-20-16 (98% reduction, p<0.00002) and CD20-T12-29-18 (75% reduction, p<0.006).
We demonstrated that CD20-TALENs are useful tools for the modification of endogenous CD20 gene and TALEN mediated CD20 knockout model will be used for studying CD20 function in BL and the efficacy of second generation CD20 antibodies and antibody conjugates against CD20 in BL.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal