Acquired coagulopathies are a common problem in Hematology, and are most often due either to medication effect, liver disease, or consumption. Among the uncommon causes of acquired coagulopathy, inhibitory auto-antibodies may develop, either in the setting of autoimmune diseases, in the setting of lymphoproliferative disorders, or as isolated inhibitory immunoglobulins. Uncommonly, the adsorption of coagulation factors from the circulation into the tissues by extracellular deposition of pathologic amyloid results in an acquired factor deficiency, due to clearance of factor from the circulation that exceeds the body's ability to produce factor. When amyoidosis does cause a coagulapathy, it is most often the result of the adsorption of Factor X by the amyloid protein, resulting in an acquired Factor X deficiency. However, there are rare reports of amyloidosis being associated with other factor deficiencies. We report a case of amyloidosis that was associated with a severe bleeding diathesis, with the etiology of the bleeding disorder being due to both acquired Factor V deficiency and concomitant acquired von Willebrand Disease.
A previously healthy 51-year-old gentleman presented to an outside medical center for evaluation and management of recurrent bleeding episodes. The patient had a prior medical history significant only for right ankle trauma in the year 2005, following which he underwent a total of 4 surgical procedures; there was no excessive bleeding complicating the patient's surgeries. He was then in his usual state of health until September, 2012 when he developed onset of severe abdominal pain and was admitted to the outside facility. Following hospitalization for several months at the outside facility, he was admitted to our institution. Physical examination was remarkable for extensive ecchymoses, and for splenomegaly to 18 cm. span by exam, confirmed by imaging. CT scan showed multiple peri-caval and periaortic nodes present up to 1.7 cm in size, with shotty inguinal lymph nodes. A complete blood count showed White blood count 21,600, hemoglobin 8.0 g/dL, hematocrit 24%, platelet count 370,000, Hepatic function studies and renal function studies, as well as electrolytes, were normal on admission. Coagulation studies revealed Prothrombin Time prolonged at 16.8 seconds (normal < 12.7), aPTT prolonged at 44. Mixing patient plasma with equal volume normal plasma corrected both the PT and aPTT. Detailed factor assays showed markedly decreased Factor V activity of 27%; Ristocetin Cofactor activity was markedly decreased at 49%, but von Willebrand antigen was elevated at 213%. Multimer analysis was consistent with Type II vWD (see figure 1). The patient received fresh frozen plasma and Humate P, with transient correction of the bleeding diathesis. This permitted inguinal lymph node biopsy, which documented AL amyloidosis. Extraction of the protein from the lymph node documented AL lambda light chain amyloid (see figure 2). Marrow biopsy documented IgG lambda multiple myeloma. The patient was treated using Bortezumib plus Dexamethasone, and achieved a complete remission, with normalization of the coagulation parameters and factor levels over the following several months. His bleeding diathesis has fully resolved, and Karnofsky performance status improved to 100%.
Although there are several case reports of acquired von Willebrand disease on the basis of amyloidosis, and several case reports of acquired Factor V deficiency on the basis of amyloidosis, this appears to be the first reported case of both acquired vWD and acquired Factor V deficiency on the basis of amyloidosis.
Normal von Willebrand protein multimers (top) by gel electrophersis, and patient's multimers by gel electrophoresis (bottom), consistent with Type II vWD.
Normal von Willebrand protein multimers (top) by gel electrophersis, and patient's multimers by gel electrophoresis (bottom), consistent with Type II vWD.
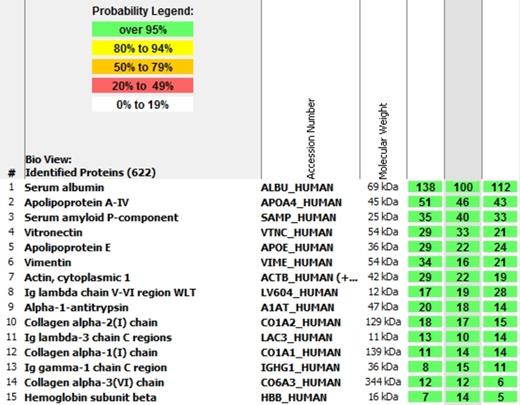
Spectroscopic Analysis of the proteins extracted from the patient's lymph node, showing the presence of immunoglobulin lambda light chain (numbers 8 and 11).
Spectroscopic Analysis of the proteins extracted from the patient's lymph node, showing the presence of immunoglobulin lambda light chain (numbers 8 and 11).
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal