Abstract
Myelofibrosis (MF) is characterized by activation of the JAK-STAT pathway, with the JAK2 V617F mutation found in 50-60% of patients. Although JAK inhibitors, such as FDA-approved ruxolitinib, have been effective in reducing splenomegaly and mitigating symptoms, patients uniformly exhibit “disease persistence” which is equated with a lack of hematologic or molecular remissions, or with loss of clinical improvement over time. Prior studies using cell lines or primary patient samples have shown that the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT signaling pathway is dysregulated in MPNs and is a potential therapeutic target (Kamishimoto et al, Cell Signal 2011; Huang et al, ASH 2009 Abstract 1896; Vannucchi et al, ASH 2011 Abstract 3835; Khan et al, Leukemia 2013). In CLL and other B-cell malignancies, the PI3K pathway is constitutively upregulated and is dependent on PI3Kδ. Idelalisib is a δ-isoform-specific PI3K inhibitor that is efficacious in patients with CLL and indolent NHL. Herein, the specific aims of our study were: 1) to determine whether the PI3Kδ isoform is expressed in progenitor cells from MF patients, and 2) to evaluate the inhibitory effects of idelalisib on basal and thrombopoietin (TPO)-stimulated AKT/S6RP phosphorylation (p-AKT/p-S6RP) in cell lines and in primary samples from MF patients who were either on chronic ruxolitinib (RUX) therapy or were not exposed to ruxolitinib (RUX-naïve or off-therapy at the time of sample collection).
To evaluate isoform expression, CD34+ cells from the peripheral blood of MF patients were sorted by FACSAria and cell lysates were analyzed by Simple Western using Peggy (ProteinSimple) with recombinant protein as a positive control. For cell line studies, BaF3/MPL W515L and UT-7/TPO cells were stimulated with recombinant human TPO and incubated with idelalisib. Whole cell lysates were analyzed by Western blot to quantify the % of p-AKT and p-S6RP levels compared to idelalisib-untreated cells. For MF patient samples, PBMCs were isolated from the whole blood of MF patients who were either RUX-naïve or on chronic RUX therapy and treated for 2 hours with idelalisib. Antibodies specific to p-AKT Ser473 and pS6RP Ser235/236 were used to quantify the proportion of p-AKT and pS6RP in basal and TPO-stimulated CD34+/CD3-/CD14-/CD19-/CD66- gated cells.
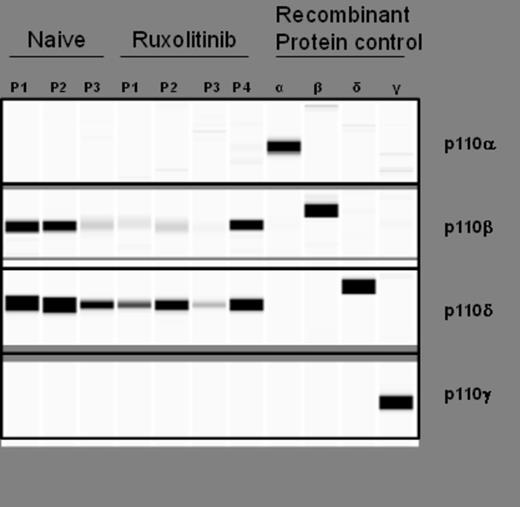
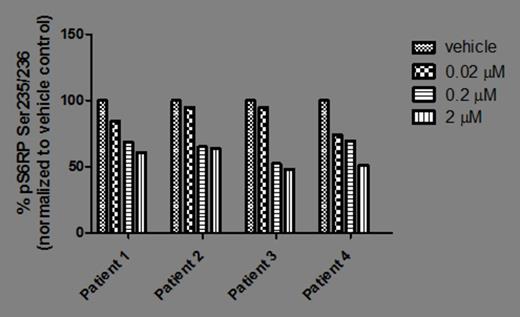
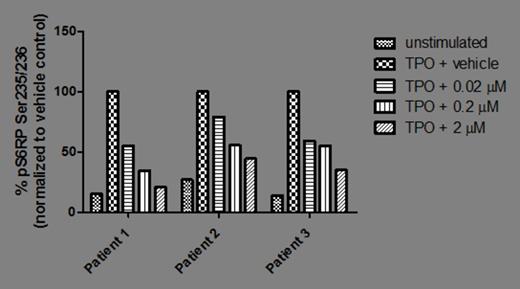
The PI3Kδ isoform was found to be the predominant isoform expressed in 3 of 3 RUX-naïve and 4 of 4 chronic RUX patients tested; PI3Kβ was expressed at lower levels and no PI3Kα or γ was detected (Figure 1 ). In BaF3/MPL cells, p-AKT levels decreased by 51%, 64% and 67%, with 0.1, 1.0, 2.0 µM idelalisib, respectively, when compared to idelalisib-untreated cells; p-S6RP levels decreased by 24%, 27%, and 41%, respectively. Similarly, for UT-7/TPO cells, p-AKT decreased by 11%, 44%, and 55%, and p-S6 decreased by 13%, 28% and 48%, respectively. In CD34+ cells from RUX-naïve patients (n=3), p-AKT and p-S6RP levels decreased with increasing concentrations of idelalisib (0.02, 0.2, 2 µM). All patients on chronic RUX treatment demonstrated decreased p-AKT (n=3) and p-S6RP (n=4 basal, n=3 TPO-induced; patient 4 was only tested for basal) levels with increasing concentrations of idelalisib in both basal (Figure 2A ) and TPO-stimulated (Figure 2B ) assays. All 4 chronic RUX and 2 of 3 RUX-naïve patients tested carried the JAK2 V617F mutation.
PI3Kδ is the major PI3K isoform expressed in both RUX-naïve and chronic RUX treated myelofibrosis patients. Recombinant protein was used as a positive control for each antibody.
PI3Kδ is the major PI3K isoform expressed in both RUX-naïve and chronic RUX treated myelofibrosis patients. Recombinant protein was used as a positive control for each antibody.
The PI3Kδ isoform was identified as the predominant isoform expressed in CD34+ cells from MF patients. In both cell lines and patient samples, idelalisib inhibits the PI3K/AKT pathway, with a dose-dependent decrease of p-AKT and p-S6RP. Inhibition was observed for both RUX-naïve and chronic RUX-treated patients. Studies are underway to evaluate the effects of idelalisib on progenitor colony formation and induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.
* Meadows and Nguyen are first co-authors
Meadows:Gilead: Employment, Equity Ownership. Queva:Gilead: Employment, Equity Ownership. Lannutti:Gilead, Acetra, Effector: Consultancy, Employment, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees. Kashishian:Gilead: Employment, Equity Ownership. Jun:Gilead: Employment, Equity Ownership. Coutre:Gilead: Research Funding. Dansey:Gilead: Employment, Equity Ownership. Gotlib:Gilead: Consultancy, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal