Abstract
EB virus (EBV) is associated with heterogeneous lymphomas. Hodgkin's lymphoma (HL) cells are embedded in non-neoplastic bystanders: B, T cells, and macrophages. Without these bystander cells, the lymphoma cells are incapable of being engrafted in immunodeficient mice. In this context, the bystanders are tumor-supportive “inflammatory niche”. Recently, EBV-infected cells produce exosomes that contain EBV specifically encoded miRNAs (EBV-miRNAs). The miRNAs are transferred to cells, and involved in tumor metastasis. However, the detailed mechanism is unknown. Accordingly, we hypothesized that exosomal EBV-miRNAs might redirect tumor surrounding immune cells from tumor reactive into tumor-supportive “inflammatory niche”.
We evaluated the expression of EBV-miRNAs in EBV+HL clinical specimens by in situ hybridization, their functional characterization in vitro, and their effects on persistent infection and tumor development in vivo humanized NOG mice model. Moreover, in order to clarify its sorting mechanism, trans factor and cis factor which determined secreted and non-secreted miRNAs was analyzed by use of mass-spectrograhy and next-generation sequencing.
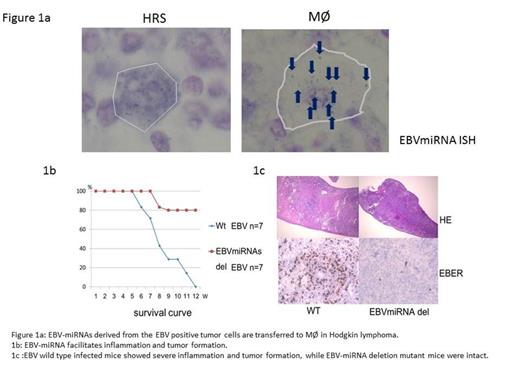
The EBV-miRNAs effects were potent on monocyte/macrophage Mo/Mf in inducing CD69, IL-10, and TNF, suggesting that EBV-miRNAs might polarize Mo/Mf into tumor associated Mf (TAM). EBV-miRNAs suppress tumor cell proliferation in vitro, implying that it works as tumor-suppressor in the tumor cells, while they are required to develop LPD in vivo, which seems contradict to the result in vitro. These results suggest that EBV-miRNAs intra-cellularly regulate the tumor cells to adjust to the surrounding circumstances, for example, to escape from immune surveillance, and inter-cellularly regulate Mo/Mf to support the tumor survival or development. Most importantly, exosomal EBV-miRNAs derived from the tumor cells were transferred to Mf in human EBV+ HL samples.
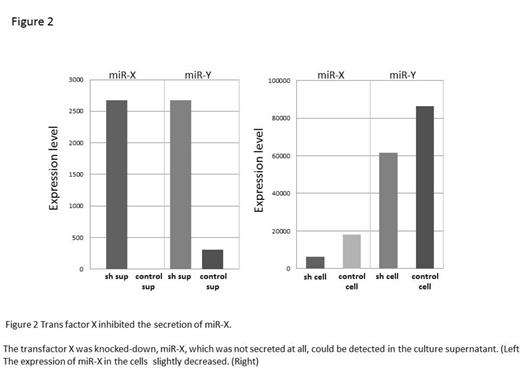
Interestingly, one EBV coded miRNA was not secreted at all, though it abundantly expresses in the cells. The miRNA has been reported to strongly promote cell proliferation in EBV infected tumor cells. It made us hypothesized that the sorting system of secretary and non-secretary miRNAs is critical in the formation of “inflammatory niche”. In order to clarify the mechanism of the sorting, the chimeric miRNA was constructed then, we determined the sequence, which regulates secretion and non-secretion, and purified the protein complex, which specifically bound to the sequence. Mass spectrography and successive knockdown assay, the trans factor which inhibits secretion was identified.
Moreover, the next sequencing analysis for the small RNAs revealed that abundant EBV-coded small RNAs occupied RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), and that non-secreted EBV-miRNA was specifically modified. It is now under investigation whether the modification is involved in the sort mechanism between secretary and non-secretary miRNAs.
Taken together, EBV-miRNAs have critical roles in intra- and inter-cellular manner. Especially, the functions as an inter-cellular communicator might be important in the tumor formation and the mechanism needs further investigation.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal