Abstract
Programmed death 1 (PD-1) protein is a key immune-checkpoint receptor expressed by activated T cells and it mediates immunosuppression. It has been recently shown that the blockade of PD-1 or its ligand, PD-L1, by monoclonal antibodies may lead to significant antitumor effects. In diffuse large B-cell lymphoma PD-L1 has been reported expressed by tumor cells and PD-1 by tumor-associated T cells. The dosage of soluble programmed death ligand 1 (sPD-L1) protein in the blood of adults with cancer has never been performed during a clinical trial. We evaluated the clinical impact of PD-L1 level measured at the time of diagnosis for newly diagnosed aggressive diffuse large B-cell lymphomas.
Translating a previous study (NEJMed2004; 350: 1287) in the rituximab era, the Groupe Ouest-Est des Leucemies et des Autres Maladies du Sang (GOELAMS) 075 study is a multicenter randomized trial in which adults 18 to 60 years old with untreated histologically proved CD20 positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma were randomly assigned to receive 8 courses of R-CHOP or, high-dose chemotherapy associated to rituximab followed by autologous stem cell support (clinicaltrials.gov: NCT00561379). Patients were required to have an Ann Arbor stage of I or II with bulk greater or equal to 7 cm or, III or IV with 0 to 3 adverse prognostic factors as defined by the age-adjusted International Prognostic Index. The population of interest consisted of 288 of the 340 consecutively enrolled patients with available plasma collected at the time of diagnosis before any treatment. Soluble PD-L1 was measured using an ELISA assay. The median follow-up was 41.4 months.
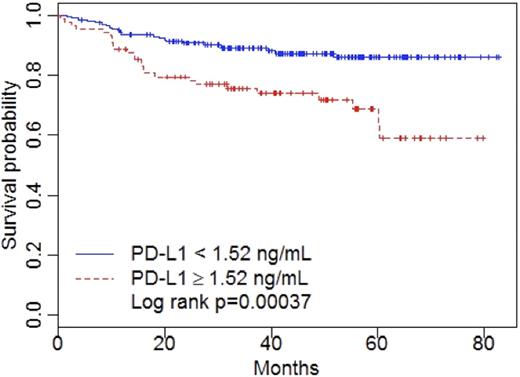
sPD-L1 levels were found significantly increased in the plasma collected at diagnosis for patients compared to healthy -gender and age matched- subjects’ levels (P<0.0001). The optimal cut-off point for PD-L1 measured at diagnosis was found to be equal to 1.52 ng/mL. Eighty-nine (30.9%) patients had a PD-L1 level greater than the cut-off point as compared to two (3%) controls. The high-level sPD-L1 group was significantly associated with bone marrow involvement, more than one extranodal localization and, 2-4 performance ECOG status. None of the other patients' characteristics, including the assigned arms of randomization and, the positive vs. negative FDG-PET scan response at the intermediate evaluation, was associated with high PD-L1 level. The PD-L1 immunohistochemical analysis showed that 55 out of the 73 interpretable tissue microarrays presented at least 5% of PD-L1-positive tumor cells. No association was found between sPD-L1 and tumor PD-L1 expressions (p=0.5). The 73 patients were representative of our 288 patients' cohort, with significantly decreased overall survival for patients with a high level of sPD-L1 compared to those with low sPD-L1 levels (64.6 vs. 86.7%, P=0.007). Cell-of-origin analysis using Hans’s criteria on the tissue microarrays did not shown any correlation between elevated sPD-L1 and GC or non-GC origin.
Patients with elevated PD-L1 experienced a poor prognosis with a three-year overall survival of 76 vs. 89 percent (P<0.001).
There was no difference of overall survival rates between the two arms of treatment. Univariate analysis identified age greater than 50 years old, high-intermediate and, high age-adjusted International Prognostic Index score, bone marrow involvement, more than one extranodal localization, Ann Arbor stage after FDG-PET scan of III or IV, abnormal lymphocyte-monocyte score and, high level of sPD-L1 as factors associated with poor survival. High level of sPD-L1, bone marrow involvement and, abnormal lymphocyte-monocyte score were found after multivariate analysis to be the only factors remaining significant after adjustment with a P-value <0.05. Soluble PD-L1 was detectable in the plasma and not in the serum, found elevated in lymphoma patients at diagnosis compared to healthy subjects and its level dropped back to normal value for patients in complete remission. The intention-to-treat analysis showed that elevated PD-L1 was associated with a poorer prognosis for patients randomized within the R-CHOP arm (P<0.001).
Soluble PD-L1 protein expression in peripheral blood at the time of diagnosis is a potent predicting biomarker in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and may indicate usefulness of alternative therapeutic strategies using PD1 axis inhibitors.
Fest:Roche SA France: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal