Abstract
HIV-1 is transcriptionally active in activated CD4+ T (Th) cells, and inactive in naive Th cells. Our previous work has shown that Ets-2 is a candidate transcriptional repressor of HIV-1 in naive Th cells, because the -279 to -250 upstream region of HIV-1-LTR (RATS, Repressor Activator Target Sequence), that participates in HIV-1-LTR transcriptional silencing, encompasses the AAGGAG Ets-2 binding site. In this proof of concept study, we investigated whether Ets-2 represses the expression of HIV-1.
We measured the levels of ets-2 mRNA in peripheral blood T-cells, Jurkat cells and 10 other human leukemic T, B and monocytic cell lines, before and after activation of the cells with the mitogens PMA and ionomycin (P/I). Ets-2 mRNA was synthesized in T-cells, Jurkat cells and in most cell lines tested when cultured in plain culture medium (CM), but its synthesis was severely reduced upon cell activation.
To directly assess whether Ets-2 can silence HIV-1 activation acting through the RATS sequence, we transfected Jurkat cells with (i) the plasmids HIV-1-LTR-CAT (carries the whole LTR sequence of the HIV-1 virus) or 2xRATS-CAT (carries 2 copies of the RATS sequence) or 2xmutantRATS-CAT (carries a point mutation in the Ets-2 binding site) or CMV-CAT (control), (ii) pCDNA3-ets-2 (for ets-2 overexpression) and (iii) ets-2 shRNA (to silence ets-2 expression in the cells). When Jurkat cells were transfected with HIV-1-LTR-CAT, 2xRATS-CAT or CMV-CAT, there was no transcriptional activity of the genes in CM. After activation of the cells, the expression of the transfected genes increased, except of CMV-CAT. Co-transfection of Jurkat cells with increasing amounts of pCDNA3-ets-2, led to a gradual reduction of HIV-1-LTR-CAT and 2xRATS-CAT activities upon cell stimulation, but not of CMV-CAT. No transcriptional response was observed for the 2xmutantRATS-CAT gene. Co-transfection experiments with HIV-1-LTR-CAT, 2xRATS-CAT and ets-2 shRNA, led to an increase in the activity of both reporter genes, but had no effect on the activities of 2xmutantRATS-CAT and CMV-CAT.
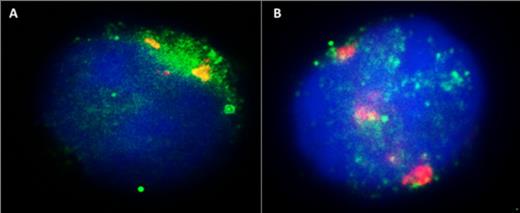
To assess whether Ets-2 binds to HIV-1 LTR directly in vivo, Jurkat cells were transfected with the plasmid HIV-1-LTR-CAT, left in CM for 24h, and then in CM±P/I for a further 12h. The cells were then attached to slides and stained for the Ets-2 protein and the HIV-1-LTR sequence by combining immunofluorescence and FISH techniques respectively. In CM condition, Ets-2 protein bound to the HIV-1-LTR sequence (Fig. 1A), whereas after P/I activation of the cells
Figure 1 Jurkat cells were transfected with the HIV-1-LTR-CAT plasmid, and were then stained for the Ets-2 protein (green spots) and HIV-LTR (red spots), and counterstained with DAPI (blue). A. Jurkat cells in CM condition. Ets-2 and HIV-LTR co-localize inside the nucleus (yellow spots). B. Jurkat cells activated with P/I for 12h. Ets-2 no more co-localizes with the HIV-1-LTR sequence.
Figure 1 Jurkat cells were transfected with the HIV-1-LTR-CAT plasmid, and were then stained for the Ets-2 protein (green spots) and HIV-LTR (red spots), and counterstained with DAPI (blue). A. Jurkat cells in CM condition. Ets-2 and HIV-LTR co-localize inside the nucleus (yellow spots). B. Jurkat cells activated with P/I for 12h. Ets-2 no more co-localizes with the HIV-1-LTR sequence.
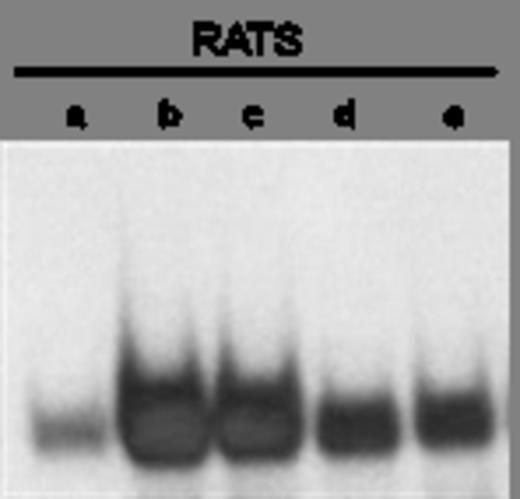
EMSA with Ets-2 protein eluted from cord blood-derived naive T-cells and an oligonucleotide probe mapping the RATS sequence. a-e represent points with decreasing amounts of protein eluates.
EMSA with Ets-2 protein eluted from cord blood-derived naive T-cells and an oligonucleotide probe mapping the RATS sequence. a-e represent points with decreasing amounts of protein eluates.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal