Abstract
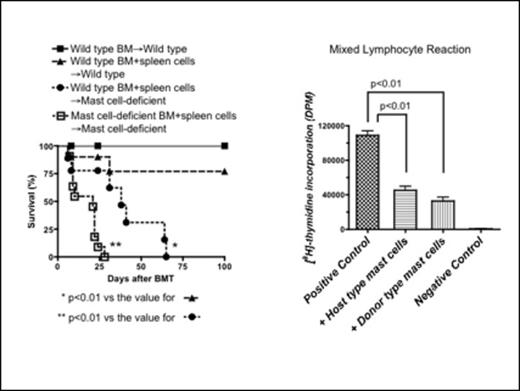
Originally mast cells have been known as effector cells in the IgE-mediated allergic responses. In addition, recent studies demonstrated that mast cells exerted pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory effects in complicated immune response depending on the situation. In allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), exact role of mast cells in graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) remains unclear. First we investigated whether host mast cells protect acute GVHD or not in a murine HSCT model using mast cell deficient mice. When lethally irradiated wild type (WT) B6 or mast cell deficient mice were transplanted with bone marrow cells and spleen cells from WT Balb/c mice, mast cell deficient B6 host mice showed significantly lower survival rate than WT B6 mice (p<0.01) due to acute GVHD. Moreover when irradiated mast cell deficient host mice (B6 derived) were given BM cells and splenocytes from mast cell deficient Balb/c mice, these mice died much faster compared to the mice receiving WT BM plus splenocytes (p<0.01) as shown below. Next, we demonstrated that bone marrow derived cultured mast cells (BMCMCs) inhibited mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR) in a dose-dependent manner, when added to the coculture (Stimulator: dendritic cells (DCs) from B6, Responder: spleen cells of Balb/c, BMCMCs from B6). In addition when mast cells generated from the same strain of responder cells (Stimulator: DCs from B6, Responder: spleen cells from Balb/c, BMCMCs from Balb/c) were added to the MLR mixture, MLR was also suppressed even in this condition. Taken together, we have clearly demonstrated that both host-type and donor-type mast cells suppressed alloreaction in vivo and in vitro. However when we used anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 monoclonal antibodies to stimulate T-cells instead of DCs, BMCMCs could not suppress the lymphoproliferation any more. It suggested that mast cells could suppress MLR via the regulation of DCs directly, not T-cells. Next we have shown that BMCMCs dominantly regulated the alloreaction in a cell contact-dependent manner by using transwell system, though mast cells contain many kinds of substances to regulate immune reactions such as IL-10. DCs highly expressed costimulatory molecules such as CD80, CD86, CD40, I-A, however expression level of these molecules was not changed during coculture of BMCMCs and DCs. Finally, we compared the MLR suppression rate between naïve and activated BMCMCs using IgE and specific antigens, however no difference was observed between them. In conclusion, both host and donor-type mast cells have a protective role against acute GVHD.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal