Abstract
Rituximab was approved in December 1997 and has since become the standard of care in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), follicular lymphoma (FL), and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Clinical trials have shown statistically significant improvements in progression-free and overall survival. The objective of this study was to estimate the real-world effectiveness of first-line rituximab plus chemotherapy (R+Chemo) relative to chemotherapy alone (Chemo Alone) in the United States (US) from 1998 to 2013.
For each cancer, we constructed a population effectiveness model from 1998-2013 comprised of 3 modules: epidemiology, utilization and survival. The epidemiology module included age group, gender, and year-specific incidence rates for each cancer from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) program from 2000-2010. Published SEER-based join-point estimates were used to extrapolate to other years. Census population data using the same age group, gender, and year strata were combined with incidence rates to project total diagnosed patient counts. The utilization module was based on SEER-Medicare linked data from 1999-2009. Drug utilization (defined as first infusion within 180 days of diagnosis for each cancer) for R+Chemo and for Chemo Alone was estimated as a proportion of all diagnosed patients, and stratified by age group, gender, and calendar year of diagnosis in the SEER-Medicare data. Utilization proportions were then multiplied by the diagnosed population counts to estimate treated patient counts for each cancer, by age group, gender, and calendar year. The survival module was calculated using SEER-Medicare data, starting from 30-days after first infusion, with follow up through 12/31/2010. For each cancer, flexible parametric (Royston-Parmar) survival models were applied to estimate restricted (10-year) mean survival times for each person, adjusted for individual patient covariates. These estimates were averaged across patients within strata defined by age group, gender and treatment. Life years lived were estimated for patients receiving R+Chemo, first by using mean survival for treatment with R+Chemo, and then by using mean survival estimates for Chemo Alone. The incremental life years saved were calculated as the difference between the projected survival from using R+Chemo and from using Chemo Alone. These differences were summed over age group, gender, and calendar year for each cancer. Monte Carlo sampling was used to estimate the 95% uncertainty intervals (UI).
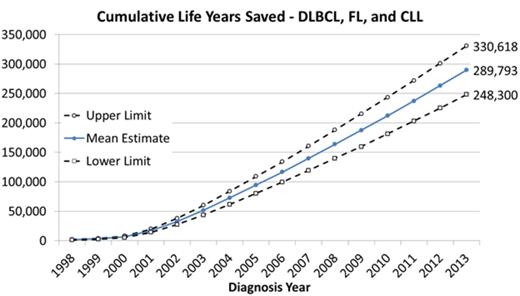
Across all three cancers, there were 289,793 cumulative life years saved (95% UI, 248,300-330,618; see Figure) from 1998 to 2013. For DLBCL, an estimated 177,952 patients were treated with R+Chemo. In these patients, an estimated 199,323 (95% UI 169,534-231,214) additional life years were lived compared to what might have occurred if Chemo Alone had been used instead. For FL, an estimated 84,303 patients were treated with R+Chemo, and an additional 80,338 (95% UI 53,876-106,709) life years were lived compared to Chemo Alone. For CLL, an estimated 14,398 patients were treated with R+Chemo, and an additional 10,132 (95% UI 4,469-15,998) life years were lived compared to Chemo Alone.
For DLBCL, FL and CLL patients treated with first-line therapy within 180 days of diagnosis in the US, approximately 290,000 cumulative life years were saved by adding rituximab to chemotherapy between 1998 and 2013. Next generation therapies may be able to extend these survival gains for patients with CLL, FL and DLBCL.
Danese:Amgen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; Medimmune: Consultancy, Research Funding. Gleeson:Amgen, Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; MedImmune: Consultancy, Research Funding. Halperin:Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; Medimmune: Consultancy, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Research Funding. Skettino:Genentech: Employment, stock Other. Reyes:Genentech, inc: Employment, Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal