Abstract
Nilotinib, a more potent and selective drug than imatinib, was approved by the FDA and EMA initially for the treatment of chronic and accelerated phase Philadelphia chromosome positive (Ph+) chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) patients resistant or intolerant to prior therapy including imatinib and subsequently for the treatment of newly-diagnosed Ph+ CML patients in the chronic phase (CML-CP). The aim of the present study was to investigate efficacy and safety profile of nilotinib in a Turkish population of newly-diagnosed Ph+ CML-CP patients and to evaluate the effects of these results on prognosis according to current treatment guidelines.
The study was planned as a multicenter, open-label, one-arm phase II clinical trial. All patients were planned to be treated with nilotinib (AMN107, Tasigna®) 300 mg BID for 24 months. Herein, efficacy results of the patients who completed the first year of the study are presented.
Of the 112 patients included in the study, data for 94 patients who completed 12 months of the study up to April 29, 2013 were analyzed. Of these 94 patients, 16 were excluded within this period and 78 completed the first year of the study within the median 371 days (range, 339-401 days) or median 12.4 months (range, 11.3-13.4 months). General characteristics of the patients are presented in Table 1.
General characteristics of the patients
| Characteristics . | . |
|---|---|
| Age, year | 46.5 (range 19-78) |
| Gender (Female/Male) | 37 (%39.4)/57 (%60.6) |
| Palpable spleen size (maximum distance below the rib margin) (baseline), cm | 0.0 (0-17) |
| Baseline Leukocyte count (range), K/mm3 | 29.2 (1.7-289.4) |
| Baseline Platelet count (range), K/mm3 | 343.0 (75-1,268) |
| Characteristics . | . |
|---|---|
| Age, year | 46.5 (range 19-78) |
| Gender (Female/Male) | 37 (%39.4)/57 (%60.6) |
| Palpable spleen size (maximum distance below the rib margin) (baseline), cm | 0.0 (0-17) |
| Baseline Leukocyte count (range), K/mm3 | 29.2 (1.7-289.4) |
| Baseline Platelet count (range), K/mm3 | 343.0 (75-1,268) |
Treatment-related characteristics of the patients are presented in Table 2.
Treatment-related characteristics of the patients
| . | N . | . | 80% Confidence Interval . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cumulative MMR rate by 12th month | 94 | 58 (61.7) | 54.6-68.4 |
| Time to MMR | 58 | ||
| Days | 184.8±84.7 | ||
| Months | 6.2±2.8 | ||
| BCR-ABL level at 3rd month | 87 | ||
| <%10 | 75 (86.2) | 80.2-90.8 | |
| ≥%10 | 12 (13.8) | 9.2-19.8 | |
| CCyR rate at 6th month | 84 | 76 (90.5) | 85.0-94.4 |
| CCyR rate at 12th month | 74 | 67 (90.5) | 84.6-94.7 |
| . | N . | . | 80% Confidence Interval . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cumulative MMR rate by 12th month | 94 | 58 (61.7) | 54.6-68.4 |
| Time to MMR | 58 | ||
| Days | 184.8±84.7 | ||
| Months | 6.2±2.8 | ||
| BCR-ABL level at 3rd month | 87 | ||
| <%10 | 75 (86.2) | 80.2-90.8 | |
| ≥%10 | 12 (13.8) | 9.2-19.8 | |
| CCyR rate at 6th month | 84 | 76 (90.5) | 85.0-94.4 |
| CCyR rate at 12th month | 74 | 67 (90.5) | 84.6-94.7 |
Data are presented as mean±standard deviation or number (%), where appropriate.
MMR (Major molecular rate): BCR-ABL/control gene ratio of ≤%0.1 measured by RQ-PCR as %
CCyR (Complete cytogenetic response): Patients with 0% Ph+ metaphases
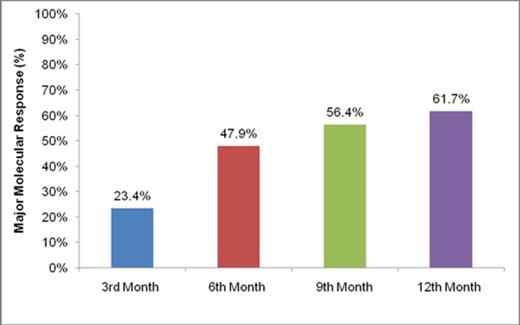
Cumulative MMR rates at 3rd, 6th 9th, and 12th months of the patients are shown in Figure 1.
According to the results of interim analysis of this first prospective CML study conducted on Turkish population, the cumulative MMR rate by 12th month (primary endpoint) (61.7%) appears to be similar to that of the ENESTnd study. From the 3rd month, rapid and increasing MMR rates were reported and median time to MMR was 6.5 months. At both 6th and 12th month, high CCyR rates (both 90.5%) were also established. At all landmark evaluations, most of the patients rapidly achieved high rates of cytogenetic and molecular responses to nilotinib assessed by both 2009 and 2013 ELN optimal response criteria, and only one patient had disease progression. These results suggest that more rapid and greater efficacy was achieved with nilotinib during the 1st year of the study in comparison to historical data with imatinib and that nilotinib might improve short-term responses when started in the first-line setting.
The rate of patients with BCR-ABL ≤10% at 3rd month, which is very important according to the current treatment guidelines, was 86.2%.The results of the present study revealed that efficacy of nilotinib, which is a licensed alternative for the treatment of newly diagnosed Ph+ CML-CP in Turkey, might provide a new standard of treatment.
Saydam:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, Turkey: Consultancy, Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees. Haznedaroglu:Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, Turkey: Honoraria, Research Funding. Yavuz:Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, Turkey: Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees. Ali:Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, Turkey: Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees. Guvenc:Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, Turkey: Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees. Sonmez:Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, Turkey: Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees. Akkaynak:Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, Turkey: Employment. Dag:Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, Turkey: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal