Abstract
Adults with newly-diagnosed and persistent ITP usually respond to steroid based treatments such as prednisone but relapse with tapering. One 4-day cycle of Dexamethasone (dex) at 40 mg/day in newly diagnosed ITP resulted in a lasting effect in 50% of patients (pts) in 1 study. An Italian study showed that 3 cycles of dex are better than 1 cycle. Approximately 50% of pts with chronic ITP experience a complete or partial response (CR & PR) to rituximab, yet only 20% of pts have a lasting, unmaintained response after 3 years. Mechanistically, rituximab (which depletes B cells but not plasma cells) and dexamethasone (which may be the most potent anti-plasma cell agent) are a logical combination in treatment of antibody-mediated diseases such as ITP. In 2 studies of newly-diagnosed pts, dex 40mg/day x 4 followed by rituximab was more effective than dex alone (one study added more dex half way through). In our pilot study, pts at Weill Cornell Medical College (WCMC) with all stages of ITP were treated with a combination of rituximab (R) and usually 3 cycles of dex. The outcome of this combination was retrospectively analyzed.
Combination of standard-dose rituximab (weekly x 4) and usually 3 4-day cycles of 28mg/m2 (max. 40mg) dex at 2-week intervals (R+3Dex) was explored in 67 pediatric and adult pts with ITP at WCMC. Patients were monitored with CBCs obtained weekly and then at less frequent intervals if a response was achieved. Best response (after 8 weeks to avoid transient effects of dex) was determined. Patients were categorized as CR (platelet count≥100x109/L) or PR (50-100x109/L). Relapse was defined as either two consecutive platelet counts <50x109/L and/or need for additional therapy. The duration of response was calculated from date of first rituximab administration to relapse or latest follow-up as of July 31st 2013.
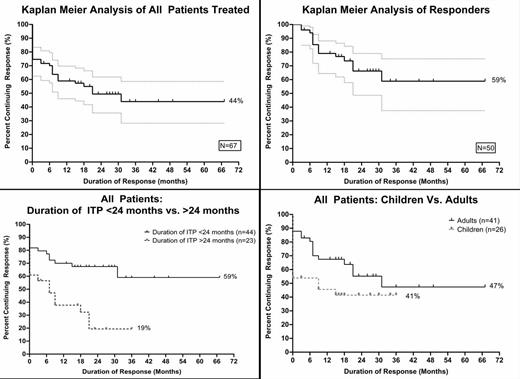
Overall, 50 of 67 pts treated with R+3Dex achieved a best response of either a CR (n=43) or a PR (n=7) at 8 weeks or later from start of therapy for an overall response rate of 75%. Seventy-three percent of pts received R+3Dex; variations were primarily in the timing and amount of dex given. Fifteen responders, 9 CRs and 6 PRs, relapsed at a median of 9 months. Seventy percent of the responders (or 52% of all pts treated) maintain a continuous response with platelet counts ≥ 50 x 109/L as of their last visit at a median f/u of 20 months. Kaplan Meier Analysis estimates 44% of all pts treated (Figure) and 59% of responders (Figure) maintained a best response without relapse at 67 months after initiating treatment. If only those with ITP ≤ 24 months are included, the estimated long term response rate is 59% (p=0.0017) versus only 19% for those with a duration of ITP > 24 months (Figure). Of 36 responding children and adults who had ITP ≤ 24 months, 29 continued to respond as of last follow up. Adults initially responded better than children (p=0.0019) but the long-term responses were not different (Figure). Pts achieving a CR had longer response than those achieving a PR.
Adverse events related to R+Dex were usually mild-moderate, although 3 pts had serum sickness and 2 had transient colitis. IgG levels fell to below the lower limit of normal for age in 14 of 67 pts, 10 of whom had their IgG levels return to normal. In 6 of 14, IgG levels were < 400 mg/dl, some of whom received IVIG. Fifteen patients had serial BK/JC levels without ever detecting virus.
R+3Dex provides clearly superior results to rituximab alone. Notably, there was a 75% response rate overall (50/67 pts) compared to 50% with R alone. The 5 year response rate was almost 50% of all patients and 3/5 of responders. In patients who had had ITP for ≤ 2 years, the response is comparable to what has been reported with splenectomy. Specifically the results in the ≤ 2 year group suggest that R+3Dex is an effective way to induce indefinitely normal platelet counts in pts with a “short” duration of ITP. R+3Dex was tolerable although patients had difficulty with 3 cycles of dex. The 21% rate of hypogammaglobulinemia, higher than that seen with R alone, is also evidence of the mechanism of R+3Dex affecting both B cells and plasma cells. The lasting, long-lived, unmaintained responses observed in this study suggest that this combination therapeutic strategy should be further tested in a controlled trial in patients with newly diagnosed, persistent, and early chronic ITP, whether or not they have been previously treated with other agents.
Bussel:Sysmex: Research Funding; Cangene: Research Funding; Symphogen: Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees; Shionogi: Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Eisai: Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Ligand: Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Immunomedics: Research Funding; IgG of America: Research Funding; Genzyme: Research Funding; GlaxoSmithKline: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Amgen: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal