Abstract
ADAMTS13, the von Willebrand factor (vWF) cleaving protease, regulates platelet aggregation and microthrombi formation by cleaving high-molecular weight vWF multimers. It is expressed primarily in hepatic stellate cells, but is also found in endothelial cells. Recently, ADAMTS13 was reported to be expressed and regulated in astrocytes, microglial, neuroblastoma, and adult human brain endothelial cells. Previous in vitro studies by our group with human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) showed that ADAMTS13 can promote angiogenesis via upregulating the secretion of VEGF and phosphorylation of VEGFR2, suggesting that ADAMTS13 may also be involved in physiological processes unrelated to vWF cleavage (Lee, M., et al. Microvasc Res. 2012, 84, 109-115). Herein, we report an additional possible role of ADAMTS13 secreted by brain tumor cells to modulate tumor cell angiogenesis.
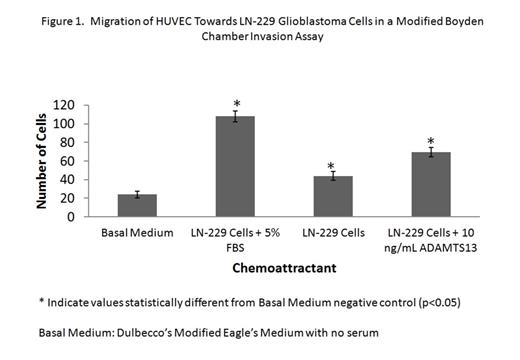
Using a human ADAMTS13 immunoassay, we detected ADAMTS13 in U-87 and LN-229 glioblastoma cell lysates, SW-1088 astrocytoma cell lysates, as well as in the supernatants of all cell lines (> 2.0 ng/mL). Co-incubation of U-87, LN-229, and SW-1088 tumor cell conditioned media with recombinant vWF indicated that brain tumor-secreted ADAMTS13 is biologically active in cleaving vWF multimers (measured by ELISA). Secretion of VEGF was upregulated in LN-229 and SW-1088 cell lines by ADAMTS13. 939 pg/mL and 674 pg/mL of VEGF were measured in LN-229 and SW-1088 cell lysates, respectively, after incubation with 100 ng/mL ADAMTS13. Incubation of LN-229 glioblastoma cells with 10 – 500 ng/mL rh-ADAMTS13 or 50 ng/mL VEGF165 did not affect tumor cell proliferation. No change in tumor cell proliferation was observed when LN-229 cells were incubated with a polyclonal antibody against ADAMTS13 in serum free media supplemented with 10 ng/mL ADAMTS13 or media supplemented with 5% FBS, suggesting that ADAMTS13 secreted by brain tumor cells may be involved in extracellular signaling of endothelial cells.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal