Abstract
We have established animal models of MDS and acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) using NRASD12 and overexpression of BCL-2 (Omidvar Cancer Res 2007). These models have identified a novel MDS biomarker, the RAS:BCL-2 complex (Le Pogam, Leuk Res 2013) and a BH3 mimetic inhibitor, ABT-737, was shown to target leukemic cells and increase life span in both models (Beurlet, Blood 2013, Gorombei, EHA 2013). Here we have studied the benefit of an immunotherapeutic approach in HR-MDS by taking advantage of the reported immunomodulating effect of azacitidine (AZA) (Goodyear, Blood 2010) and of a non-specific DNA vaccine (pVAX14) we have designed.
pVAX14 is a non-specific DNA plasmid which, in an APL mouse model , gives similar survival to the specific PML-RARA DNA we previously designed (Padua, Nat Med 2003) (results submitted to ASH 2013). pVAX14 is a novel construct containing GC-rich sequences and coding for unique peptides, 3 of which we have shown to be immunogenic; ATRA was combined for its immunomodulatory properties. Survival efficacy was measured in mice treated with AZA alone (1mg/kg intraperitoneally 3 times per week until death), pVAX14 (6 weekly injections of 50 mg DNA injected intradermally, ATRA (10 mg 21-day release pellets) or their combinations, and untreated controls. MDS was monitored with biomarkers previously validated for this model, (Beurlet Blood 2013): peripheral blood (PB) counts, PB blasts (Mac1hi/Gr1lo) and spleen cell AKT, MEK1 and ERK1/2 levels by the Nanoimmunoassay (NIA) (Fan, Nat Med 2009). Immunomonitoring was based on lymphocyte subpopulations including Memory T-cells (CD4+/CD44hi/CD62Llo), IFNg production (ELISPOT) and Toll-like receptor-9 (TLR-9) activation measured on MYD88 transcripts by RQ-PCR.
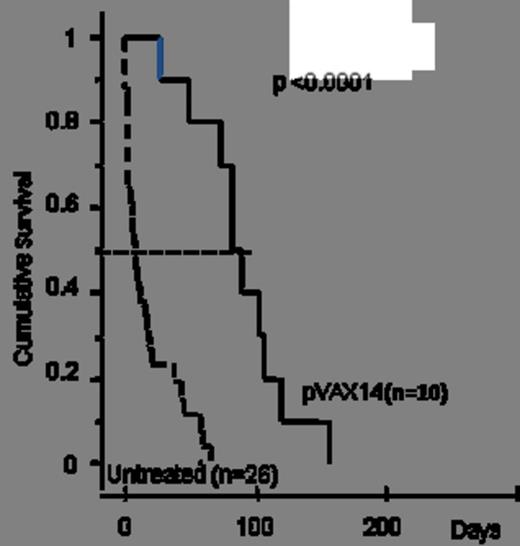
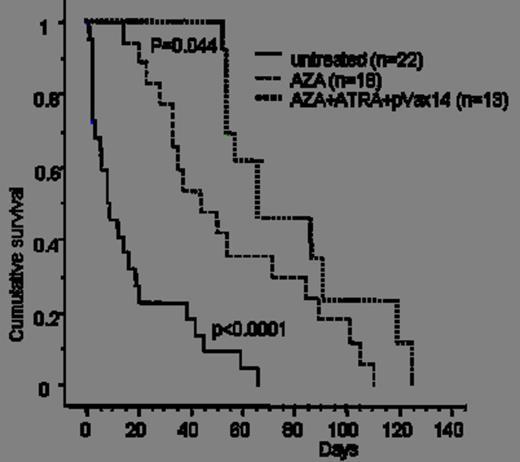
1) Survival benefit: in a first cohort of HR-MDS mice, pVAX14 treatment significantly prolonged survival (median survival 100 days in treated versus 10 days in untreated mice) (Kaplan Meier p<0.0001, Fig. 1). In a second pilot cohort, AZA+pVAX14+ATRA appeared superior (4/4 mice alive at 70 days) to AZA+pVAX14 or AZA+ATRA (2/4 alive at 70 days in both groups) and AZA alone (1/5 alive at 70 days). In a third larger confirmatory cohort, median survival was 65 days with the AZA+pVAX14+ATRA combination, 40 days with AZA alone (Kaplan Meier p= 0.044 compared with AZApVAX14+ATRA) and 10 days in untreated mice (p<0.0001 compared with AZA alone) (Fig. 2).
2) Hematological parameters: survival advantage of mice treated with pVAX14 alone, AZA alone and AZA+pVAX14+ATRA was corroborated with lack of leukemic progression assessed on days 13, 32 and 55, as shown by stable platelet counts and peripheral blasts (Mac-1hi/GR-1lo population) and downregulation of RAS signaling proteins with dephosphorylation of AKT, MEK1 and ERK1/2.
3) Enhanced immune responses: survival advantage and absence of leukemic progression were correlated with enhanced immune responses: increased IFNg production (p<0.03) and expression of MYD88 (p<0.05) were seen in mice treated with pVAX14 alone compared to untreated mice); Tmem were significantly increased in treated mice, with values highest for AZA+pVAX14+ATRA (p<0.005 compared to untreated HR-MDS mice).
1) AZA increases survival in this HR-MDS model. Immune mechanisms seem to be implicated but we are currently analyzing other potential mechanisms of action, including DNA methylation 2) pVAX14+ATRA as add-on therapy to AZA further improves survival, and potentiates the immune responses initiated by AZA. This adjuvant DNA immunotherapy may thus be a promising approach for MDS treatment.
pVAX14 extends survival of HR-MDS mice.
AZA alone extends survival of HR-MDS mice, with additional survival improvement obtained by the AZA+ATRA+pVAX14 combination.
AZA alone extends survival of HR-MDS mice, with additional survival improvement obtained by the AZA+ATRA+pVAX14 combination.
PG and CLP contributed equally to this work.
Pierre:Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding. Christine:VivaVacs: Equity Ownership, I have patents pending through INSERM/Paris-Diderot related to technology employed in this present study., I have patents pending through INSERM/Paris-Diderot related to technology employed in this present study. Patents & Royalties, Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees. Padua:Vivavacs: Equity Ownership, I have patents pending through INSERM/Paris-Diderot related to technology employed in this present study., I have patents pending through INSERM/Paris-Diderot related to technology employed in this present study. Patents & Royalties, Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
PG and CLP contributed equally to this work.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal