Abstract
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) are considered potential tools or targets for immunotherapy. However, current knowledge concerning methodologies to manipulate their development or function remains limited. Here, we investigated the role of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)–protein kinase B (PKB)–mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) axis in human pDC development, survival, and function. In vitro pDC generation from human cord blood–derived CD34+ hematopoietic progenitors was reduced by pharmacologic inhibition of PI3K, PKB, or mTOR activity, and peripheral blood pDCs required PI3K-PKB-mTOR signaling to survive. Accordingly, activity of this pathway in circulating pDCs correlated with their abundance in peripheral blood. Importantly, introduction of constitutively active PKB or pharmacologic inhibition of negative regulator phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) resulted in increased pDC numbers in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, MHC class II and costimulatory molecule expression, and production of IFN-α and TNF-α, were augmented, which could be explained by enhanced IRF7 and NF-κB activation. Finally, the numerically and functionally impaired pDCs of chronic hepatitis B patients demonstrated reduced PI3K-PKB-mTOR activity. In conclusion, intact PI3K-PKB-mTOR signaling regulates development, survival, and function of human pDCs, and pDC development and functionality can be promoted by PI3K-PKB hyperactivation. Manipulation of this pathway or its downstream targets could be used to improve the generation and function of pDCs to augment immunity.
Introduction
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) represent a specialized DC subset that is recognized for its unique ability to rapidly produce large amounts of type 1 interferons (IFN-αβ) on the interaction with viruses or nucleic acids of self or nonself origin.1 Besides direct antiviral activity through the production of IFN-αβ, pDCs have been implicated in playing a broader role in immunity. pDC activation results in the production of additional proinflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, and it stimulates the expression of MHC class I, MHC class II, and costimulatory molecules. These combined functions enable pDCs to activate T helper cells, cytotoxic T lymphocytes, natural killer cells, and plasma cell differentiation. Moreover, pDC-derived cytokines can act as adjuvants for other DC subsets such as myeloid or conventional DC. In contrast, tolerogenic functions of pDC, including the generation of regulatory T cells, have also been described. Similar to other DC subsets, pDC thus show the dual capability of being able to initiate as well as regulate immunity.1-3
In accordance with their broad role in the regulation of immunity, the possibilities to use pDC as either tools or targets for immunotherapy are being increasingly explored. Activation of dysfunctional tumor-resident pDCs may be achieved by administration of TLR agonists,4,5 and methods to induce antitumor responses by either targeting antigen to endogenous pDCs or injection of antigen-loaded pDCs are currently being investigated.6-8 In addition, the reduced pDC numbers and functionality observed in patients with persistent viral infections such as human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis B virus (HBV), and hepatitis C virus has prompted research aiming to manipulate patient pDCs to promote antiviral immunity.9-11 The development of strategies to manipulate pDC immunity would greatly benefit from the identification of intracellular signal transduction pathways or transcription factors that regulate differentiation, survival, and function of pDCs. However, our current knowledge concerning methodologies to manipulate molecular mechanisms involved in pDC development and functionality remains limited.
In mice, mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) has recently been associated with both TLR9-induced IFN-α production and pDC development.12,13 mTOR activation is achieved through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K).14,15 PI3K generates 3-phosphorylated inositol lipids, causing activation of downstream signaling resulting in the activation of protein kinase B (PKB; also called c-Akt) that regulates, among others, mTOR, glycogen synthase kinase-3β and Forkhead box O transcription factor activity. Downstream targets of mTOR include p70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase (S6K). Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) acts as a cell-intrinsic negative regulator of PI3K-dependent signaling through dephosphorylation of 3-phosphorylated inositol lipids.15
The PI3K-PKB-mTOR signaling pathway has been shown to regulate the differentiation and function of human myeloid dendritic cells (DCs),16-22 and PI3K seems to be involved in IFN-α production by human pDCs.23 In the present study, we show that this signaling module also regulates the development and survival of human pDCs. We observed a correlation between the activity of this pathway in circulating pDCs and their abundance in peripheral blood, and we found reduced spontaneous and TLR-induced PI3K-PKB-mTOR activity in the numerically and functionally impaired pDCs present in the blood of chronic hepatitis B patients. Interestingly, in vitro and in vivo pDC development from human cord blood–derived CD34+ hematopoietic precursors could be significantly increased through PI3K-PKB hyperactivation. Moreover, increased activation of this pathway augmented the expression of MHC class II and costimulatory molecules, and it enhanced stimulation-induced production of IFN-α and TNF-α, which could be explained by enhanced IRF7 and NF-κB activation. These findings not only demonstrate the crucial role of the PI3K-PKB-mTOR pathway in human pDC biology but also may provide novel approaches to manipulate pDC development, survival, and function to regulate immunity.
Methods
Reagents
Where indicated the pharmacologic inhibitors LY294002 (LY; 10μM unless indicated otherwise; BIOMOL Research Laboratories), PKB inhibitor VIII (VIII; 3μM unless indicated otherwise; Calbiochem), rapamycin (Rapa; 1μM unless indicated otherwise; BIOMOL Research Laboratories), or VO-OHpic trihydrate (VO-OHpic; 10nM; Sigma-Aldrich) were added to the cultures. HSV-1 (HSV; multiplicity of infection 10) was provided by G. M. G. M Verjans (Department of Virology, Erasmus MC-University Medical Center Rotterdam, The Netherlands). Synthetic TLR ligands included CpG-2336 (CpG-A; class A; 10 μg/mL; Coley Pharma) and loxoribine (Lox; 0.4mM; Invivogen). Protocols for the acquisition of human (cord) blood samples were approved by the medical ethics committee of the Erasmus MC-University Medical Center in Rotterdam, The Netherlands, and the medical ethics committee of the University Medical Center in Utrecht, The Netherlands. Informed consent was provided according to the Declaration of Helsinki.
Culture of pDCs
Peripheral blood pDCs.
PBMCs were isolated from buffy coats obtained from healthy blood donors using Ficoll (GE Healthcare) density gradient centrifugation. pDCs were isolated from the PBMC fraction by CD19+ cell depletion followed by positive selection using anti–BDCA-4-PE and anti-PE–coated microbeads (Miltenyi Biotec). Isolated pDCs were analyzed for purity and viability by staining for BDCA-2 (Miltenyi Biotec) and 7-AAD (eBioscience), and they were only used for experiments if > 95% pure and viable. pDCs were cultured in RPMI 1640 (Lonza) containing 8% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS; Sigma-Aldrich), penicillin/streptomycin (Invitrogen), 2mM l-glutamine (Lonza), 10mM HEPES (Lonza), and 20 ng/mL IL-3 (Miltenyi Biotec).
CD34-derived pDCs.
Umbilical cord blood samples were obtained ex uterine according to legal guidelines. CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPCs) were isolated from mononuclear fractions through positive selection using anti-CD34–coated microbeads and MS separation columns (both Miltenyi Biotec) to a purity of 85% to 98%, used immediately, or stored at −150°C until use. pDCs were generated by coculture of 12 500 OP9-Control cells24,25 and 25 000 CD34+ HPC in MEMα (Invitrogen) containing 20% heat-inactivated FBS, penicillin/streptomycin, 5 ng/mL Flt3 ligand (PeproTech), and 5 ng/mL IL-7 (PeproTech). Cytokines were refreshed after 1 week, and cells were analyzed after 2 weeks of coculture unless indicated otherwise.
Retroviral transduction of CD34+ cells
The retroviral DNA constructs LZRS-myrPKB-IRES-eGFP and LZRS-IRES-eGFP, retrovirus production using the retroviral packaging cell line Phoenix-ampho, and transduction of CD34+ progenitors with viral supernatant in retronectin-coated wells were described previously.19 For in vitro cultures, CD34+ HPCs were transduced in RPMI 1640 supplemented with 8% heat-inactivated FBS, penicillin/streptomycin, 20 ng/mL Flt3 ligand, 20 ng/mL thrombopoietin (PeproTech), and 10 ng/mL IL-7. CD34+ HPCs used for in vivo mouse experiments were transduced in IMDM medium (Invitrogen) supplemented with 8% heat-inactivated FBS, penicillin/streptomycin, 50μM β-mercaptoethanol (Merck), 2mM l-glutamine, 50 ng/mL Flt3 ligand, and 50 ng/mL stem cell factor (PeproTech).
Analysis of cell surface phenotype, cytokines, signaling proteins, and apoptosis by flow cytometry and ELISA
Surface markers.
Labeling was performed on ice in PBS containing 1% bovine serum albumin, 1% heat-inactivated human serum, and 0.02% NaN3, using fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies against BDCA-2 (AC144; Miltenyi Biotec), BDCA-4 (AD5-17F6; Miltenyi Biotec), HLA-DR (LN3; eBioscience), CD40 (5C3; eBioscience), CD86 (2331, FUN-1; BD Biosciences), and CD123 (biotin-conjugated, 6H6; eBioscience). Binding of biotin-conjugated antibodies was visualized by a second incubation with fluorochrome-conjugated streptavidin (BD Biosciences).
Cytokines.
IFN-α– and TNF-α–producing pDCs were quantified by incubating cells with 10 μg/mL brefeldin A (Sigma-Aldrich) during the last 3 hours of 5-hour stimulation cultures. Before incubation with antibodies against IFN-α (MMHA-11; PBL InterferonSource) and TNF-α (MAb11; eBioscience), peripheral blood pDCs were fixed (30 minutes) and subsequently permeabilized (15 minutes) by incubation in 2% formaldehyde (Merck) and 0.5% saponine (VWR International). Labeling was performed on ice in 0.5% saponine. Transduced CD34-derived cultures were first labeled for CD123 and BDCA-2 on ice. To preserve enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) expression, these cells were then fixed (15 minutes) and subsequently permeabilized (5 minutes) by incubation in fixation medium and permeabilization medium (Fix&Perm; ADG Bio Research). Labeling of IFN-α (225.C; Chromaprobe) and TNF-α (MAb11; eBiosciences) was performed in permeabilization medium. Concentrations of human IFN-α were measured in 24-hour culture supernatants using commercially available ELISA kits according to manufacturer's instructions (Bender Medsystems).
Signaling proteins.
To analyze phosphorylation of signaling proteins within CD34-derived pDCs, cells were labeled for CD123 and BDCA-2 on ice, fixed (15 minutes), and subsequently permeabilized (5 minutes) by incubation in fixation medium and permeabilization medium. Labeling of phosphorylated IRF7 (pS477/pS479, K47-671), p65 (pS529, K10-895.12.50), PKB (pS473, M89-61) and S6 (S235/S236, N7-548; all BD Biosciences) was performed in permeabilization medium. Peripheral blood pDCs were fixed (10 minutes at 37°C) and subsequently permeabilized (30 minutes on ice) by incubation in lyse/fix buffer (BD Biosciences) and PERM buffer III (BD Biosciences) before labeling of S235/S236-phosphorylated S6 for 30 minutes on ice.
Apoptosis.
Apoptosis was detected in annexin buffer (10mM HEPES, 140mM NaCl, and 2.5mM CaCl2, pH 7.4). Cells were incubated with fluorochrome-conjugated annexin V (BD Biosciences) for 30 minutes on ice and subsequently taken up in 1 μg/mL propidium iodide (Sigma-Aldrich).
Assessment.
Assessment was performed using a FACSCantoII flow cytometer (BD Biosciences), and data were analyzed using FlowJo software (TreeStar). Surface markers and intracellular proteins were analyzed on viable cells, gated on forward scatter/side scatter and Aqua (Invitrogen) staining.
Transplantation of β2-microglobulin−/− NOD/SCID mice with human CD34+ progenitors
Protocols for mouse experiments were approved by the local animal experimental committee. The β2-microglobulin−/− nonobese diabetic/severe combined immune deficient (NOD/SCID) mice were bred and maintained under sterile conditions in microisolator cages and provided with autoclaved food and acidified water containing 111 mg/L ciprofloxacin (Ciproxin). Eight- to 10-week-old mice, sublethally irradiated with 250-cGy x-rays, received transplants via tail vein injections with approximately 0.5 × 106 unsorted retrovirally transduced human cord blood–derived CD34+ HPCs along with 106 irradiated (1500 cGy) CD34+-depleted human cord blood–derived accessory cells. Six weeks after transplantation, the mice were killed, and both tibiae and femora were flushed. Bone marrow cells were analyzed for the presence of human pDCs using flow cytometry.
Analysis of S6 phosphorylation in blood samples of chronic hepatitis B patients and healthy controls
Peripheral heparinized blood samples were obtained from 16 chronic hepatitis B patients (8 patients negative for HBeAg [HBeneg] and 8 patients positive for HBeAg [HBepos]). All patients were negative for antibodies against hepatitis C, hepatitis D, and human immunodeficiency virus, and they did not receive treatment at time of blood donations. A control group comprised 8 healthy subjects. Healthy subjects and HBeneg and HBepos patients were matched for age (34 ± 2 years) and sex (12 male/12 female). In addition, HBeneg and HBepos patients were matched for serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels (40 ± 5 IU/L) and HBV viral load (5.2 ± 0.6 log10 IU/mL). The study was approved by the local ethics committee, and all subjects gave informed consent before blood donation. PBMCs were isolated using Ficoll density gradient centrifugation and cryopreserved until use. We incubated 106 PBMCs in 250 μL of X-vivo medium (Lonza), supplemented with penicillin/streptomycin, 2mM l-glutamine, and 10mM HEPES at 37°C for 5 hours. CpG-A or Lox was added 15 minutes, 1 hour, 2 hours, or 4 hours before the end of culture. Fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies against CD11c and BDCA-4 were added during the last 5 minutes. After 5 hours, cultures were fixed (10 minutes at 37°C) and subsequently permeabilized (30 minutes on ice) by incubation in lyse/fix buffer (BD Biosciences) and PERM buffer III (BD Biosciences). Cells were then labeled with fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies against S235/S236-phosphorylated S6 (p-S6, N7-548; BD Biosciences) for 30 minutes on ice.
Results
PI3K-PKB-mTOR signaling is required for pDC development and survival
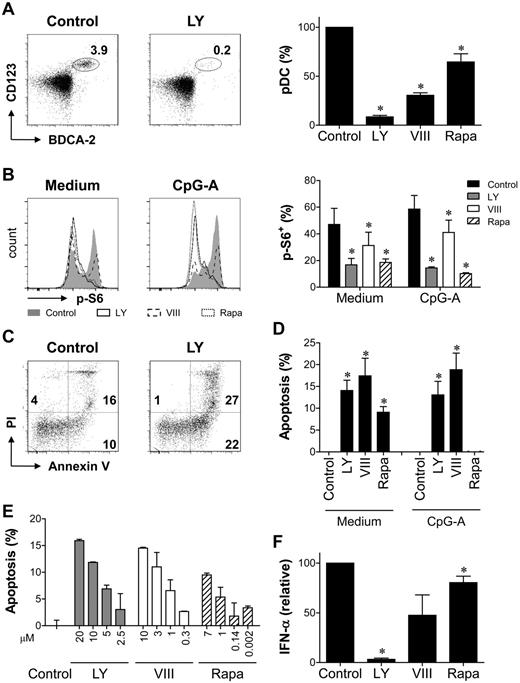
The importance of the PI3K-PKB-mTOR signaling module in pDC development was first investigated in vitro. Generation of CD123+BDCA-2+ pDC from CD34+ HPCs has been demonstrated previously.24 In cocultures of cord blood–derived HPCs and OP9 cells, pDCs could be detected after 1 week, and they were no longer present after 3 weeks for most donors (data not shown). A maximum was reached at week 2, when a population (7.7% ± 1.4%; range, 0.34%-20.1%) of CD123+BDCA-2+BDCA-4+ pDCs could be detected in control cultures (Figure 1A). Addition of PI3K inhibitor LY, PKB inhibitor VIII, or mTOR inhibitor Rapa from day 0 reduced the cell yield at day 14 with 74% ± 4%, 49% ± 6%, and 52% ± 11% respectively. In addition, continuous exposure to LY almost abrogated pDC development, whereas pDC proportions were strongly reduced by addition of VIII or Rapa (Figure 1A). In the absence of OP9 cells, pDCs could only be detected after 1 week. LY, VIII, and Rapa reduced pDC development during the first week both in the presence and in the absence of OP9 cells (supplemental Figure 1, available on the Blood Web site; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article), excluding the possibility that the loss of pDCs was because of an effect on OP9 cells. Together, these data show a nonredundant role for PI3K-PKB-mTOR signaling during CD34-derived pDC development.
PI3K-PKB-mTOR signaling is required for pDC development and survival. (A) CD34+ HPCs were differentiated toward pDCs in the presence of LY, VIII, Rapa, or their solvent dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). After 2 weeks, pDCs were identified by the expression of CD123, BDCA-2, and BDCA-4. Representative FACS plots and mean ± SEM percentage of pDCs standardized to control are shown. Data are representative of at least 3 independent experiments with different donors. (B) Peripheral blood pDCs were cultured with or without CpG-A in the presence or absence of LY, VIII, Rapa, or DMSO for 18 hours. S6 phosphorylation (p-S6) was determined. Representative FACS plots and mean ± SEM percentage of p-S6+ cells are shown (n = 4). (C-D) Peripheral blood pDCs were cultured with or without CpG-A in the presence or absence of LY, VIII, Rapa, or DMSO. Apoptosis was determined after 18 hours as the percentage of cells staining for annexin V and/or propidium iodide (PI). Apoptosis was standardized to control by subtracting the percentage of apoptotic cells in control cultures from the percentage of apoptotic cells in inhibitor cultures. Shown are representative FACS plots of unstimulated cultures (C) and mean ± SEM apoptosis standardized to control from at least 3 independent experiments with different donors (D). (E) LY, VIII, or Rapa was added to peripheral blood pDC cultures in increasing concentrations. DMSO concentration was similar in all cultures. Apoptosis was determined by Annexin V/PI staining after 18 hours and standardized to control as in panel D. Mean ± SD apoptosis in duplicate cultures is shown. (F) Peripheral blood pDCs were cultured with CpG-A in the presence or absence of LY, VIII, or Rapa (n = 3). Supernatants were harvested after 18 hours, and IFN-α concentrations were determined by ELISA and standardized to control cultures. Mean ± SEM concentrations are shown. *P < .05, paired Student t test.
PI3K-PKB-mTOR signaling is required for pDC development and survival. (A) CD34+ HPCs were differentiated toward pDCs in the presence of LY, VIII, Rapa, or their solvent dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). After 2 weeks, pDCs were identified by the expression of CD123, BDCA-2, and BDCA-4. Representative FACS plots and mean ± SEM percentage of pDCs standardized to control are shown. Data are representative of at least 3 independent experiments with different donors. (B) Peripheral blood pDCs were cultured with or without CpG-A in the presence or absence of LY, VIII, Rapa, or DMSO for 18 hours. S6 phosphorylation (p-S6) was determined. Representative FACS plots and mean ± SEM percentage of p-S6+ cells are shown (n = 4). (C-D) Peripheral blood pDCs were cultured with or without CpG-A in the presence or absence of LY, VIII, Rapa, or DMSO. Apoptosis was determined after 18 hours as the percentage of cells staining for annexin V and/or propidium iodide (PI). Apoptosis was standardized to control by subtracting the percentage of apoptotic cells in control cultures from the percentage of apoptotic cells in inhibitor cultures. Shown are representative FACS plots of unstimulated cultures (C) and mean ± SEM apoptosis standardized to control from at least 3 independent experiments with different donors (D). (E) LY, VIII, or Rapa was added to peripheral blood pDC cultures in increasing concentrations. DMSO concentration was similar in all cultures. Apoptosis was determined by Annexin V/PI staining after 18 hours and standardized to control as in panel D. Mean ± SD apoptosis in duplicate cultures is shown. (F) Peripheral blood pDCs were cultured with CpG-A in the presence or absence of LY, VIII, or Rapa (n = 3). Supernatants were harvested after 18 hours, and IFN-α concentrations were determined by ELISA and standardized to control cultures. Mean ± SEM concentrations are shown. *P < .05, paired Student t test.
The reduced pDC yield could result from inhibited differentiation, proliferation, and/or survival of precursor cells, as well as from apoptosis of fully developed pDCs. The reduced cell expansion in inhibitor cultures suggests effects on proliferation or survival, but the presence of other cell populations besides pDCs and the possible loss of pDC markers in the process of apoptosis preclude specific assessment of pDCs in CD34-derived cultures. Survival regulation by PI3K-PKB-mTOR was therefore investigated using pDCs directly isolated from peripheral blood. As shown by the reduced phosphorylation of S6, which is induced by mTOR-activated S6K14 and thus a measure of PI3K-PKB-mTOR signaling activity, LY, VIII, and Rapa inhibited spontaneous as well as CpG-A–induced PI3K-PKB-mTOR activity in peripheral blood pDCs (Figure 1B). In the absence of CpG-A, addition of all inhibitors induced apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 1C-E). The expression of survival regulators Bcl-xl and Bcl-2 was similar in all cultures (data not shown). Stimulation with CpG-A rescued the cells from Rapa-induced apoptosis but not from VIII- and LY-induced apoptosis (Figure 1D), but CpG-A–induced IFN-α secretion was reduced in all inhibitor cultures (Figure 1F). Thus, activity of PI3K, PKB, and mTOR is required for pDC survival as well as function. These data suggest that the loss of pDCs in inhibitor-containing differentiation cultures can at least partly be explained by the induction of apoptosis.
PI3K-PKB hyperactivation augments CD34-derived pDC development
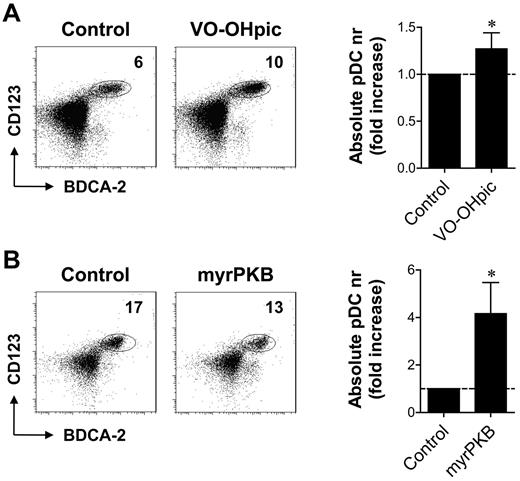
The data described in Figure 1 demonstrate a crucial function of the PI3K-PKB-mTOR axis in human CD34-derived pDC development. To analyze whether enhanced signaling through this pathway could promote pDC development, we increased PI3K-dependent signaling pharmacologically, through inhibition of PTEN. Addition of PTEN inhibitor VO-OHpic from day 0 increased the proportion as well as the absolute number of pDCs in CD34-derived pDC differentiation cultures (Figure 2A). In a second approach, pDC development from CD34+ HPCs retrovirally transduced with a construct expressing a constitutively active form of PKBα (myrPKB) was compared with pDC development from HPCs transduced with a control vector. MyrPKB-transduced cells demonstrated 14.8 ± 7.7- and 2.9 ± 1.6-fold enhanced phosphorylation of PKB and downstream target S6, respectively (supplemental Figure 2). Whereas PTEN inhibition leads to increased PI3K-dependent signaling in cells in which signaling is already activated, thus augmenting endogenous PI3K activity, myrPKB ensures constitutive PKB activity independently of extracellular signals. pDC differentiation from myrPKB-expressing HPCs resulted in increased pDC numbers (Figure 2B). Because the yields of other cell populations were also increased in these cultures, a slight decrease in the percentage of pDCs within the myrPKB-transduced HPC-derived population was observed in most experiments (Figure 2B). Nevertheless, these data show that increasing PI3K-PKB activity augments the development of pDCs.
Enhanced PI3K-PKB activity improves CD34-derived pDC development. (A) CD34+ HPCs were differentiated toward pDCs in the presence or absence of VO-OHpic. After 2 weeks, cells were counted with trypan blue exclusion and analyzed for the expression of CD123, BDCA-2, and BDCA-4 by flow cytometry. Absolute numbers of pDCs per well were calculated, and the fold increase of pDCs in inhibitor cultures compared with control cultures was determined. Representative FACS plots showing pDC percentages and mean ± SEM absolute pDC numbers are shown (n = 6). (B) CD34+ HPCs, retrovirally transduced with myrPKB or a control vector, were differentiated toward pDCs. The percentage of eGFP+ cells was analyzed 2 days after transduction to determine the transduction efficiency. After 2 weeks, cells were counted with trypan blue exclusion and analyzed for eGFP, CD123, BDCA-2, and BDCA-4 by flow cytometry. Absolute numbers of eGFP+ pDCs per well were determined and corrected for the difference in transduction efficiency. The fold increase of pDCs in myrPKB cultures compared with control cultures was determined. Representative FACS plots showing pDCs within the eGFP+ population and mean ± SEM absolute eGFP+ pDC numbers are shown (n = 6). *P < .05, Wilcoxon signed rank test.
Enhanced PI3K-PKB activity improves CD34-derived pDC development. (A) CD34+ HPCs were differentiated toward pDCs in the presence or absence of VO-OHpic. After 2 weeks, cells were counted with trypan blue exclusion and analyzed for the expression of CD123, BDCA-2, and BDCA-4 by flow cytometry. Absolute numbers of pDCs per well were calculated, and the fold increase of pDCs in inhibitor cultures compared with control cultures was determined. Representative FACS plots showing pDC percentages and mean ± SEM absolute pDC numbers are shown (n = 6). (B) CD34+ HPCs, retrovirally transduced with myrPKB or a control vector, were differentiated toward pDCs. The percentage of eGFP+ cells was analyzed 2 days after transduction to determine the transduction efficiency. After 2 weeks, cells were counted with trypan blue exclusion and analyzed for eGFP, CD123, BDCA-2, and BDCA-4 by flow cytometry. Absolute numbers of eGFP+ pDCs per well were determined and corrected for the difference in transduction efficiency. The fold increase of pDCs in myrPKB cultures compared with control cultures was determined. Representative FACS plots showing pDCs within the eGFP+ population and mean ± SEM absolute eGFP+ pDC numbers are shown (n = 6). *P < .05, Wilcoxon signed rank test.
Ectopic PKB activation promotes costimulatory molecule expression
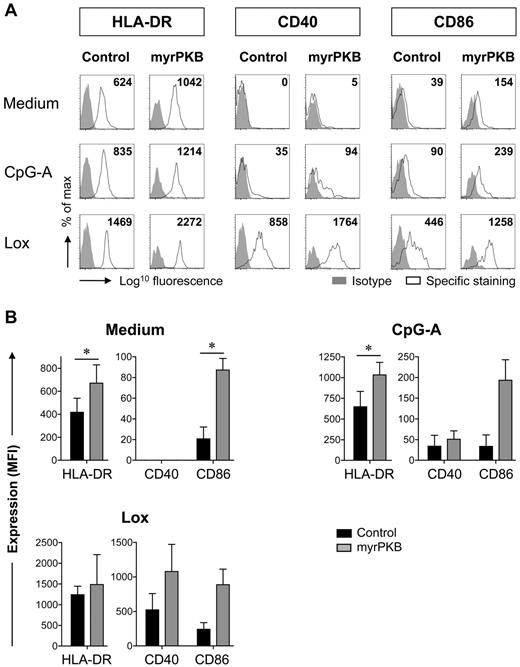
To assess the functional characteristics of pDCs generated through increased PKB activity, we evaluated MHC class II and costimulatory molecule expression. Without stimulation, pDCs isolated from peripheral blood express HLA-DR, but they show low to undetectable expression of CD40 and CD86.26 A similar pattern was observed for unstimulated CD34-derived pDCs (Figure 3A). Expression was up-regulated by stimulation with synthetic TLR7 (Lox) or TLR9 (CpG-A) ligands. Ectopic expression of myrPKB increased CpG-A– and Lox-induced HLA-DR, CD40, and CD86 expression (Figure 3A-B). In addition, the basal expression of HLA-DR and CD86 was enhanced in pDCs expressing myrPKB (Figure 3A–B), suggesting a generally improved ability to express these molecules rather than an effect on TLR-induced up-regulation. Thus, in addition to promoting pDC development, ectopic PKB activity supports the expression of MHC class II and costimulatory molecules by the resulting pDCs.
Ectopic PKB activation increases costimulatory molecule expression by pDCs. CD34+ HPCs, retrovirally transduced with myrPKB or a control vector, were differentiated toward pDCs in 2 weeks. Cells were either left unstimulated, or CpG-A or Lox was added during the last 18 hours of culture. Expression of HLA-DR, CD40, and CD86 by eGFP+CD123+BDCA-2+BDCA-4+ pDCs was determined. Specific staining was calculated by subtracting the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of the isotype control from the MFI measured for each marker (n = 3). (A) Representative FACS plots gated on eGFP+ pDCs are shown. Numbers in the FACS plots indicate the specific staining calculated for the experiment shown. (B) Mean ± SEM specific staining of eGFP+ pDC is shown. *P < .05, paired Student t test.
Ectopic PKB activation increases costimulatory molecule expression by pDCs. CD34+ HPCs, retrovirally transduced with myrPKB or a control vector, were differentiated toward pDCs in 2 weeks. Cells were either left unstimulated, or CpG-A or Lox was added during the last 18 hours of culture. Expression of HLA-DR, CD40, and CD86 by eGFP+CD123+BDCA-2+BDCA-4+ pDCs was determined. Specific staining was calculated by subtracting the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of the isotype control from the MFI measured for each marker (n = 3). (A) Representative FACS plots gated on eGFP+ pDCs are shown. Numbers in the FACS plots indicate the specific staining calculated for the experiment shown. (B) Mean ± SEM specific staining of eGFP+ pDC is shown. *P < .05, paired Student t test.
Constitutive PKB activation increases development and activation status of CD34-derived pDCs in vivo
To investigate the effect of increased PKB activity on in vivo CD34-derived pDC development, myrPKB- or control-transduced human CD34+ HPCs were transplanted into NOD/SCID β2-microglobulin−/− mice. Six weeks after transplantation, human pDCs originating from transduced HPCs could be recognized in the bone marrow by the expression of eGFP, CD123, and BDCA-2. In accordance with the increased pDC numbers observed in vitro, mice transplanted with myrPKB-transduced HPCs showed a 7-fold increase in pDC percentages within the eGFP+ population compared with mice that had received a transplant of control-transduced HPCs (Figure 4A). In addition, expression of CD86 by these pDCs was enhanced 16-fold (Figure 4B). These data further confirm the importance of PI3K-PKB-mTOR signaling in CD34-derived pDC development, and they show that augmented signaling promotes the development of pDCs with an increased activation status.
Constitutively active PKB increases development and activation status of CD34-derived pDCs in vivo. CD34+ HPCs were retrovirally transduced with myrPKB or a control vector. Day 3 unsorted cells were intravenously injected into β2-microglobulin−/− NOD/SCID mice. Six weeks after transplantation, bone marrow cells were analyzed for the expression of eGFP, CD123, BDCA-2, and CD86. The presence of CD123+BDCA-2+ human pDCs within the eGFP+ fraction and the expression of CD86 by eGFP+CD123+BDCA-2+ human pDCs was determined. (A) Shown are representative FACS plots gated on eGFP+ cells and percentage CD123+BDCA-2+ human pDCs within the eGFP+ population per mouse (control, n = 4; myrPKB, n = 5). (B) Specific CD86 staining of eGFP+ human pDCs was calculated by subtracting MFI of the isotype control from the MFI measured for CD86. Expression in different experiments was standardized to control per experiment. Shown are representative FACS plots gated on eGFP+ human pDCs and standardized CD86 expression by eGFP+ human pDCs per mouse (control, n = 3; myrPKB, n = 3). Numbers in the FACS plots indicate the specific staining calculated for the experiment shown. *P < .05, Mann-Whitney U test.
Constitutively active PKB increases development and activation status of CD34-derived pDCs in vivo. CD34+ HPCs were retrovirally transduced with myrPKB or a control vector. Day 3 unsorted cells were intravenously injected into β2-microglobulin−/− NOD/SCID mice. Six weeks after transplantation, bone marrow cells were analyzed for the expression of eGFP, CD123, BDCA-2, and CD86. The presence of CD123+BDCA-2+ human pDCs within the eGFP+ fraction and the expression of CD86 by eGFP+CD123+BDCA-2+ human pDCs was determined. (A) Shown are representative FACS plots gated on eGFP+ cells and percentage CD123+BDCA-2+ human pDCs within the eGFP+ population per mouse (control, n = 4; myrPKB, n = 5). (B) Specific CD86 staining of eGFP+ human pDCs was calculated by subtracting MFI of the isotype control from the MFI measured for CD86. Expression in different experiments was standardized to control per experiment. Shown are representative FACS plots gated on eGFP+ human pDCs and standardized CD86 expression by eGFP+ human pDCs per mouse (control, n = 3; myrPKB, n = 3). Numbers in the FACS plots indicate the specific staining calculated for the experiment shown. *P < .05, Mann-Whitney U test.
Improved cytokine production because of enhanced PKB activity
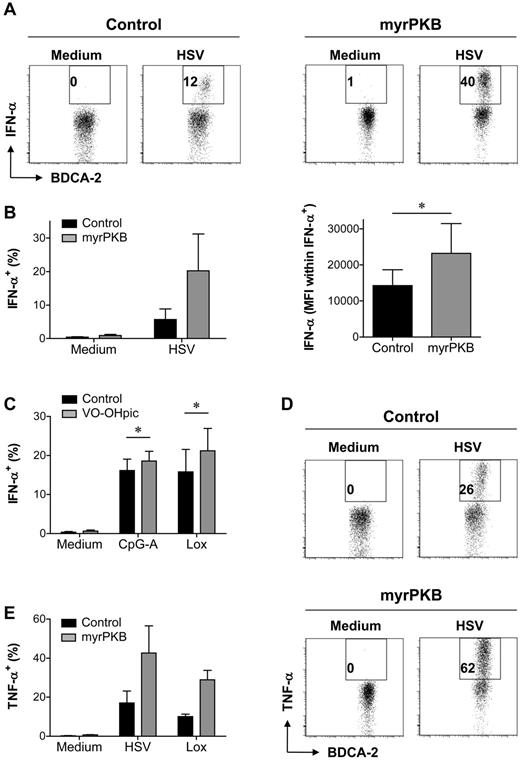
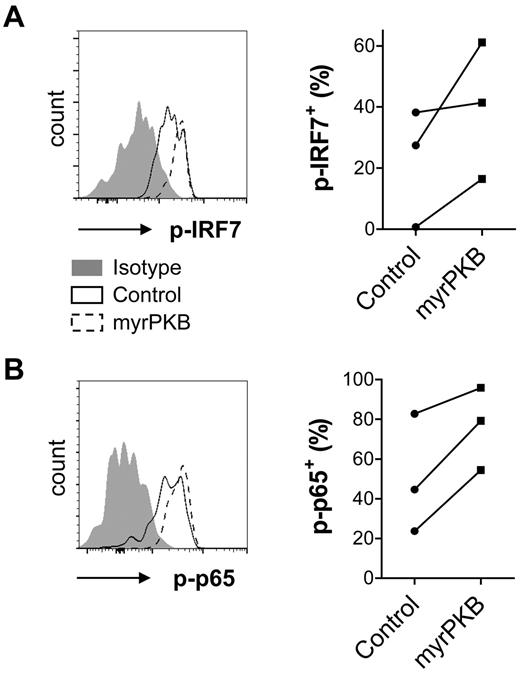
An important functional characteristic of pDCs is the secretion of inflammatory cytokines, of which IFN-α is the most pronounced. Specific assessment of cytokine production by pDCs generated from myrPKB- or control-transduced CD34+ HPCs required analysis by intracellular cytokine staining that allowed gating on eGFP+CD123+BDCA-2+ pDCs. We made use of HSV, a DNA virus that activates pDCs via both TLR9-dependent and -independent pathways,27 to stimulate IFN-α production. Compared with pDCs expressing a control construct, pDCs expressing myrPKB showed an increased ability to produce IFN-α after HSV stimulation (Figure 5A-B). Not only the percentage of IFN-α+ pDCs but also the IFN-α staining intensity within the IFN-α+ pDC population was increased (Figure 5B), suggesting enhanced IFN-α production per producing pDC. Although IFN-α could be measured in the supernatants of cultures stimulated overnight with CpG-A or Lox, we were unable to show IFN-α+ pDC by intracellular cytokine staining of 5-hour stimulated cultures (data not shown). Improved CpG-A– and Lox-induced IFN-α production was demonstrated for peripheral blood pDCs preincubated with VO-OHpic (Figure 5C), indicating that enhanced PI3K-PKB activity increases both TLR9- and TLR7-induced IFN-α production. Interestingly, the percentage of pDCs producing TNF-α in response to HSV or Lox was also increased by expression of myrPKB (Figure 5D-E). TLR-induced IFN-α secretion depends on IRF7 phosphorylation that can be promoted by mTOR-activated S6K.12 In line, expression of myrPKB enhanced HSV-induced IRF7 phosphorylation (Figure 6A). Although secretion of TNF-α is regulated through activation of canonical NF-κB transcription factors rather than PKB-dependent pathways,23 PKB-mediated NF-κB activation has been described previously.28,29 The enhanced phosphorylation of p65 NF-κB in myrPKB-expressing pDCs (Figure 6B) demonstrates increased NF-κB activity in these cells. Together, these data show that enhancing activity of the PI3K-PKB axis may promote both IRF7- and NF-κB–dependent pathways, which can be helpful to promote inflammatory cytokine production by pDCs.
Ectopic PKB activation augments IFN-α and TNF-α production. (A-B) CD34+ HPCs, retrovirally transduced with myrPKB or a control vector, were differentiated toward pDCs in 2 weeks. Cells were either left unstimulated, or HSV was added during the last 5 hours of culture. Expression of eGFP, CD123, BDCA-2, and IFN-α was analyzed by flow cytometry. The percentage of eGFP+CD123+BDCA-2+ pDCs producing IFN-α and the IFN-α staining intensity (MFI) on HSV-stimulated eGFP+CD123+BDCA-2+IFN-α+ pDCs was determined. Representative FACS plots showing eGFP+ pDC (A), and mean ± SEM percentage of IFN-α–producing pDCs and IFN-α staining intensity within the IFN-α+ pDCs (B) are shown (n = 3). (C) Peripheral blood pDCs were cultured in the presence or absence of VO-OHpic. After overnight preincubation, pDCs were cultured for 5 hours in medium, CpG-A, or Lox. Mean ± SEM percentage of IFN-α–producing pDCs of at least 4 independent experiments with different donors is shown. (D-E) CD34+ HPCs were cultured as for panels A and B. Cells were left without stimulus, or HSV or Lox was added during the last 5 hours of culture. The percentage of eGFP+CD123+BDCA-2+ pDCs producing TNF-α was determined. Representative FACS plots showing eGFP+ pDC (D) and mean ± SEM percentage of TNF-α–producing pDCs (E) are shown (n = 3). *P < .05, paired Student t test.
Ectopic PKB activation augments IFN-α and TNF-α production. (A-B) CD34+ HPCs, retrovirally transduced with myrPKB or a control vector, were differentiated toward pDCs in 2 weeks. Cells were either left unstimulated, or HSV was added during the last 5 hours of culture. Expression of eGFP, CD123, BDCA-2, and IFN-α was analyzed by flow cytometry. The percentage of eGFP+CD123+BDCA-2+ pDCs producing IFN-α and the IFN-α staining intensity (MFI) on HSV-stimulated eGFP+CD123+BDCA-2+IFN-α+ pDCs was determined. Representative FACS plots showing eGFP+ pDC (A), and mean ± SEM percentage of IFN-α–producing pDCs and IFN-α staining intensity within the IFN-α+ pDCs (B) are shown (n = 3). (C) Peripheral blood pDCs were cultured in the presence or absence of VO-OHpic. After overnight preincubation, pDCs were cultured for 5 hours in medium, CpG-A, or Lox. Mean ± SEM percentage of IFN-α–producing pDCs of at least 4 independent experiments with different donors is shown. (D-E) CD34+ HPCs were cultured as for panels A and B. Cells were left without stimulus, or HSV or Lox was added during the last 5 hours of culture. The percentage of eGFP+CD123+BDCA-2+ pDCs producing TNF-α was determined. Representative FACS plots showing eGFP+ pDC (D) and mean ± SEM percentage of TNF-α–producing pDCs (E) are shown (n = 3). *P < .05, paired Student t test.
Enhanced IRF7 and p65 phosphorylation in myrPKB-expressing pDCs. CD34+ HPCs were transduced and cultured as described in the legend for Figure 5. HSV was added during the last 5 hours of culture. Expression of eGFP, CD123, BDCA-2, phosphorylated IRF7 (p-IRF7), and phosphorylated p65 (p-p65) was analyzed by flow cytometry. The percentage of eGFP+CD123+BDCA-2+ pDCs expressing p-IRF7 (A) or p-p65 (B) was determined. Representative FACS plots showing eGFP+ pDCs and percentages per independent experiment are shown (n = 3).
Enhanced IRF7 and p65 phosphorylation in myrPKB-expressing pDCs. CD34+ HPCs were transduced and cultured as described in the legend for Figure 5. HSV was added during the last 5 hours of culture. Expression of eGFP, CD123, BDCA-2, phosphorylated IRF7 (p-IRF7), and phosphorylated p65 (p-p65) was analyzed by flow cytometry. The percentage of eGFP+CD123+BDCA-2+ pDCs expressing p-IRF7 (A) or p-p65 (B) was determined. Representative FACS plots showing eGFP+ pDCs and percentages per independent experiment are shown (n = 3).
Reduced PI3K-PKB-mTOR activity in pDCs from HBepos chronic hepatitis B patients
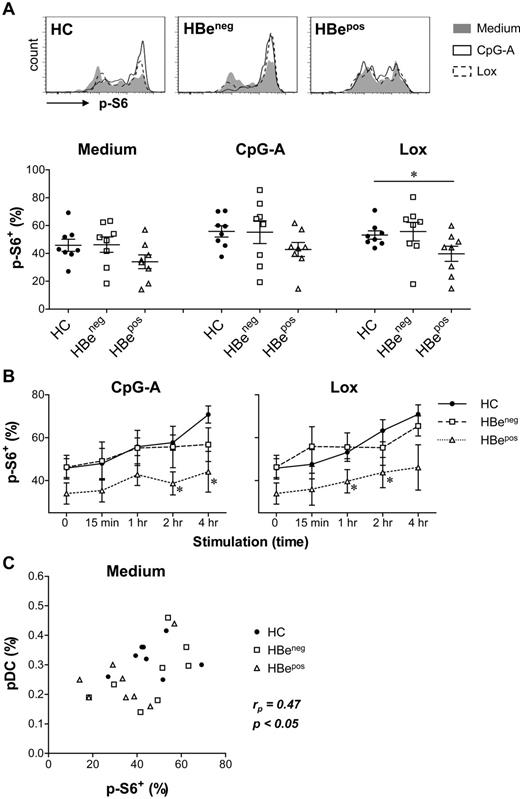
The regulatory role of PI3K-PKB-mTOR in pDC development and function prompted us to assess the activity of this pathway in pDCs from chronic hepatitis B patients. For these patients, impaired pDC numbers and functionality have been described previously.10,26,30,31 In particular, pDCs derived from patients positive for HBeAg (HBepos patients) display functional defects,26 and loss of HBeAg has been associated with partial restoration of circulating pDC numbers and function.30 We compared spontaneous and TLR-induced PI3K-PKB-mTOR signaling activity in pDCs from HBepos patients, HBeneg patients and healthy individuals through analysis of S6 phosphorylation. Because 5-hours culture in medium alone slightly increased S6 phosphorylation compared with S6 phosphorylation observed directly after thawing (data not shown), all cells were cultured for 5 hours and CpG-A or Lox were added 4 hours, 2 hours, 1 hour, or 15 minutes before the end of culture. In unstimulated pDCs, similar S6 phosphorylation was observed for pDCs from HBeneg patients and healthy subjects, whereas 25% ± 9% decreased phosphorylation was found in pDCs from HBepos patients (Figure 7A-B). In addition, the time-dependent increase of S6 phosphorylation observed in pDC from healthy subjects and HBeneg patients after stimulation with CpG-A or Lox was strongly reduced in HBepos patient pDCs (Figure 7A-B). Finally, we observed a weak but significant correlation between the spontaneous S6 phosphorylation levels in pDCs and their percentage within the total PBMC population (Figure 7C). Together, these data demonstrate reduced spontaneous and TLR-induced PI3K-PKB-mTOR activity in the numerically and functionally impaired pDCs of HBepos chronic hepatitis B patients.
Decreased S6 phosphorylation in pDCs from HBepos chronic hepatitis B patients. PBMCs from healthy subjects (HC), HBepos and HBeneg chronic hepatitis B patients (all matched on age and sex; HBeneg and HBepos patients matched for serum ALT levels and HBV viral load) were cultured for 5 hours. CpG-A or Lox was added 4 hours, 2 hours, 1 hour, or 15 minutes before the end of culture. S6 phosphorylation (p-S6) was analyzed within the CD11c−BDCA-4+ pDC population. Results are representative for 6 (15-minute, 2-hour, 4-hour stimulation) or 8 (medium and 1-hour stimulation) subjects per group. (A) Representative FACS plots and percentages p-S6+ pDCs of unstimulated and 1-hour stimulated pDCs are shown. (B) Mean ± SEM percentages p-S6+ pDCs are shown for each condition. Unstimulated cultures are represented by 0. (C) Percentages p-S6+ pDCs of unstimulated pDCs, and the proportion of unstimulated pDCs within the PBMC population were determined. Data from HC, HBeneg, and HBepos patients were combined, and the Pearson rank correlation coefficient (rp) was calculated. Significance and rp of the correlation are indicated. *P < .05, unpaired t test compared with HC.
Decreased S6 phosphorylation in pDCs from HBepos chronic hepatitis B patients. PBMCs from healthy subjects (HC), HBepos and HBeneg chronic hepatitis B patients (all matched on age and sex; HBeneg and HBepos patients matched for serum ALT levels and HBV viral load) were cultured for 5 hours. CpG-A or Lox was added 4 hours, 2 hours, 1 hour, or 15 minutes before the end of culture. S6 phosphorylation (p-S6) was analyzed within the CD11c−BDCA-4+ pDC population. Results are representative for 6 (15-minute, 2-hour, 4-hour stimulation) or 8 (medium and 1-hour stimulation) subjects per group. (A) Representative FACS plots and percentages p-S6+ pDCs of unstimulated and 1-hour stimulated pDCs are shown. (B) Mean ± SEM percentages p-S6+ pDCs are shown for each condition. Unstimulated cultures are represented by 0. (C) Percentages p-S6+ pDCs of unstimulated pDCs, and the proportion of unstimulated pDCs within the PBMC population were determined. Data from HC, HBeneg, and HBepos patients were combined, and the Pearson rank correlation coefficient (rp) was calculated. Significance and rp of the correlation are indicated. *P < .05, unpaired t test compared with HC.
Discussion
Despite their key function in immunity, current knowledge on methodologies to manipulate pDC development or function remains limited. The present study identified the PI3K-PKB-mTOR axis as a possible target. In vitro generation, survival, and function of human pDCs were dependent on PI3K-PKB-mTOR signaling, and in vivo activity of this pathway correlated with the presence of circulating pDCs. Furthermore, the numerically and functionally impaired pDCs from chronic hepatitis B patients demonstrated reduced spontaneous and TLR-induced PI3K-PKB-mTOR activity. Importantly, our data demonstrate that human pDC development and function can be improved by enhancing activity of this pathway. Both in vitro and in vivo, PI3K-PKB hyperactivation resulted in increased pDC numbers, augmented MHC class II and costimulatory molecule expression, and enhanced production of cytokines including IFN-α.
Inhibition of PI3K, PKB, or mTOR during human CD34-derived pDC development resulted in significantly reduced pDC yields, demonstrating a nonredundant role for the PI3K-PKB-mTOR signaling module. We and others have reported a critical function for this pathway in modulating the homeostasis of other human DC subsets.16,19-22 Whereas in those studies differentiation of CD34- and monocyte-derived myeloid DCs in the presence of LY or Rapa seemed normal except for the reduced yields, here we show decreased proportions of pDCs after PKB or mTOR inhibition and almost abolished pDC development in the presence of LY. The disadvantage of pDCs compared with other cells generated in these cultures could reflect inhibited differentiation. However, reduced survival during or after differentiation could also contribute, as shown by the inhibitor-induced apoptosis of peripheral blood pDCs. In contrast to human myeloid DCs, in vitro models exclusively generating human pDCs are lacking, precluding separate investigation of precursor proliferation, survival, and differentiation. The severely reduced expansion of inhibitor cultures suggests a role for the PI3K-PKB-mTOR signaling pathway in proliferation, which would be in accordance with its described function in myeloid DC progenitors.19 In line with the inhibition of DCs observed in rapamycin-treated mice,32 the PI3K-PKB-mTOR dependency of human myeloid DCs described previously16,19-22 and of pDCs reported here together suggest a central function of this pathway in human DC development.
PI3K-PKB-mTOR signaling seemed not only essential but also rate-limiting during development of human pDCs. Introduction of a constitutively active PKB mutant augmented the in vitro yields of pDCs as well as other cell populations present, whereas pharmacologic inhibition of PTEN specifically promoted pDC numbers resulting in increased pDC percentages. This discrepancy is likely explained by the fact that myrPKB ensures PKB-dependent signaling in all cells, whereas enhancing PKB activity through PTEN inhibition requires Flt3 ligand–induced PI3K activation, the latter of which is restricted to the DC lineage.13 The strongly increased pDC development from myrPKB-transduced human progenitors found not only in vitro but also in vivo suggests that promoting activity of this signaling module could be used to increase pDC numbers in a therapeutic setting.
Besides enhancing their numbers, increased PKB activity promoted the expression of MHC class II and costimulatory molecules by pDCs. Increased TLR-induced up-regulation could be responsible for the high expression in TLR-stimulated cells, but the enhanced expression by unstimulated pDCs suggests an activation-independent effect. Moreover, treatment of peripheral blood pDCs with VO-OHpic during CpG-A- or Lox-stimulation had no effect, whereas CD34-derived pDCs differentiated in the presence of VO-OHpic showed a modestly increased expression (data not shown). Although the use of different models and experimental strategies will evidently affect experimental outcome, on the basis of our data the enhanced expression of MHC class II and costimulatory molecules seems to be cell-intrinsic. In contrast, whereas PKB hyperactivation also increased IFN-α production, this required an activation signal independent of PKB activity. This is in accordance with the observation that S6K, activated by mTOR, promotes IRF7 phosphorylation by stabilizing the TLR9-MyD88 complex,12 indicating that the PI3K-PKB-mTOR signaling module can enhance but not initiate IFN-α secretion. The enhanced IRF7 phosphorylation found in myrPKB-expressing pDCs likely contributes to their increased IFN-α production. Moreover, the increased phosphorylation of p65 NF-κB suggests PKB-mediated NF-κB activation, as has been described previously.28,29 This enhanced NF-κB activity, which was found even in the absence of activation stimuli (data not shown), could explain the enhanced costimulatory molecule expression and TNF-α production by myrPKB-expressing pDCs. It has been demonstrated previously that inhibition of PI3K/PKB activity does not alter TLR-induced TNF-α production and costimulatory molecule expression.23 Although these data suggest that PKB-mediated NF-κB activation is not required for TLR-induced NF-κB–dependent processes, our study shows that these processes can be promoted by increased NF-κB activity induced by ectopically enhanced PI3K/PKB signaling. Other mechanisms, such as a general increase in mRNA translation because of high PKB activity,33,34 or effects on TLR expression, CpG uptake or CpG-TLR9 colocalization,35 could contribute to the enhanced functionality of myrPKB-expressing pDCs. It is however clear that both IRF7- and NF-κB–dependent pDC functions are promoted by enhanced PKB activity.
PI3K-PKB-mTOR–mediated regulation of pDC development, survival, or function is relevant in various pathologic and therapeutic settings. Impaired pDC numbers and functionality have been described for chronic hepatitis B.10,26,30,31 As described here, pDC from HBepos patients show impaired spontaneous and TLR-induced PI3K-PKB-mTOR activity, whereas HBeneg patient pDCs demonstrate activity comparable to pDCs from healthy subjects. These data are in accordance with the findings that in particular HBepos patients have reduced pDC numbers with a severely impaired ability to produce IFN-α10,26 and that loss of HBeAg is associated with partial restoration of circulating pDC numbers and function.30
Several mechanisms could underlie the ineffective PI3K-PKB-mTOR signaling in HBepos patient pDCs. Immunomodulatory qualities of HBeAg have been suggested previously,36 but addition of HBeAg did not reduce S6 phosphorylation in pDCs from healthy subjects (Woltman et al26 and data not shown). In contrast, HBsAg does have a direct effect on PI3K-PKB-mTOR activity,26 and increased HBsAg serum levels have been reported in HBepos patients compared with HBeneg patients.37 Specific information on HBsAg serum levels of patients included in the present study is lacking, but the HBepos and HBeneg patients had comparable serum HBV-DNA and ALT levels. Because neither HBV-DNA nor ALT levels correlated with S6 phosphorylation levels (data not shown), direct effects of viral load and liver damage or inflammation can most likely be excluded. A role for altered TLR expression also seems unlikely, because altered expression in chronic hepatitis B has been suggested for TLR9 but not for TLR7,38,39 whereas not only CpG-A– but also Lox-induced S6 phosphorylation was reduced in HBepos patient pDCs. Finally, continued viral challenge and pDC activation can lead to negative feedback, exhaustion of pDCs, and/or altered autophagy levels40 that could contribute to their impaired PI3K-PKB-mTOR activity. Further research is required to unravel the exact mechanisms involved.
The correlation between PI3K-PKB-mTOR signaling and the presence of circulating pDCs suggests that therapeutic application of rapamycin could result in pDC loss, but studies investigating this for human subjects are lacking. Because PI3K-PKB hyperactivation results in improved development of pDCs with an enhanced activation status and functionality, manipulation of this signaling module or its downstream targets could be used therapeutically, for example in the treatment of cancer or persistent infections. For such applications, potential side effects such as the risk of autoimmunity because of dysregulated pDC activation41-45 have to be taken into account. In addition, PI3K-PKB-mTOR signaling regulates several other important processes in other cells and is not restricted to pDCs. Therefore, surface molecules specifically expressed by pDCs could be targeted to ensure pDC-specific gene manipulation, but this would only allow manipulation of the functionality of existing pDCs. In vivo targeting of specific pDC progenitors is currently not possible in humans because a definition of such progenitors is lacking, but ex vivo manipulation of pDC development and function for cell-based therapies could be an option. Although these and other issues need to be resolved before our findings can be translated into novel therapies, similar strategies have been applied to promote the functionality of murine and human myeloid DCs without significant side effects.18,46 This indicates that with careful consideration of the disease and potential side effects, the PI3K-PKB-mTOR axis may provide a useful therapeutic target.
In conclusion, PI3K-PKB-mTOR signaling regulates human pDC development, survival, and function. Enhanced activity of this pathway not only increases development of pDCs but also their activation status and cytokine production ability. This knowledge may help in understanding the loss of functional pDCs in certain diseases and may contribute to the development of novel immune modulatory treatment strategies.
The online version of the article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr B. Blom (Department of Cell Biology and Histology, AMC, Amsterdam, The Netherlands) for help in setting up the in vitro CD34-derived pDC differentiation system, E. van der Linden (Department of Immunology, UMC Utrecht, Utrecht, The Netherlands) for technical assistance, and Dr J. C. Zúñiga-Plücker (Sunnybrook Health Sciences Center, Toronto, ON) for providing the OP9 cells.
Authorship
Contribution: L.v.d.L. designed and performed experiments, analyzed data, and wrote the paper; A.v.d.B. and R.S.B. performed experiments and analyzed data; M.B. and H.L.A.J. provided essential analytical tools and expertise; A.B. designed experiments; and P.J.C. and A.M.W. designed experiments and wrote the paper.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Andrea M. Woltman, Erasmus MC-University Medical Center, Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, L-244, 's-Gravendijkwal 230, 3015 CE Rotterdam, The Netherlands; e-mail: a.woltman@erasmusmc.nl.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal