Abstract
Abstract 802
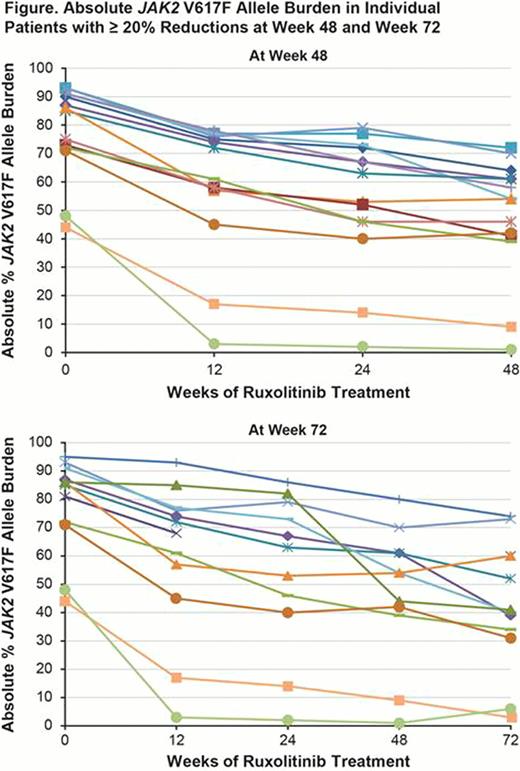
Ruxolitinib is a potent oral JAK1 & JAK2 inhibitor that has demonstrated superiority over traditional therapies for the treatment of MF. In the two phase 3 studies, ruxolitinib demonstrated rapid and durable reductions in splenomegaly and improved disease-related symptoms and quality of life compared with placebo (COMFORT-I) and best available therapy (BAT; COMFORT-II) for pts with or without the JAK2 V617F mutation. Change in JAK2 V617F allele burden (%V617F) as a metric of molecular response to treatment in JAK2 V617 F–positive pts was investigated as an exploratory endpoint. Previously, we reported allele burden reductions in pts receiving ruxolitinib in the COMFORT-II study and demonstrated a positive correlation with reduction in spleen volume after 24 and 48 wk of treatment (Vannucchi, et al. Haematologica.2012); here, we evaluate the correlation between changes in %V617F and spleen size reduction after 72 wk of ruxolitinib therapy.
COMFORT-II is a randomized (2:1), open-label, phase 3 study evaluating the safety and efficacy of ruxolitinib (n = 146) compared with BAT (n = 73) in pts with primary MF (PMF), post–polycythemia vera MF (PPV-MF), and post–essential thrombocythemia MF (PET-MF). Allele burden was measured from blood samples using allele-specific quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) using the method outlined in Levine et al, 2006, using an Applied Biosystems ABI 7900 real-time PCR analyzer. Pts were stratified by absolute reduction in %V617F (< 10%, 10% to < 20%, ≥ 20%) and results were correlated with achievement and duration of a ≥ 35% reduction from baseline in spleen volume, as measured by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans.
Overall, 110 (76%) pts in the ruxolitinib group and 49 (71%) pts in the BAT group were JAK2V617 F–positive at baseline. More pts in the ruxolitinib arm had ≥ 10% V617F reductions compared with BAT at wk 48 (Table; 41%
Patients who received ruxolitinib had larger reductions in JAK2 V617F allele burden compared with BAT. %V617F reductions were gradual over the course of the study and continued between wk 48 and 72 in some pts. In JAK2 V617 F–positive pts, reductions in %V617F were associated with spleen responses; in pts with a ≥ 20% reduction, spleen volume reductions were sustained out to 72 wk. These results, along with findings from COMFORT-I and the phase 1/2 study, suggest that ruxolitinib has the potential to alter the course of disease through a reduction in the burden of JAK2V671 F–mutated cells.
Vannucchi:Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Passamonti:Sanofi: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Al-Ali:Sanofi Aventi: Consultancy, Honoraria; celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria. Harrison:Shire: Honoraria, Research Funding; Sanofi: Honoraria; YM Bioscience: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Sirulnik:Novartis: Employment. Stalbovskaya:Novartis: Employment, Equity Ownership. Squires:Novartis : Employment. Burn:Incyte: Employment, Equity Ownership. Knoops:Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Cervantes:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Speakers Bureau; Teva Pharmaceuticals: Advisory Board, Advisory Board Other; Pfizer: Advisory Board, Advisory Board Other; Celgene: Advisory Board, Advisory Board Other; Sanofi-Aventis: Advisory Board, Advisory Board Other; Novartis: AdvisoryBoard Other, Speakers Bureau. Barbui:Novartis: Honoraria. Gisslinger:Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; AOP Orphan Pharma AG: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Kiladjian:Incyte: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Shire: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal