Abstract
Abstract 5134
The incidence of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in kidney cancer patients has been reported at 1. 2–3. 2% with an estimated hazard ratio for death of 1. 3–3. 2. Computed Tomography (CT) scans are used frequently to stage cancer, and as the resolution of the scans increases more incidentally discovered asymptomatic VTE are being diagnosed. Currently, it is unclear if incidentally found VTE have the same effect on survival as symptomatic VTE in kidney cancer patients.
We undertook a retrospective case-control analysis of all kidney cancer patients treated at our institution between January 1, 2005 and July 1, 2012. Cases with VTE were matched in a ratio of 1:2 to controls by gender, age and stage at cancer diagnosis. All charts were reviewed for comorbidities at cancer diagnosis, cancer type, stage, and treatment plan. We reviewed imaging studies to identify the location of the VTE and whether it was unsuspected – which was defined as a VTE found on a CT which was indicated for cancer staging.
From a cohort of 1166 primary kidney cancer patients we identified 68 (5. 8%) patients who developed a VTE. There were 30 cases of pulmonary embolism (PE), 24 lower extremity deep vein thrombosis (DVT), 5 DVT of the upper extremity and neck and 9 intra-abdominal VTE. Of these, 35% were discovered incidentally and 65% were symptomatic.
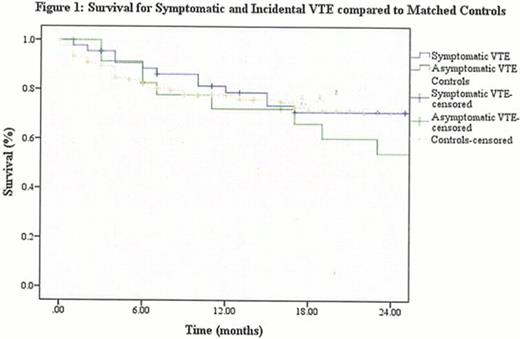
Compared to matched controls, all patients with VTE did not have worsened survival (hazard ratio [HR] = 0. 87; 95% CI: 0. 54–1. 42). As demonstrated in Figure 1, symptomatic and incidentally discovered VTE were at no increased risk of death compared to controls (HR = 0. 72; 95% CI: 0. 40 – 1. 31 and HR = 1. 12; 95% CI: 0. 61 – 2. 27 respectively). Also, when looking specifically at symptomatic and incidentally discovered pulmonary embolisms, no difference in survival was detected (HR = 1. 44; 95% CI: 0. 68 – 3. 06 and HR = 0. 78; 95% CI: 0. 31 – 1. 97 respectively).
In this analysis of kidney cancer patients we found a high rate of VTE (5. 8%) of which 35% were found incidentally on CT staging. The results from this study show that kidney cancer patients with VTE do not have worse survival outcomes than those without VTE. Moreover, the difference in survival between patients with any symptomatic VTE or PE does not differ from incidentally found VTE or PE.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal