Abstract
Abstract 4804
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is one of the classic myeloproliferative neoplasms characterized by a reciprocal translocation of BCR and ABL t(9;22)(q34;q11). Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) have revolutionized the management of CML in inducing rapid and prolonged responses. However; clonal evolution (CE) is considered a poor prognostic factor and a criterion for accelerated phase (AP) CML by the World Health Organization (WHO). Deletion of chromosome Y (−Y) is frequently considered an age-related abnormality and the exact prognostic value has not yet been determined.
To determine if –Y carries an impact on the clinical outcome of male pts with CML.
All male patients diagnosed with chronic phase CML in our institution between 1993 and 2011 were screened for -Y. Data were collected in a retrospective manner and compared (using t-test) to male patients with sole BCR-ABL translocation after excluding patients with advanced stages (accelerated phase, blast phase). Demographics, laboratory tests, cytogenetic analysis, molecular testing and survival data were abstracted. Kaplan-Meier estimates of overall survival were used via JMP software v9.0. Institutional Review Board (IRB) approval was obtained for this study in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration.
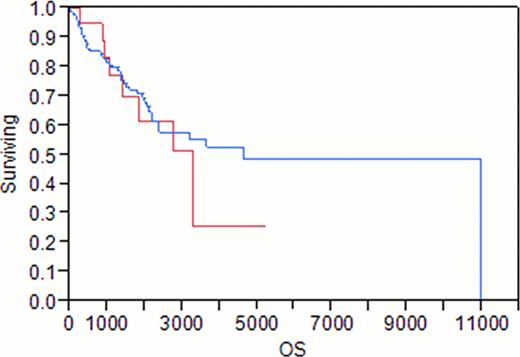
20 of 162 (12%) males with CML were found to have –Y abnormality (group 1). CML male patients with sole Philadelphia chromosome abnormality were the control cohort (group 2). In group1; the median age was 57 years, BMI 27.7, hemoglobin 12.2 g/dL, white blood cell count (WBC) 32.8 x109/L, platelet 270 x109/L, and peripheral blood blasts 1%. Sokal risk was low in 30%, intermediate in 65% and high in 5% of pts. Nine pts (45%) were treated with interferon (IFN) prior to TKI. In group 2; the median age was 54 years, hemoglobin 12 g/dL, WBC 57 x109/L, and platelet 282 x109/L. Sokal risk was low in 37%, intermediate in 47%, and high in 16%. 46 of 142 patients (32%) had received previous interferon therapy. All patients in both groups had chronic phase CML at the time of diagnosis, with a median bone marrow cellularity of 95%. In group 1, 14 of 20 pts (70%) received imatinib, all of whom achieved a complete hematological response (CHR), 7 of 14 pts (50%) had partial cytogenetic response, 2 of 14 pts (14%) achieved a complete cytogenic response (CCyR);1 (7%) pt achieved CCyR within 12 months and an additional 1 (7%) by 18 months). Two pts of 12 (16%) achieved at least a major molecular response (MMR); one of whom (8%) achieved a complete molecular response (CMR). In comparison, 107of 142 pts (75%) in group 2 received imatinib, all of whom achieved CHR. Twenty-one pts (20%) achieved partial cytogenetic remission. CCyR was more frequently achieved than group 1 (48/107 pts (45%), p 0.026); 24 pts (22%) achieved CCyR within 12 months of therapy and an additional 10 pts by 18-months. MMR and/or CMR was higher in group 2 compared to group 1 (34 /101 (34%), p 0.18); 16 (16%) of which were CMR. In group 1; 6 (30%) pts had disease progression; 4 of 20 pts (20%) progressed to blast phase (BP) and 2 pts (10%) progressed to AP, compared to 32 (22%) pts in group 2 (p 0.17); 22 (15%) of whom progressed to BP and 10 (7%) patients progressed to AP. Median overall survival was 110 months in group 1 compared to 155 months in group 2 (log rank p=0.48). On multivariate analysis, CCyR was an independent factor for a better OS (p 0.03), but not –Y (p 0.7).
Loss of the Y chromosome in chronic myelogenous leukemia is an infrequent phenomenon (12%). Although patients with –Y had a statistically significant less chance to achieve CCyR, loss of the Y chromosome did not affect the progression rate or overall survival. Larger scale studies are needed to confirm our observations
Red= Y
Blue= -Y
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal