Abstract
Abstract 471
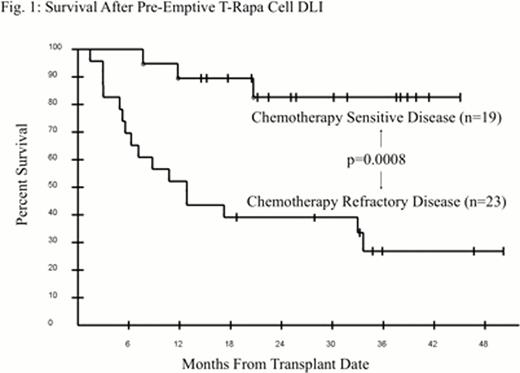
Lymphoma progression remains an obstacle after allogeneic HCT, particularly after non-myeloablative conditioning in patients with high-risk histology (non-indolent; Kahl et al; Blood, 2007) and chemotherapy refractory disease (Bishop et al; Cancer, 2010). In murine models, rapamycin-resistant T cells favorably modulated the balance between GVHD, graft rejection, and GVT effects. To translate this, we conducted a multi-center phase II trial (NCT0074490) of T-Rapa cells infused as a pre-emptive DLI after low-intensity allogeneic HCT; here, we report overall outcome of patients with high-risk lymphoma diagnoses, many of whom were chemotherapy refractory. T-Rapa cells were manufactured by ex vivo culture of donor CD4+ T cells using CD3/CD28 co-stimulation and IL-4, IL-2, and rapamycin for 12-days (T-Rapa12) or 6-days (T-Rapa6), and administered (2.5 × 107 cells/kg) at d14 post-HCT. Both populations of T-Rapa cells expressed a mixed Th2/Th1 phenotype with minimal T-Reg content. Patients (n=42) received outpatient-intensity chemotherapy (typically, EPOCH-FR) until CD4 count was < 200 cells/μl, and then received an HLA-matched sibling mobilized allograft and GVHD prophylaxis of cyclosporine plus short-course sirolimus (to d14 post-HCT); conditioning consisted of fludarabine (120 mg/m2) and cyclophosphamide (1200 mg/m2). Table I details the high-risk diagnoses, pre-treatment history (median of 4 prior regimens), remission status at time of HCT (7/42 [17%] in CR), and presence of chemotherapy refractory disease (stable or progressive disease to prior therapy: 23/42 pts, 55%). T-Rapa cell infusion was relatively safe, with no engraftment syndrome or d100 TRM; incidences of grade II-IV acute, late acute, and classical chronic GVHD were 17%, 34%, and 36%, respectively. Initial mixed donor/host chimerism converted to predominate donor chimerism after T-Rapa cell DLI (Table I). Overall median survival probability at 24 months post-HCT is 85.7% for patients with chemotherapy sensitive disease vs. 39.1% for patients with chemotherapy refractory disease (Fig. 1; p=0.0008). All deaths were due to progressive disease except for 2 infection-related deaths at days 162 and 359 post-HCT; all surviving patients are in CR. Survival was not statistically significantly influenced by DLI type (T-Rapa12 vs. T-Rapa6) or histology-type (NHL vs. HD). Pre-emptive DLI using donor T-Rapa cells after low-intensity conditioning is safe and very effective in patients with high-risk lymphoma diagnoses and chemotherapy sensitive disease; for such patients, future randomized trials should compare low-intensity T-Rapa cell therapy to other transplantation regimens. For patients with high-risk lymphoma diagnoses and chemotherapy-refractory disease, we are evaluating a modification to the current platform that incorporates high-dose sirolimus therapy.
| Patient Characteristics . | Chimerism Resultsc . | CD3 . | CD15 . | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Patients | n = 42 | Day 14 post-HCT | 57 (12-97) | 46 (8-94) |
| Age (median, range) | 44 (23-68) | Day 28 post-HCT | 77 (37-100) | 76 (29-98) |
| Sex (male/female) | (26/16) | |||
| # of Prior Therapies (mean, range) | 4 (1-6) | Day 100 post-HCT | 89 (51-100) | 93 (35-100) |
| Histologya | n=26 total (62%) | Survival Resultsd | 24 Mo. Surv. Prob. | |
| NHL Category | n=12 | ChemoSens/T-R12 | 78.6% (n=7) | |
| DLBCL | n=5 | ChemoSens/T-R6 | 85.7% (n=12) | |
| DLBCL-tr | n=2 | ChemoRefr/T-R12 | 41.7% (n=11) | |
| DLBCL-EBV | n=3 | ChemoRefr/T-R6 | 36.4% (n=12) | |
| PlasmacytoidDC | n=3 | All NHL | 57.4% (n=26) | |
| T Cell | n=16 total (38%) | All HD/Grey Zone | 68.8% (n=16) | |
| HD Category | n=12 | |||
| HD | n=4 | |||
| Grey Zone | ||||
| Chemo. Responseb | 23/42 (55%) | |||
| Refractory (SD/PD) | 19/42 (45%) | |||
| Sensitive (PR/CR) | ||||
| Complete Remission | 7/42 (17%) | |||
| At Time of HCT | ||||
| Patient Characteristics . | Chimerism Resultsc . | CD3 . | CD15 . | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Patients | n = 42 | Day 14 post-HCT | 57 (12-97) | 46 (8-94) |
| Age (median, range) | 44 (23-68) | Day 28 post-HCT | 77 (37-100) | 76 (29-98) |
| Sex (male/female) | (26/16) | |||
| # of Prior Therapies (mean, range) | 4 (1-6) | Day 100 post-HCT | 89 (51-100) | 93 (35-100) |
| Histologya | n=26 total (62%) | Survival Resultsd | 24 Mo. Surv. Prob. | |
| NHL Category | n=12 | ChemoSens/T-R12 | 78.6% (n=7) | |
| DLBCL | n=5 | ChemoSens/T-R6 | 85.7% (n=12) | |
| DLBCL-tr | n=2 | ChemoRefr/T-R12 | 41.7% (n=11) | |
| DLBCL-EBV | n=3 | ChemoRefr/T-R6 | 36.4% (n=12) | |
| PlasmacytoidDC | n=3 | All NHL | 57.4% (n=26) | |
| T Cell | n=16 total (38%) | All HD/Grey Zone | 68.8% (n=16) | |
| HD Category | n=12 | |||
| HD | n=4 | |||
| Grey Zone | ||||
| Chemo. Responseb | 23/42 (55%) | |||
| Refractory (SD/PD) | 19/42 (45%) | |||
| Sensitive (PR/CR) | ||||
| Complete Remission | 7/42 (17%) | |||
| At Time of HCT | ||||
DLBCL, diffuse large B cell lymphoma; DLBCL-tr, transformed; DLBCL-EBV, Epstein Barr Virus related; Plasmacytoid DC, dendritic cell; HD, Hodgkins Disease; SD, stable disease; PD, progressive disease; PR/CR is partial or complete response.
Grey Zone Lymphoma and Hodgkins Disease were pooled for statistical analyses.
Chemotherapyresponse, as determined after last regimen prior to study entry.
Chimerism determined by VNTR-PCR at days 14, 28, and 100 post-HCT (mean and range of values shown); CD3, T cell chimerism; CD15, myeloid cell chimerism.
Survival by Kaplan-Meier analysis; 24 month median survival probability values shown; T-R12 and T-R6 indicates recipient of T-Rapa cells manufactured for 12 days vs. 6 days.
Levine:TxCell: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; University of Pennsylvania: financial interest due to intellectual property and patents in the field of cell and gene therapy. Conflict of interest is managed in accordance with University of Pennsylvania policy and oversight, financial interest due to intellectual property and patents in the field of cell and gene therapy. Conflict of interest is managed in accordance with University of Pennsylvania policy and oversight Patents & Royalties. June:Novartis: Research Funding, institution owned patents have been licensed by Novartis, institution owned patents have been licensed by Novartis Patents & Royalties. Mato:Celgene, Milennium, Genentech, Seattle Genetics: Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal