Abstract
Abstract 4684
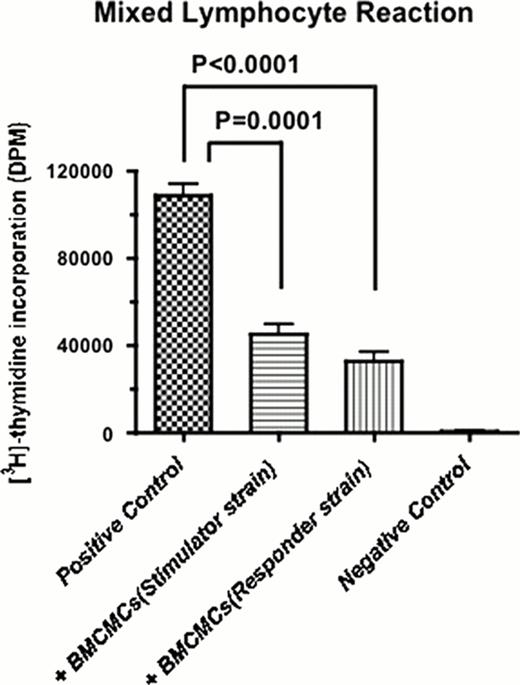
Mast cells have long been known as effector cells in the various IgE-mediated allergic responses. However, recent studies demonstrated that mast cells play various roles in immune reactions in coordination with other immune cells. That is, mast cells exert pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory effects depending on the situation. In addition, mast cells have association with tumor development. In allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), only a few have reported that the numbers of mast cells were correlated with the severity of acute GVHD in the skin. However, exact role of mast cells in GVHD remains unclear. With the purpose of potential application of mast cells in a clinical HSCT for GVHD, mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR) was performed to clarify whether mast cells impaired the alloreaction or not. To generate bone marrow derived cultured mast cells (BMCMCs), BM cells from mice were incubated in complete RPMI containing IL-3 for 6 weeks. As shown in the figure, we showed that MLR was strongly inhibited when BMCMCs from the stimulator strain were added to the coculture (Stimulator (S): DCs obtained from C57BL/6, Responder (R): splenocytes from Balb/c, BMCMCs from C57BL/6). Next, when BMCMCs from the responder strain were added to the coculture, MLR was also suppressed (S: DCs obtained from C57BL/6, R: splenocytes from Balb/c, BMCMCs from Balb/c).
In conclusion, mast cells suppressed lymphocyte proliferation induced by allo-DCs in an MHC-independent manner. Just like mesenchymal stem cells, cell therapy utilizing cultured mast cells may reduce GVHD severity.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal