Abstract
Abstract 468
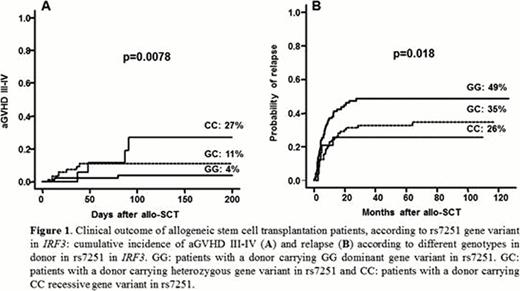
AML is worldwide the most frequent indication for allo-SCT. This is most likely due to the curative potential of the graft versus leukemia (GVL) effect associated with the procedure. Unfortunately, GVL and GVHD are intimately linked. Thus, it is important to identify markers predictive of severe GVHD, to balance the risk of this complication and the risk of relapse in a particular AML patient. The innate immune system, as the initial regulator of the inflammatory response, mediates an important role in these reactions. After conditioning regimen, toll-like receptors initiate the innate inflammatory response by activating intracellular signaling cascades that converge on the activation of NF-κB and interferon regulatory factor-3 (IRF3). IRF3 activation in bone marrow derived dendritic cells (DCs) results in natural killer (NK) cell activation inducing an anti-tumor NK response. We hypothesized that genetic variability in IRF3 in either the donor or the recipient could impact on the degree of the inflammatory response and on GVHD and GVL effect allo-SCT. We analysed the effect of two frequent single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in IRF3 (rs7251 and rs2304205), which are inherited in a haplotype, on the GVHD and GVL in 249 patients diagnosed with AML and submitted to HLA-identical sibling allo-SCT. Those patients with a donor carrying dominant GG gene variant in rs7251 (45% of the donors) had, as compared to GC (44%) and CC (11%) variants, lower aGVHD III-IV incidence (4% vs 11% vs 27%; p=0.0078) (Figure 1A), higher relapse incidence (49% vs 35% vs 26%; p=0.018) (Figure 1B), and lower TRM (7% vs 24% vs 18%; p=0.0065). This clinical impact on severe aGVHD, relapse, and TRM was retained at multivariate analysis. Further, GG gene variant in rs7251 when present in the patient was also associated with lower aGVHD III-IV incidence (4% vs 13% vs 24%; p=0.009), higher relapse incidence (50% vs 34% vs 31%; p=0.014), and with a trend for a lower TRM (9% vs 19% vs 23%; p=0.064). Patients carrying AA dominant gene variant in rs2304205 in IRF3 presented a higher relapse incidence than the rest of genotypes (50% vs 39% vs 18%, p=0.0068). However, this impact was not retained at multivariate analysis. Functional studies in 180 healthy individuals showed that after stimulation of peripheral blood with cytomegalovirus (CMV) peptides, GG gene variant in rs7251 presented lower IFN-γ serum production than the rest of individuals, and GG gene variant was associated with lower number of IFN-γ producing mature NK cells, lower number of cytotoxic NK cells against K562 cell line and lower proliferation of T cells after antigen presentation by DCs. In conclusion, we show that a particular gene variant in IRF3 in the donors is associated with a low incidence of severe aGVHD and high incidence of relapse in AML patients submitted to allo-SCT. This finding could be explained by its effect in the inflammatory and adaptive immune response, with lower IFN-g production, lower lymphocyte proliferation after antigen presentation by DCs and lower mature NK cell response. Thus, these results suggest that, if possible, when transplanting an AML patient with a low risk of relapse it might be preferable to select a donor harbouring GG in rs7251 in IRF3, and when transplanting an AML patient with a high risk of relapse after the transplant it might be preferable to consider select a donor GC or CC in rs7251 in IRF3.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal