Abstract
Abstract 4117
Hemophilia is an X-linked bleeding disorder resulting from a mutation in coagulation factor VIII (F.VIII). A major drawback of current plasma-derived or recombinant F.VIII therapy is the formation of F.VIII antibodies (inhibitors). Inhibitor formation is a T cell-dependent, B cell-mediated immune response to foreign infused F.VIII. Myeloid derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) are potent suppressors of T cell and B cell responses and are currently under study for therapeutic applications in transplantation and autoimmune diseases. However, the mechanisms of MDSC development and function remain unknown, and in vitro propagation of MDSCs has been a challenge. We hypothesized that MDSCs might be effective in inhibiting F.VIII inhibitor formation in the hemophilia A model.
We developed a novel method for generating MDSCs in vitro by culturing bone marrow cells from hemophilia A mice with hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), hereafter referred to as HSC-conditioned myeloid cells (H-MCs). DCs were propagated from the bone marrow with GM-CSF and IL-4, whereas H-MCs were propagated from the bone marrow with GM-CSF and HSCs. Granulocyte contaminants were removed on day 2 and the remaining monocytic populations were harvested on day 5. Expression of cell surface antigens was analyzed by flow cytometry. Arginase1 and iNOS levels were compared by qPCR, with or without LPS stimulation. The in vitro suppressive capacity of the H-MCs was determined by a mixed leukocyte reaction culture. Splenic T cells from hemophilia A mice were stimulated by irradiated DCs (at a 1–20 ratio, APC to T cell) and recombinant F.VIII. Additional irradiated DCs or H-MCs were added in graded numbers as regulators. The proliferative response was determined by 3H-thymidine incorporation. The phenotype of cultured CD4+ T cells was characterized by intracellular staining for Foxp3 and IFN-gamma and analyzed by flow cytometry. Inhibition of B cells by H-MCs was determined by a CFSE dilution assay. Purified splenic B cells were labeled with CFSE and stimulated by Ig-M and IL-4. APCs (spleen cells) or H-MCs were added at a ratio of 1:10 (APC to B cell). The proportion of proliferating B cells was determined by CFSE dilution of B220 stained cells. In the COX-2 suppression assay, CFSE labeled B cells were treated with varying concentrations of the selective inhibitor of COX-2, NS398. The suppressive effect of H-MCs on B cells in vivo was determined by simultaneously administering H-MCs (I.V) and F.VIII (I.V.) to hemophila A mice on day 0 and rechallenging with recombinant F.VIII on days 2 and 4. WT B6 mice and hemophilia A mice without H-MC transfer served as controls. Plasma anti-F.VIII antibody titers were measured on day 12 by a modified ELISA assay.
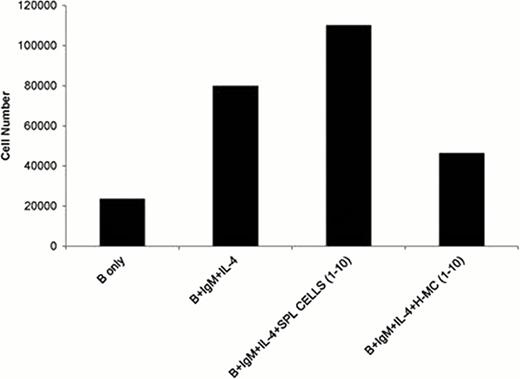
H-MCs expressed low levels of costimulatory molecules but high levels of the inhibitory molecule B7-H1 and immunoregulatory enzyme arginase-1. In contrast, DCs expressed high levels of costimulatory molecules and MHC class II. In vitro studies demonstrated that the H-MCs markedly inhibited antigen specific T cell proliferation induced by dendritic cells in response to recombinant F.VIII (Fig. 1). H-MCs altered the T cell response in hemophilia A mice by promoting the expansion of regulatory T cells and inhibiting IFN-γ producing CD4+ T cells. When the H-MCs were cocultured with B cells isolated from hemophilia A mice, in the presence of Ig-M and IL-4, the H-MCs abrogated B cell activation and proliferation directly (Fig. 2). H-MCs may be modulating the B cell response through the Cox-2 pathway, as inhibition of Cox-2 through NS398 led to the restoration of B cell proliferation. More importantly, adoptive transfer of H-MCs into hemophilia Amice, at the time of F.VIII infusion, markedly suppressed anti-F.VIII antibody formation (Fig. 3).
These results suggest that HSC conditioned myeloid cells may represent a potential therapeutic approach to induction of immune tolerance in patients with hemophilia A andother immune disorders.
H-MCs can suppress the proliferation of T cells induced by DCsin response to F.VIII. *p<0.05.
H-MCs can suppress the proliferation of T cells induced by DCsin response to F.VIII. *p<0.05.
H-MCs effectively inhibit the expansion of B cells stimulated by IgMand IL-4. * p<0.05.
H-MCs effectively inhibit the expansion of B cells stimulated by IgMand IL-4. * p<0.05.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.



This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal