Abstract
Abstract 3725
Activation of PI3K has been shown to be required for the proliferation and survival of cancer cells. A selective PI3K-delta inhibitor, GS-1101/CAL-101, has produced promising results in the treatment of lymphoid malignancies. More recently, new chemical entities targeting PI3K have been developed, with pharmacologic and pharmacodynamic features distinct from CAL-101. We sought to determine the activities of two structurally related PI3K inhibitors, TGR-1202 and TGR-5237, in B- and T cell lymphoma models.
The activity of TGR-1202 on individual PI3K isoforms was determined in a cell free system using the PI3K HTRF Assay Kit, and in a cell based assay using the Flow2CAST kit that measures the induction of CD63 surface expression on human whole blood basophils as a marker for PI3K-delta signaling. The cytotoxicity of TGR-1202 and TGR-5237 was studied in 4 mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) cell lines, 1 T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) cell line (P12), and 1 cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL) cell line (H9). Growth inhibition was determined using the ATP-based Cell Titer Glo assay, and apoptosis was determined by flow cytometry using the Alexa Fluo kit. The potency of ublituximab was determined in antigen recognition studies using the Human Whole Blood B-cell depletion assay. Cell cycle progression was evaluated using a Guava cell cycle assay kit in 4 lymphoma cell lines, including Daudi, Raji, U266B1, and DB.
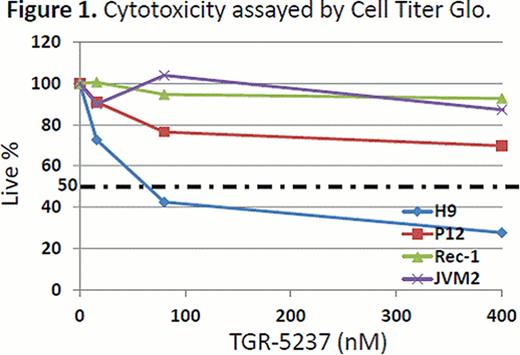
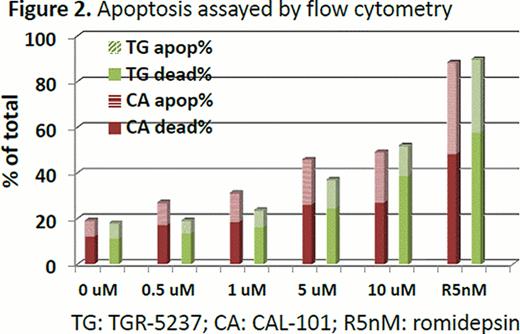
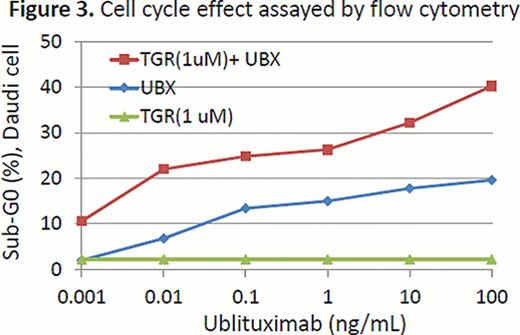
In the enzyme based assay, TGR-1202 demonstrated marked potency against PI3K-delta, with a half maximal effective concentration (EC50) at 22 nM. TGR-1202 was 48- to 10,000-fold more selective for the PI3K-delta relative to the alpha, beta, and gamma isoforms. In the cell based assay, the EC50 of TGR-1202 for PI3K-delta was 67 nM, compared with 92 nM with CAL-101. In the cytotoxicity assay of TGR-5237, the concentration required to inhibit growth by 50% (IC50) ranged from 10 uM to 50 uM for the 4 MCL cells and the T-ALL cell P12. Surprisingly, the CTCL cell line H9, was exquisitely sensitive to TGR-5237, with IC50 below 0.1 uM (Figure 1). TGR-5237 induced concentration-dependent apoptosis in WSU-NHL, with its potency comparable to CAL-101 (Figure 2). TGR-1202 caused a concentration-dependent accumulation of cells in the G2-M phase in Raji, Daudi, U266B1, and DB. While TGR-1202 was not cytotoxic to CD20+ B-cells at the 1 uM concentration, combination of 1 uM TGR-1202 with ublituximab increased CD20+ cell depletion by 20% at the 0.1–10 ng/ml concentrations. Last, the combination of TGR-1202 and ublitiximab markedly increased the percentage of cells in sub-G0 phase in Daudi and Raji cells, indicative of their synergy in causing apoptosis (Figure 3).
Two novel PI3K-delta inhibitors, TGR-1202 and TGR-5237, disrupted cell cycle progression, induced apoptosis, and inhibited cell growth and proliferation in B- and T cell lymphoma models. TGR-1202 enhanced the activity of a novel CD20 monoclonal antibody, ublituximab, in CD20 positive lymphoma cells.
Sportelli:TG Therapeutics, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Miskin:TG Therapeutics, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Vakkalanka:Rhizen Pharmaceuticals: Employment, Equity Ownership. Viswanadha:Incozen Therapeutics: Employment. O'Connor:Millenium Pharmaceuticals, Inc: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; TG Therapeutics, Inc: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics, Inc: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Allos Therapeutics, Inc: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal