Abstract
Abstract 3672
Bortezomib, a proteasome inhibitor, is effective in relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) and achieves responses in up to 50% of patients. While its mechanisms of action are broad, in MCL, brotezomib causes cell cycle arrest and induces apoptosis through oxidative/ER stress-mediated up-regulation of noxa. DA-EPOCH-R is an effective platform in MCL. We set out to assess the efficacy of bortezomib in combination with DA-EPOCH-R in newly diagnosed MCL and to assess the efficacy of maintenance bortezomib following induction.
Treatment was divided into three parts: Part A - bortezomib (1.3 or 1.5 mg/m2) on days 1, 4, 8 and 11 for one cycle; Part B - bortezomib (1.3mg/m2) on days 1 and 4 of DA-EPOCH-R (as previously described) for 6 cycles; Part C patients in CR or PR after Part B and without significant neurotoxicity were randomized to maintenance bortezomib (1.3 mg/m2 d 1, 4, 8 and 11 q 8 wks for 18 mos) or observation.
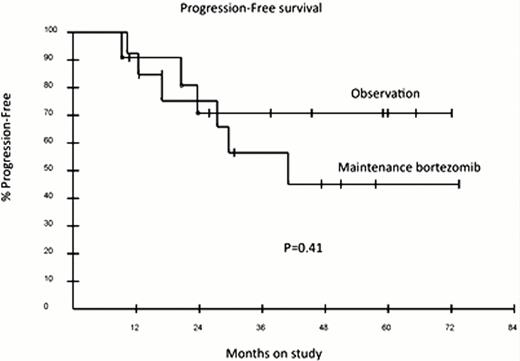
Patient characteristics (n=43): median (range) age 58 (41–75); 45% were aged 60y or over; male sex 32 (73%); stage IV disease 100%. At 48 months (with 57 months median potential follow-up), PFS is 50% and OS is 80%. Twenty-four patients randomized to maintenance bortezomib (13) or observation (11) had a similar PFS (p=0.41) (see attached curve). Overall, 50% of patients had at least grade 2 neurotoxicity. At the recommended 1.3mg/m2 dose of bortezomib, 33% of patients required a dose reduction or discontinuation of drug. Other significant toxicities were neutropenic fever/infection in 8% of cycles and grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia in 34% of cycles.
Bortezomib in combination with DA-EPOCH-R is an effective strategy in patients of all ages with MCL. Maintenance bortezomib (versus observation) does not improve the PFS. However, compared to our historical patients treated with DA-EPOCH-R alone, patients who received DA-EPOCH-R and bortezomib have a significantly better PFS at 48 months (50% versus 19%, respectively). These preliminary results suggest that bortezomib with immunochemothearpy may improve PFS. Accrual continues and responses will be correlated with translational end-points on biopsied tissue sampled before and after bortezomibalone (Part A).
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal