Abstract
Abstract 3436
Platelet refractoriness or lack of platelet increase after platelet transfusion is seen in a fraction of patients who receive platelet transfusion support. Antibodies may develop against specific platelet surface proteins or be directed against HLA-Class I components resulting in the removal of the platelets from the circulation. Donor platelet crossmatching with patient serum is typically required to determine compatible platelet units, ones for which patient antibodies will not result in subsequent platelet loss following transfusion.
The objective of this study was to determine if the percent calculated Panel Reactive Antibodies (cPRA) for class I HLA antigens could predict the percent of positive platelet crossmatches (XM). In this way, the blood bank could have better ability to predict the number of platelet units to set up for crossmatching, in order to find compatible units. Platelet XM were performed using the Capture-P® Immucor Gamma® and cPRA levels were determined by Luminex® assay using One Lambda® single-antigen HLA-class I beads. A retrospective review of platelet XM performed on patients at UAMS and their donors during 2008–2012 was performed. Patients who had two or more platelet XM completed were included in the study in order to reduce donor bias, due to potential reduced HLA diversity in the platelet donor pool. For each patient the mean percentage of all positive platelet XM performed was calculated. These results were compared with the corresponding mean percent cPRA levels against class I HLA antigens. Additionally, the cPRA value of each patient was compared with the subsequent most contiguous platelet XM performed. The “ideal” relationship of cPRA to platelet XM would be 1:1, and therefore a plot of % cPRA vs % XM would have a slope of one. Patient % cPRA vs % XM were plotted and the slopes compared with the ideal plot, and the correlation coefficients were calculated using Microsoft® Excel®.
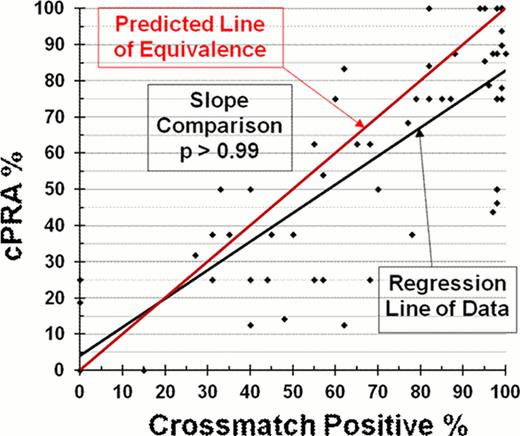
A total of 50 patients (37 females and 13 males) were included in the study. The mean age of these patients was 59 years (range 26–77 years). Majority of the patients (41/53) had multiple myeloma while a small number of patients had other diagnoses (aplastic anemia 2/53; diffuse large B cell lymphoma 1/53; Grade III follicular lymphoma 1/53; Multicentric Castleman's disease 1/53; multicentric Castlemans's disease with progression to large B cell lymphoma 1/53; Von Williebrand's disease type 2b 1/53; Refractory cytopenia with multilineage dysplasia and fibrosis 1/53; and cirrhosis 1/53). Of these, one patient had 111 platelet crossmatches performed and four patients had multiple cPRA levels done. The average positive platelet XM was 61% (range 0–100%) and the average cPRA level was 66% (range 0–100%). Data are presented in the Figure. Comparisons of slopes of measured data and predicted ideal data are indistinguishable, p>0.99. Therefore, the percent cPRA is predictive of the percent positive platelet XM.
Thus, a higher % cPRA would predict a greater number of positive platelet XM, and thereby alert the blood bank that additional platelets units may be required for finding XM compatible platelet units.
Plot of % cPRA vs % positive platelet XM reveals indistinguishable slopes (p>0.99), therefore indicating that the % cPRA is predictive of the % positive platelet XM.
Plot of % cPRA vs % positive platelet XM reveals indistinguishable slopes (p>0.99), therefore indicating that the % cPRA is predictive of the % positive platelet XM.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal