Abstract
Abstract 3345
Adults with newly-diagnosed ITP usually respond to initial prednisone treatment but typically relapse upon its tapering or discontinuation. Patients with persistent/chronic ITP treated with prednisone have an even lower likelihood of a lasting response. Dexamethasone (Dex) has been reported to have curative effects in newly diagnosed patients. Rituximab (Ritux) is thought to be effective in newly diagnosed patients but only yields a long term response in 20–25% of chronic ITP patients. Recently, newly-diagnosed previously-untreated patients received a single cycle of 4 days of Dex 40 mg/day or 4 infusions of 375mg/m2 Ritux combined with Dex. R+Dex in that study yielded a 63% response at 6 months and 34% at 3 years without additional treatment, which was more effective than Dex alone.
Given the additive activity of these two drugs, 59 patients at Weill-Cornell Medical College with ITP of any duration were treated with 4 infusions of 375mg/m2 rituximab and three 4-day cycles of high-dose dexamethasone at 2-week intervals (R+Dex). Optimal response was assessed after 8 weeks as complete remission (CR, platelet count≥100×109/L) or partial remission (PR, 50–100×109/L). Long term outcome was also assessed and both were related to clinical variables. Data was compared to that of rituximab alone using the previous study from our center (Cooper BJH 2004). AIPF values were gathered prior to treatment until 12 weeks after treatment initiation.
All but 5 patients had been previously treated with a median of 2 therapies (range 0–7). Assessing optimal response achieved, 44/59 (74.5%) patients responded, with a CR in 64% and a PR in 10%. Only 1/28 patients with ITP < 1yr relapsed (at 12 months). Duration of ITP less than 24 months (p=0.0426) and being an adult predicted better optimal responses (p=0.0154).
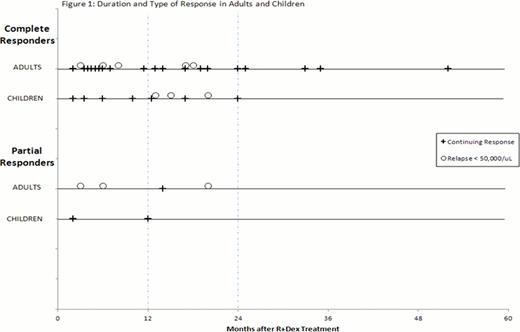
Of the original 44 responders, 33/59 patients [74% of responding adults and 77% of responding children] had ongoing responses at last f/u at a median of 14 months without the need for further ITP treatment (Figure). Eleven of the 44 relapsed (25%) including the one at 12 months mentioned above. Two additional patients relapsed who had ITP for 1–2 years prior to R+Dex and the other 8 patients who relapsed had ITP for greater than 3 years, 5 of whom had had ITP for 6+ years.
Additionally, 53 of the 59 patients were genotyped for β1-tubulin gene. Of the ten patients with heterozygote genotypes, 9 (90%) responded to combination R+Dex treatment and 32 of the 43 wild type patients responded to treatment (p=0.46). There were no overt differences in the AIPF levels over the first 12 weeks between responders and non-responders. No AIPF differences were seen between the heterozygote and wild type patients for the β1-tubulin gene.
In our previous study of rituximab alone, 54% of the 57 adult patients responded to rituximab treatment, compared to 86% of the 36 adult patients who responded to R+Dex treatment. R+Dex responders were found to have a longer duration of lower B cell numbers when compared with responders to rituximab alone, preliminarily demonstrating the additive effect of the 2 medications.
Adverse events related to R+Dex generally were mild but one patient was hospitalized with colitis, two others experienced serum sickness reactions and dexamethasone was sometimes difficult to tolerate.
R+Dex is active and appears clearly superior to rituximab alone in this single-center, pilot study. Adults and patients who have a shorter duration of ITP (< 1–2 years) fare better but children and those with a longer duration of ITP still have a 1/3 chance of a lasting response. The absence of homozygote β1-tubulin SNP's in this population made interpretation of its effect difficult. High dose Dex is not always easy to tolerate but helps maintain the count during the treatment course of 32 days. A prospective, randomized trial is planned.
Basciano:Alexion: Consultancy. Ghanima:Roche Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding. Bussel:Amgen: Family owns Amgen stock Other, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Cangene: Research Funding; GlaxoSmithKline: Family owns GSK stock, Family owns GSK stock Other, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Genzyme: Research Funding; IgG of America: Research Funding; Immunomedics: Research Funding; Ligand: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Eisai: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Shionogi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Sysmex: Research Funding; Portola: Consultancy. Off Label Use: The use of romiplostim in pediatric patients was examined in this study.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal