Abstract
Abstract 3171
Changes in plasma volume, the intravascular portion of the extracellular fluid volume, can be estimated by measuring changes in the levels of hemoglobin and hematocrit in the blood. In addition to hemoglobin & hematocrit levels, we are also able to use standard dilution techniques with radiolabeled albumin to accurately measure plasma volume changes. It is not known if plasma volume changes influence outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndromes. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of plasma volume changes in patients presenting with the acute coronary syndromes.
Consecutive patients presenting to a single tertiary care center from January 2001 to December 2010 with non ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) or ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) were enrolled. Admission hemoglobin (Hbpre) & hematocrit (Hctpre) and discharge hemoglobin (Hbpost) and hematocrit levels (Hctpost) were obtained. Plasma volume changes were measured and a validated formula (ΔPV = ((Hbpre/Hbpost) × (100-Hctpost/100-Hctpre)-1) × 100%) was used to calculate the changes in plasma volumes. A detailed chart review was performed to collect information about baseline variables such as age, gender, hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, smoking status, and congestive heart failure. The Framingham Risk score was also calculated for each individual. Survival analysis was carried out for plasma volume changes of -20% - 0%, 0 – 20%, and ≥20%. Mortality data was collected from the social security death index for the first 60 days post-discharge.
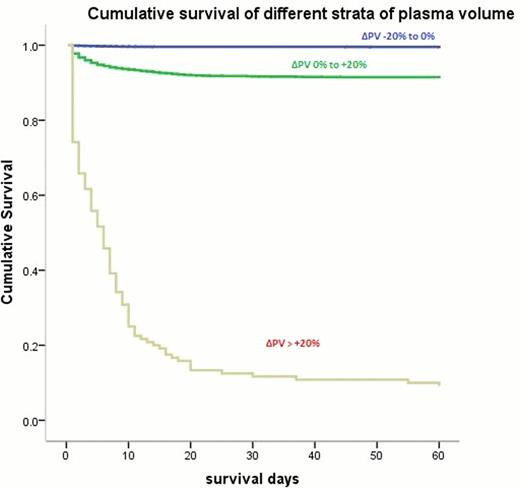
A total of 9770 patients with confirmed NSTEMI or STEMI (mean age 61.8 ± 4.8 years, 48.8% women) were included in the final analysis. Mean pre admission hemoglobin (Hbpre) was 10.2 ± 1.4 g/dl and post admission hemoglobin (Hbpost) was 10.4 ± 1.3 g/dl. Change in plasma volume, ΔPV, was categorized into one of four categories, with 131 (1.3%) ≤20%, 6126 (62.7%) -20% - 0%, 3393 (34.7%) 0 – 20%, and 120 (1.2%) ≥20%. There were 509 deaths within 60 days of discharge. Change in plasma volume was found to be an independent predictor of mortality (HR 5.71; 95% CI 4.75 – 6.86, p = 0.0001) in a Cox proportional hazard model. Most of the deaths occurred during the first thirty days as demonstrated by the Kaplan – Meier's survival curve (Figure 1). Receiver operating curve showed an area under the curve of 0.876 for changes in plasma volume.
This study shows that hemoglobin and hematocrit, although simple tests, can provide important prognostic information strongly predictive of short term mortality in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Further studies are required to see if monitoring of plasma volume and correction with pharmacological agents such as diuretics may lead to better outcomes.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal