Abstract
Abstract 3164
Cryopreservation of Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSC) is a standard procedure for both allogeneic cord blood and autologous HSC transplantation. PBSC are routinely used for the latter; the graft is usually thawed bedside and shortly reinfused without any manipulation. Infusion-related toxicity is usually mild, although severe reactions have been reported, mostly in patients with co-morbidities at baseline. Indeed, cell viability decreases over time after thawing. Washing the thawed graft was reported to improve both clinical tolerance and cell viability. It is however not routinely carried out as it is time-consuming and may result in clinically relevant HSC loss. The fully automated solution SmartWash™ (Biosafe, Switzerland) is designed to wash a thawed graft in a clinical setting. We report here its validation through an international, prospective, multicenter trial.
A pre-clinical and a clinical study were designed and sequentially carried out in 4 European Centers (Basel, Florence, Marseille and Murcia) to assess the reproducibility and feasibility of the SmartWash™ system. During the pre-clinical phase, 10 PBSC Units/Center (total: 40 procedures) from patients who permanently lost the indication to the transplant were thawed and split in two aliquots: one was washed and the other was left unmanipulated. A shared protocol targeted to assess recovery, viability and stability of thawed PBSC at different time-points was developed; in particular, an ISHAGE-modified flow cytometry method was implemented in order to improve the evaluation of thawed CD34+ cells. Clinical grade hydroxyethyl starch (Voluven® 6%,Fresenius, Germany) was validated and used as washing solution. Following the validation of the method, a prospective, observational clinical trial was started after approval of the competent Authorities. Twenty-five consecutive patients across the 4 Centers underwent an autologous PBSC transplantation according to the local practice and indications; all the grafts were washed by Smartwash™. Cellular recovery, clinical tolerance and transplant outcome were collected according to a shared protocol.
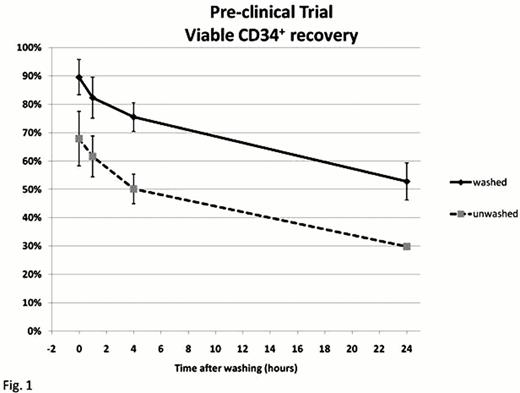
All the washing procedures were completed without any laboratory problems in the participating centers. In the pre-clinical study the recovery of total CD34+ cells in the washed product was 101.2%±27.0 as compared to the pre-freezing value, with a viability of 87.2%±10.0, always showing an advantage over the unwashed samples at all considered time-points (0,1,4 and 24 hours after washing, respectively, Fig. 1). The workload of the procedure, as compared to the unwashed process, resulted in a 40 minutes prolongation for each thawed product, among which only 12 minutes were devoted to active time work, whilst 28 minutes consisted in automatic processing.
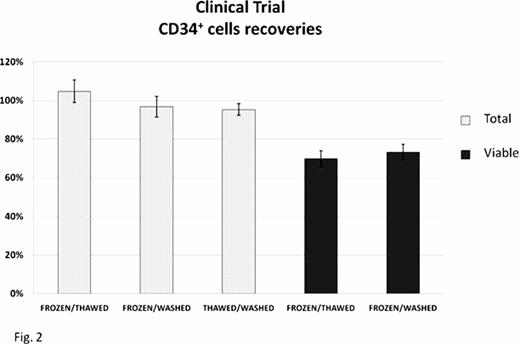
In the clinical trial, patients received a median of 4.32×106 CD34+ cells/Kg (1.32–27.92), as measured before cryopreservation. Recoveries of both total and viable CD34+ cells after thawing and washing are reported in the Fig. 2, replicating the results of the pre-clinical study. Infusion-related toxicity was negligible (1 grade-1 toxicity out of 25 patients). All patients achieved both neutrophil and platelet sustained engraftment at a median of 11 (9–19) and 13 (7–19) days, respectively.
SmartWash™ is an efficient and safe automated method to wash thawed PBSC grafts in a closed, clinical-grade system. Its feasibility and reproducibility was confirmed in an international, multicenter, clinical study. The washed product is stable and clinically feasible for several hours after thawing.
Saccardi:Biosafe SA: Research Funding. Boieri:Biosafe SA: Research Funding. Loutan:Biosafe SA: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal