Abstract
Abstract 3106
Induction therapy followed by ASCT is the standard therapy for the newly diagnosed younger patients with MM. Recently, new drugs such as lenalidomide or bortezomib have shown the promising results as an induction treatment. However, these drugs are not available in many countries as a front line treatment and many different type of induction treatment regimens including old regimens are used. We evaluate the efficacy and safety of the brief course of high dose dexamethasone (HD) and the response adapted PAD (Bortezomib, Adriamycin, Dexamethasone) or VAD (Vincristine, Adriamycin, Dexamethasone) induction chemotherapy in the newly diagnosed younger patients with MM.
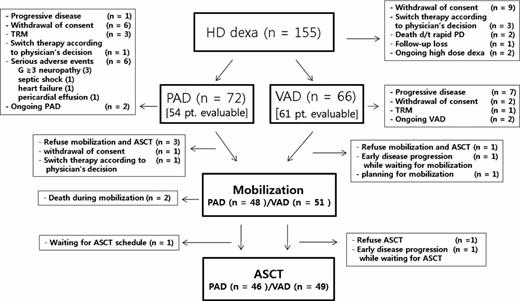
One hundred fifty five newly diagnosed patients with MM from 23 institutions received 2 cycles of HD followed by PAD or VAD chemotherapy according to the response to the HD. PAD 4 cycles were given to nonresponsders and VAD 2 cycles were given to who achieved more than PR to HD. The primary endpoint was CR + nCR rate after ASCT. Among 155 patents enrolled this study from November 2009, 29 patients (19%) have been dropped out. This trial will be continued until total 210 patients will be enrolled. The trial is registered on National Cancer Institute website, number NCT01255514.
One hundred fifty five patients (88 male, 69 female) were enrolled (median age; 57). 34 (22%) patients had ISS stage I, 64 (41%) stage II and 55 (35%) stage III. Thirty six (26%) patients had abnormal cytogenetics. In FISH analysis, there were 25% del13, 9% del17, 21% t (4; 14), 13% t (14; 16) and 26% t (11; 14). Among the 115 evaluable patients, CR + PR rate was 53% (61/115) after 2 cycles of HD. 61 patients (53%) received subsequent VAD chemotherapy and 54 patients (47%) received PAD chemotherapy. Among the evaluable patients, CR + PR rate after induction therapy was 83% (79%, 48/61 in VAD group vs. 89%, 48/54 in PAD group). 95 patients finished ASCT. CR + nCR rate after ASCT were 74% (74% in VAD group vs 73% in PAD group). Mortality rate of this trial was 15% (17/115). The cause of death was disease progression (n=5), bleeding (n=1) and infections (n=11). Among 115 patients in whom VAD or PAD chemotherapy was actually performed, 1 year OS was 88.1%. (VAD arm 90.7% versus PAD arm 86.1% (P=0.105): median follow-up; 16.6 months).
Risk adapted approach using initial HD response showed good response results after ASCT compared with previous trial (CR + nCR rate of IFM 2005-01 trial-Bortezomib+dexa induction & ASCT was 35%, J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:4621–9) The MM patients who showed poor response to HD also showed similar good response rate after ASCT compared with the patients who had good response to HD in this trial. PAD re-induction therapy after failure of initial steroid induction treatment might overcome the inferior results in the high risk MM patients. Our data shows that almost half of the patients who responded to HD can be saved of novel agents during induction treatment, and PAD can successfully rescue the other half who are not sensitive to HD. Therefore, initial steroid response adapted strategy might be the more cost-effective approach in the newly diagnosed ASCT eligible MM patients.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal