Abstract
Abstract 2763
Patients with HL recurring after stem cell transplantation (SCT) are mostly incurable. Therefore development of new agents and strategies is an impellent medical need in this setting. BDM is a hybrid purine analogue/bi-functional alkylator active in B-cell tumors. Despite preliminary evidences of efficacy in refractory HL, the molecular mechanisms underlying the potential activity of BDM towards malignant H-RS cells were never explored.
We investigated patterns of BDM cytotoxicity (12.5 to 100 mmol/L) in a panel of HL-derived cell lines (L1236, L428, KMH2, HDLM2, L540) and its time-dependent (8, 24, 48, 72 hrs) effects on genes involved in DNA-damage stress and repair response, apoptosis and cell cycle checkpoints by Q-RT-PCR. BDM induced a significant time- and dose-dependent inhibition of growth and survival in all cell types. L1236 cells displayed the highest sensitivity to the agent with an IC50, at 48 hrs, of 10.7 mmol/L, as opposed to KMH2, L428, L540 and HDLM2 cells with IC50 of 11.1, 12.4, 14.8 and 16.2 mmol/L, respectively. BDM elicited a dose-dependent increase of apoptosis (30% to 50% at 72 hrs) in all cell lines, as shown by Annexin-V/propidium iodide staining. The exquisite sensitivity to BDM of L1236 cells was confirmed by clonogenic assays, since these cells, after a 24 hr exposure, showed the lowest IC50 for secondary colony formation (0.7± 0.06 mmol/L) as compared to all other cell lines (IC50 range: 3.1 ± 0.28 to 15.0 ± 1.27 mmol/L).
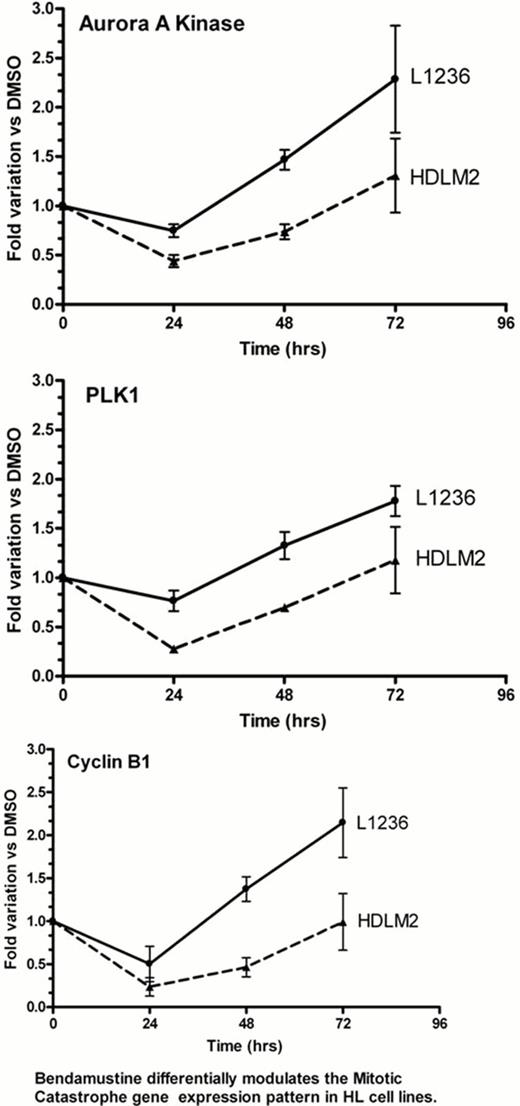
Most notably, however, BDM, within the same concentration range, activated different cell death subroutines among the various cell lines. Q-RT-PCR disclosed that BDM-induced cell death in L1236 was mainly dependent on triggering of apoptosis, as shown by the early (8–24 hrs) up regulation of the proapoptotic genes NOXA and p21, but not p27, without appreciable changes in expression levels of genes related to activation of the mitotic catastrophe process, i.e. PLK1, Aurora A kinase (AAK), and cyclin B1. In contrast, induction of mitotic catastrophe was a main determinant of BDM action on KMH2, L428 and L540 cells, as shown by early (8 hrs) and sustained (48 hrs) down-regulation of PLK1, AAK and cyclin B1 genes, without early changes in NOXA and p21 expression levels. This was confirmed by highly aberrant mitosis and further multinucleation. Interestingly, BDM induced the sequential activation of both these cell death pathways in HDLM2 cells only. In this cells, the early (8–24 hrs) down regulation of PLK1, AAK and cyclin B1 genes, was later (48–72 hrs) followed by a significant induction of NOXA, p21 and p27 genes. The highest sensitivity of L1236 cells to BDM correlated with the delayed (72 hrs) induction of the DNA-repair genes EXO-1 and ATR, but not ATM, as opposed to the earlier (24 hrs) and sustained up regulation of these DNA-repair genes, and of ATM, in all other cell types. Accordingly, only after 72 hrs from exposure to BDM, the proliferation-related genes C-MYC, E2F2 and cyclins (D1, D2) were up regulated in surviving L1236 cells, along with a >70% reduction in G0/G1 cells, a significant (48%) increase of cells in the G2 phase of the cell cycle and a 20% increment of those in S phase. Conversely, in the other cell lines, S phase accumulation (35% to 60.5% increase) and up regulation of proliferation-related genes in surviving cells occurred, as early as 24 hrs after exposure to BDM.
Overall, these results indicate that BDM affects different cell death pathways among HL-derived cell lines. Specifically, in L1236 cells the agent induces the early up regulation of proapototic genes and G2 arrest, accompanied by a delayed activation of DNA repair genes. This changes may lead to cell death through apoptosis rather than mitotic catastrophe which, conversely, appeared the predominant cell death pathway activated by BDM in the other cell lines. Notably, while determinants of BDM toxicity in ‘bona fide’ HL cell lines consistently overlap with those described for tumor B-cells of non-Hodgkin lymphomas (mitotic catastrophe), L1236 cells display a different response pattern to the agent, more reminiscent of BDM action on myeloma tumor cells. Since only L1236 cells are clonotypically related to primary H-RS cells from which were derived, our results suggest that optimal BDM dosing and scheduling in HL may be different from those adopted for other B-cell tumors. In this sense, a lower BDM dosing through a weekly schedule is currently being tested at our institution in refractory HL.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal